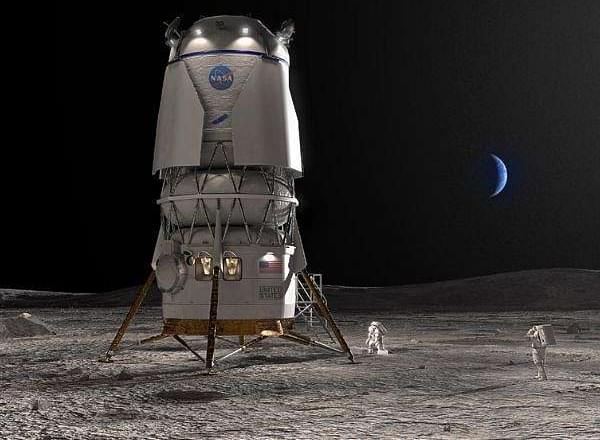
NASA has launched the 2026 Human Lander Challenge, inviting U.S.-based university students to propose fresh concepts for life support and environmental systems vital to long-duration spaceflight. The program, part of the Artemis campaign, focuses on advancing Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) technologies needed to sustain astronauts on the Moon and future missions to Mars.
The challenge seeks undergraduate and graduate teams to design systems-level solutions across four subtopics: noise control, sensor reduction in health monitoring hardware, potable water dispensing, and fluid transfer between lunar or Martian surface assets. Proposals must improve ECLSS reliability in areas such as air, water, and waste management.
“A robust ECLSS transforms a spacecraft like a lander from just hardware into a livable environment, providing breathable air, clean water, and safe conditions for astronauts as they explore the Moon,” said Kevin Gutierrez, acting office manager for the Human Landing Systems Missions Systems Management Office at NASA Marshall. “Without ECLSS we can’t sustain human presence on the Moon or take the next steps toward Mars. The subtopics in the 2026 Human Lander Challenge reflect opportunities for students to support the future of human spaceflight.”