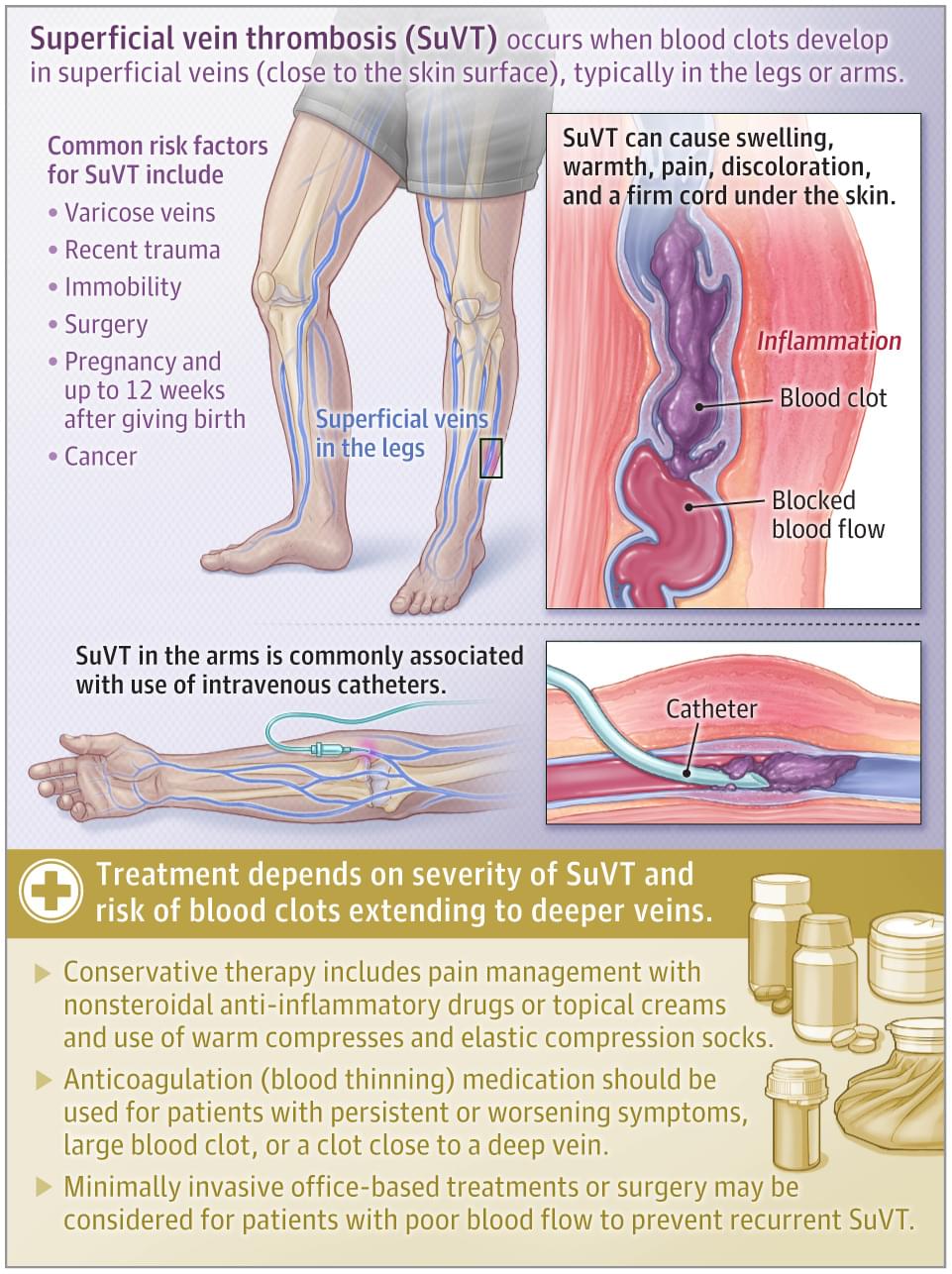
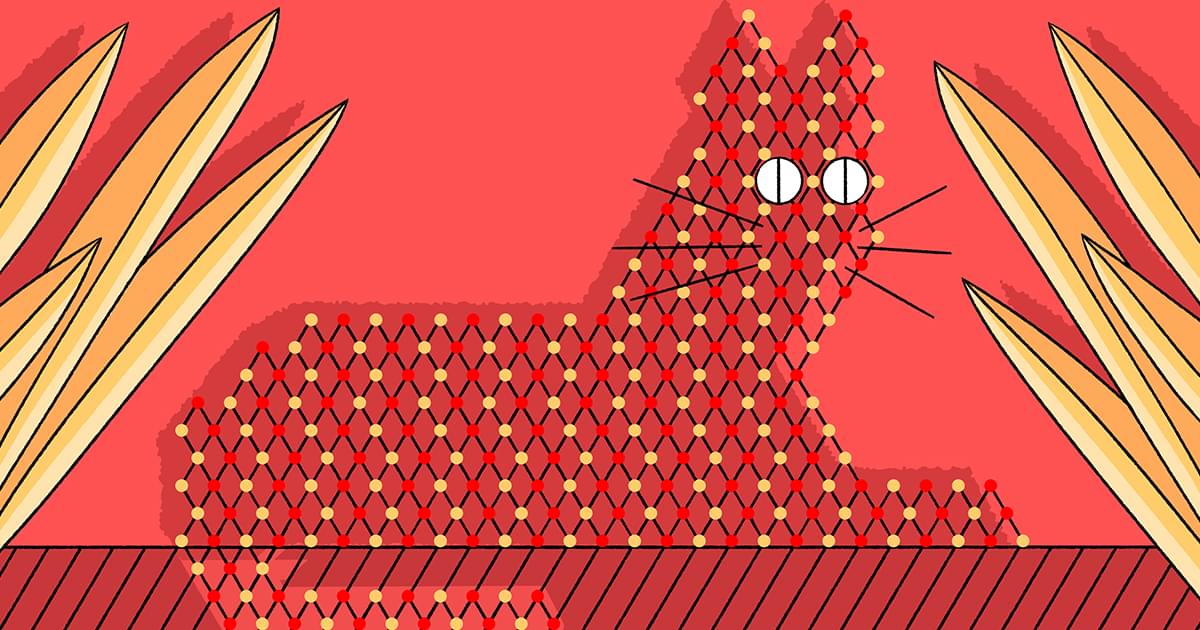
Neural networks power today’s AI boom. To understand them, all we need is a map, a cat and a few thousand dimensions.


Adjuvant chemotherapy use almost doubled in premenopausal patients with node-positive tumors and with a low to intermediate genomic risk from 2019 to 2022 but decreased for patients with node-negative disease.
Question What are the patterns of adjuvant chemotherapy use for early-stage hormone receptor (HR)–positive, ERBB2-negative breast cancer by genomic risk and nodal status?
Findings In this cohort study of 504 937 women, adjuvant chemotherapy use nearly doubled in premenopausal patients with node-positive tumors and low or intermediate 21-gene recurrence score from 2019 to 2022 but decreased for women with node-negative disease.
Meaning The findings highlight the variability in genomic assay use to inform adjuvant systemic therapy recommendations in HR-positive, ERBB2-negative breast cancer.

Scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz have discovered that while brain neuron changes, including cell loss, may begin in early life, a drug long-approved for other conditions might be repurposed to slow this damage, offering new hope for those with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other cognition issues.
The study was published today in the journal Cell Reports Medicine.
“This drug improved one measure of cognition and reduced a blood measure of neuron death in people with AD in a relatively short period of time in its first clinical trial,” said the study’s senior author Professor Huntington Potter, Ph.D., director of the University of Colorado Alzheimer’s and Cognition Center at CU Anschutz.
