An invisible force has long eluded detection within the halls of the world’s most famous particle accelerator—until now.


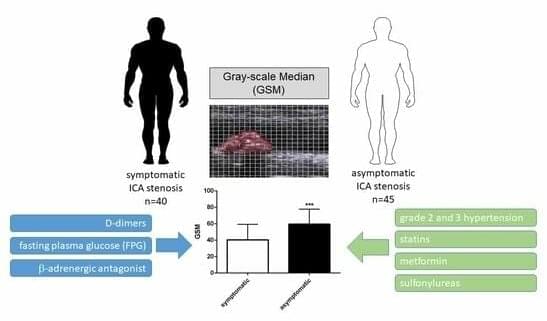
Background: The identification of clinical factors affecting the gray-scale median (GSM) and determination of GSM diagnostic utility for differentiating between symptomatic and asymptomatic internal carotid artery (ICA) stenosis. Methods: This study included 45 patients with asymptomatic and 40 patients with symptomatic ICA stenosis undergoing carotid endarterectomy (CEA). Echolucency of carotid plaque was determined using computerized techniques for the GSM analysis. Study groups were compared in terms of clinical risk factors, coexisting comorbidities, and used pharmacotherapy. Results: Mean GSM values in the symptomatic group were significantly lower than in the asymptomatic group (p < 0.001). Both in the univariate as well as in the multiple regression analysis, GSM was significantly correlated with D-dimers and fasting plasma glucose levels and tended to correlate with β-adrenoceptor antagonist use in the symptomatic group. In asymptomatic patients, GSM was associated with the presence of grade 2 and grade 3 hypertension, and tended to correlate with the use of metformin, sulfonylureas, and statin. Independent factors for GSM in this group remained as grade 3 hypertension and statin’s therapy. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis revealed that GSM differentiated symptomatic from asymptomatic ICA stenosis with sensitivity and specificity of 73% and 80%, respectively. Conclusion: The completely diverse clinical parameters may affect GSM in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients undergoing CEA, whose clinical characteristics were similar in terms of most of the compared parameters. GSM may be a clinically useful parameter for differentiating between symptomatic and asymptomatic ICA stenosis.
Support this channel on Patreon to help me make this a full time job: https://www.patreon.com/whatdamath (Unreleased videos, extra footage, DMs, no ads)Alter…
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links/Affiliates: Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.u…
Dr. John Cramer, 92-year-old nuclear physicist, discusses participating in the first mitochondrial transplant trial for aging and his longevity theory.
Some links are affiliate links so we will earn a commission when they are used to purchase products.
If you would like to support our channel please consider joining our Patreon / modernhealthspan.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
BiOptimizers — 15% off Code MHBIO: https://tinyurl.com/yt-bioptimize-202…(Magnesium Breakthrough, Gluten Guardian)
Stemregen — 10% off Code MODERN: https://tinyurl.com/yt-stemregen-2025… (Stem cell mobilization)
Renue — 15% off Code MHS: https://tinyurl.com/yt-renue-20251214 (Lipo NMN)
Seeking Health — 10% off Code Richard10: https://tinyurl.com/yt-seekinghea-202… (Histamine Nutrients)
AX3 — 20% off Code MODERN20: https://tinyurl.com/yt-ax3-20251214 (Astaxanthin)
n1o1 — 10% off Code Modern: https://tinyurl.com/yt-n1o1-20251214 (Nitric Oxide Lozenges)
These are affiliate links — using them supports the channel at no extra cost to you.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Dr. John Cramer is a 92-year-old emeritus professor at the University of Washington who has spent decades researching nuclear physics and quantum mechanics. Now, he’s turned his attention to longevity, and he’s not just theorizing. Dr. Cramer is participating in Mitrix’s groundbreaking mitochondrial transplantation trial, which aims to replace damaged mitochondrial DNA with healthy versions grown in bioreactors.
In this conversation, Dr. Cramer explains why he believes mitochondrial dysfunction is the root cause of aging, not just another hallmark. He discusses how energy depletion cascades into all other aging symptoms, why previous interventions like telomere extension haven’t delivered, and what markers will be tracked throughout his trial. He also shares his personal longevity protocol, including rapamycin, senolytics, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
This is one of the first detailed discussions of autologous mitochondrial transplantation for aging in humans.


