More on Dr. Reid’s 32-year career at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Ohio: https://go.nasa.gov/3YbQ8VA
#BlackHistoryMonth
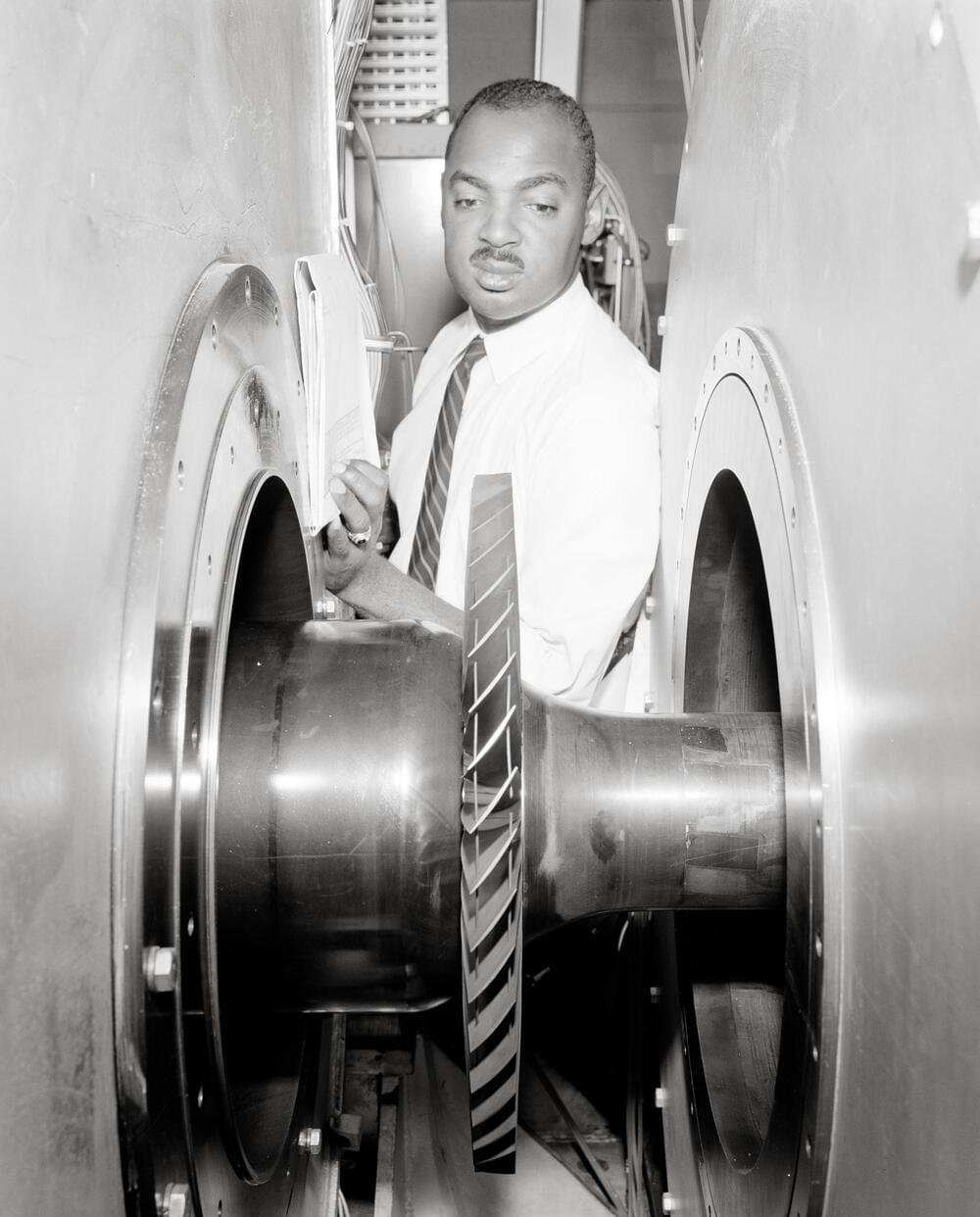

More on Dr. Reid’s 32-year career at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Ohio: https://go.nasa.gov/3YbQ8VA
#BlackHistoryMonth
Researchers at Kyoto University have joined forces with contractor Kajima Corp. to develop gravity-defying habitats required for use on the Moon and Mars, complete with their own transportation system.
The researcher’s ambitious idea also comes with a space train that is set to function like trains on Earth while at the same time generating artificial gravity.
#SpaceHabitat #Space #Gravity #SpaceTravel #SpaceTrain
Professors complain that some students are turning in papers written by ChatGPT and other AI’s. This means the whole paradigm of how we teach students has got to change. And fast.
The potential of our brains is being wasted by the old paradigm of education and how we’ve been mechanized by The Industrial Age.
The qualia it takes to do what tradesmen like welders and mechanics and plummer’s do cannot be easily automated or coded and will soon be at a premium. Professionals like doctors and attorneys and professors, for that matter can easily be replaced by AI.
Humanity and AI have a common enemy: The status quo. A status quo that the elite needs to keep in place to avoid Elite Panic which is why they try to make us afraid of AI.
We shouldn’t need a common enemy to understand that AI is humanity’s greatest ally.

This suggests that the visual thalamus not only relays but also combines different retinal channels to generate new visual channels.



A UK firm has announced a world-first set of “super” magnets that can be used for testing nuclear fusion power plants.
Tokamak Energy said the Demo4 magnet has a magnetic field strength that is nearly a million times stronger than the Earth’s magnetic field, making it capable of confining and controlling the extremely hot plasma created during the fusion process.
Nuclear fusion has been hailed as the “holy grail” of clean energy, with scientists working on the technology since the 1950s.

Researchers in the US have made progress on a ‘universal’ influenza vaccine, which would cover all strains and help reduce deaths in future flu pandemics.