Reduced coronary blood flow, measured with an artificial intelligence-based imaging tool, predicted future cardiovascular events in patients with suspected stable coronary artery disease. These findings were presented at EACVI 2025, the congress of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI).
Stable coronary artery disease (CAD) refers to the common syndrome of recurrent, transient episodes of chest symptoms, often manifesting as angina. Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is a noninvasive heart scan that is used as the first-line investigation for patients with suspected stable CAD.
AI tools and FFR-CT explained While CCTA clearly shows blockages in coronary arteries, it is limited in its ability to estimate reduced blood flow, which is necessary to diagnose angina. An artificial intelligence-based tool has been developed that analyzes CCTA images and provides an estimate of blood flow, termed CT-derived fractional flow reserve (FFR-CT).
Questions to inspire discussion.
Launch Economics & Viability.
🚀 Q: What launch cost makes space data centers economically competitive? A: Space data centers become cost-competitive with ground systems when launch costs drop to approximately $200/kg, according to Google’s Suncatcher paper, making the economics viable for moving compute infrastructure off-Earth.
💰 Q: Why might SpaceX pursue a $1.5 trillion IPO valuation? A: The projected $1.5 trillion SpaceX IPO valuation is speculated to fund the capital-intensive race to establish space-based data centers and secure the best orbital positions before competitors.
🏢 Q: Which companies can realistically build space data centers first? A: Vertically integrated organizations like SpaceX, Relativity Space, and Blue Origin lead because they control launch infrastructure, can self-fund deployment, and serve as their own customers for space compute capacity.
🛰️ Q: How would space data centers physically connect GPUs across satellites? A: Multiple free-flying satellites in formation (like 20+ Starlink satellites) use inter-satellite optical connections to enable communication between GPUs, creating high-density computing clusters in orbit.
🚀 Q: How will SpaceX reduce launch costs for space data centers?
A: SpaceX plans to build a lunar mass driver that will launch massive data centers into deep space at lower cost than using Starship rockets, with the mass driver eventually becoming the cheaper and more efficient method after initial Starship-based launches establish the infrastructure.
🏭 Q: What facilities will SpaceX build on the lunar base?
🔹 Q: What specific cost advantages does SPARC offer beyond eliminating underwriting fees? A: SPARC reduces friction, cost, and time by bypassing the traditional investment banking process entirely, eliminating promotional fees and creating a cleaner, more transparent process than traditional SPACs.
🔹 Q: How would Tesla shareholders get early access to SpaceX shares through SPARC? A: Tesla shareholders would receive special rights to acquire SpaceX shares at the IPO price before the public, potentially through warrants at a discounted price, allowing them to benefit from SpaceX’s future growth.
🔹 Q: What advantage does SPARC provide Tesla investors over traditional IPO allocation? A: SPARC enables more equitable allocation of SpaceX shares to Tesla investors, avoiding the traditional gated process that benefits Wall Street bankers’ friends and their preferred clients.
🔹 Q: How could SpaceX share access impact Tesla’s stock price? A: The SPARC structure allowing Tesla shareholders to receive warrants for SpaceX shares at discounted prices could potentially boost Tesla’s stock price by providing unique value to existing shareholders.
Pricing Control.
🔹 Q: Who controls pricing in SPARC versus traditional IPO? A: SPARC allows the public to set the price rather than banker control, giving SpaceX more control over pricing decisions compared to traditional IPO where investment banks determine valuation.