AI’s rise to fame in the mainstream happened with OpenAI’s GPT-3 launch in 2020, which became a benchmark for large language models and quickly spread through startups via APIs. While Big Tech now races toward AGI and superintelligence, experts warn current systems remain limited, governance unprepared, and safety oversight crucial as AI capabilities accelerate faster than human control.
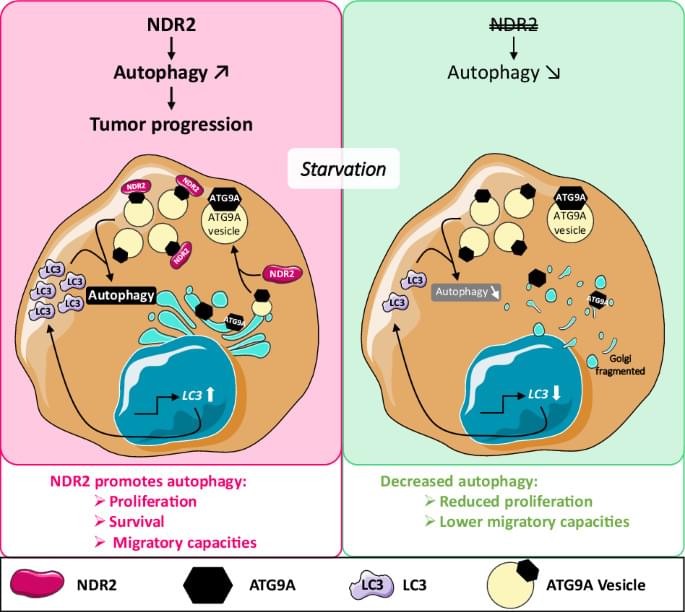
Biojout, T., Bergot, E., Taylor, J. et al. Cell Death Discov. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-025-02889-9

Last year, a research team led by UCLA achieved a milestone scientists had pursued for half a century. They succeeded in making radioactive thorium nuclei interact with light by absorbing and emitting photons, similar to how electrons behave inside atoms. First envisioned by the group in 2008, the breakthrough is expected to transform precision timekeeping and could significantly improve navigation systems, while also opening the door to discoveries that challenge some of the most basic constants in physics.
The advance comes with a major limitation. The required isotope, thorium-229, exists only as a byproduct of weapons-grade uranium, making it extremely rare. Researchers estimate that just 40 grams of this material are currently available worldwide for use in nuclear clock research.
A new study now shows a way around this obstacle. An international collaboration led by UCLA physicist Eric Hudson has developed an approach that uses only a small fraction of the thorium needed in earlier experiments, while delivering the same results previously achieved with specialized crystals. Described in Nature, the technique is both straightforward and low cost, raising the possibility that nuclear clocks could one day be small and affordable enough to fit into everyday devices like phones or wristwatches. Beyond consumer electronics, the clocks could replace existing systems used in power grids, cell phone towers, and GPS satellites, and may even support navigation where GPS is unavailable, such as in deep space or underwater.
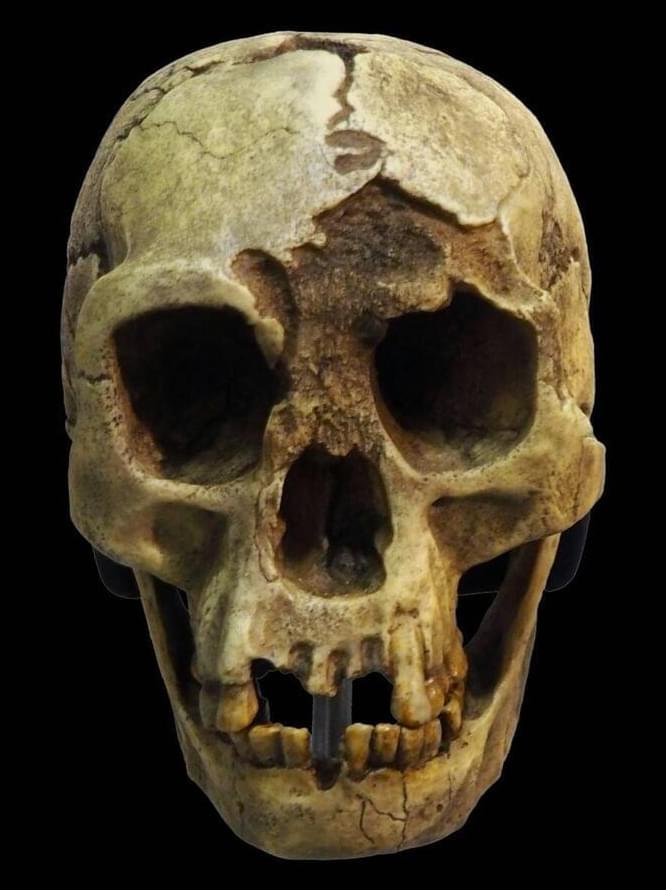
About 50,000 years ago, humanity lost one of its last surviving hominin cousins, Homo floresiensis (also known as “the hobbit” thanks to its small stature). The cause of its disappearance, after more than a million years living on the isolated volcanic island of Flores, Indonesia, has been a longstanding mystery.
Now, new evidence suggests a period of extreme drought starting about 61,000 years ago may have contributed to the hobbits’ disappearance.
Our new study, published today in Communications Earth & Environment, reveals a story of ecological boom and bust. We’ve compiled the most detailed climate record to date for the site where these ancient hominins once lived.