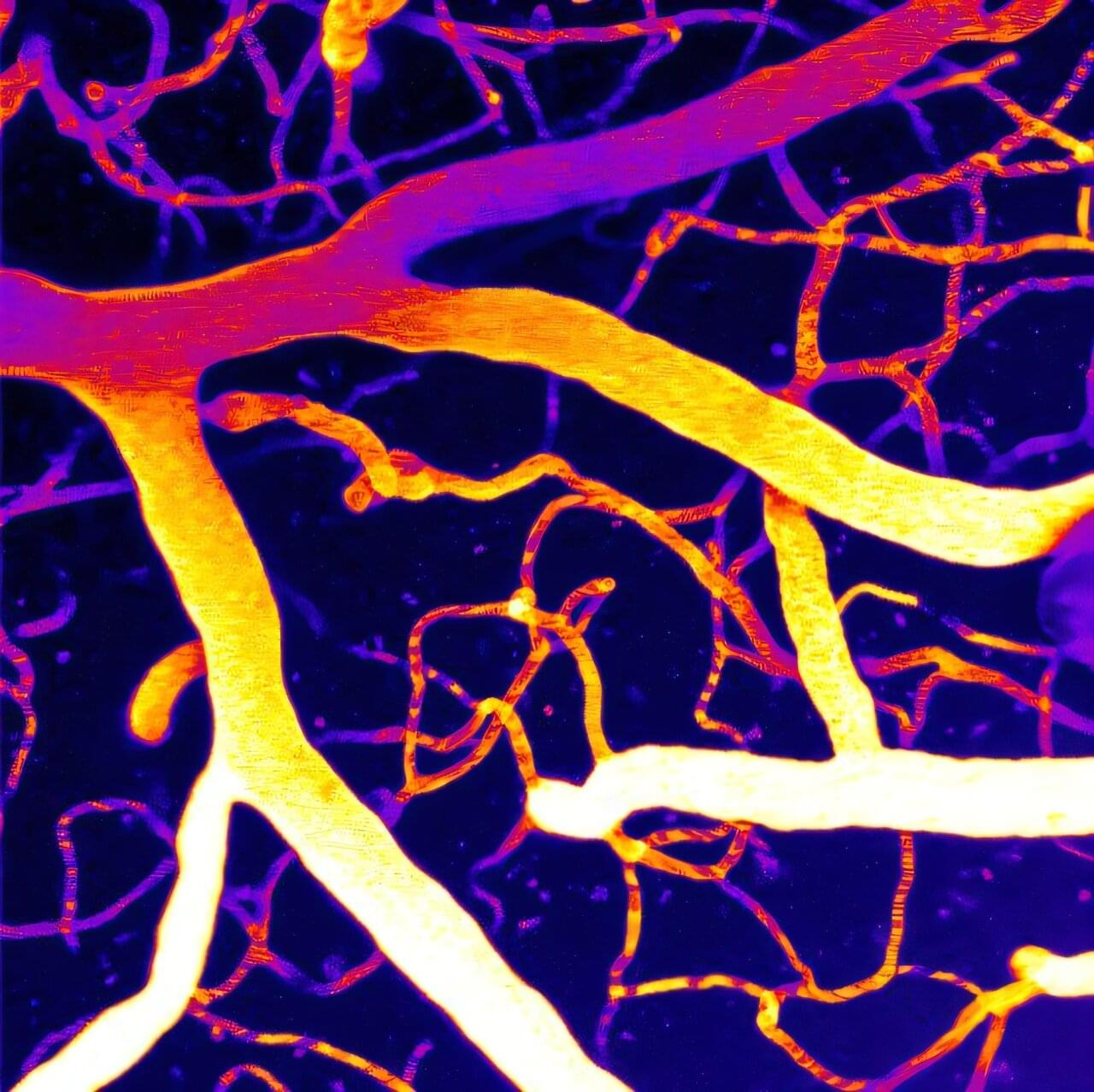
A possible new treatment for impaired brain blood flow and related dementias is on the horizon. Research by scientists at the University of Vermont Robert Larner, M.D. College of Medicine provides novel insights into the mechanisms that regulate brain blood flow and highlights a potential therapeutic strategy to correct vascular dysfunction.
Their preclinical findings, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggest that adding a missing phospholipid back into a person’s circulatory system could restore normal brain blood flow and reduce symptoms of dementia.
“This discovery is a huge step forward in our efforts to prevent dementia and neurovascular diseases,” says principal investigator Osama Harraz, Ph.D., assistant professor of pharmacology at Larner College of Medicine.