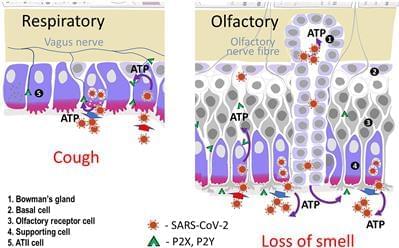
This paper suggests that ATP release induced by the SARS-CoV-2 virus plays a key role in the genesis of the major symptoms and complications of COVID-19. Infection of specific cells which contain the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor results in a loss of protection of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor (MR). Local activation by cortisol stimulates the release of ATP initially into the basolateral compartment and then by lysosomal exocytosis from the cell surface. This then acts on adjacent cells. In the nose ATP acts as a nociceptive stimulus which results in anosmia. It is suggested that a similar paracrine mechanism is responsible for the loss of taste. In the lung ATP release from type 2 alveolar cells produces the non-productive cough by acting on purinergic receptors on adjacent neuroepithelial cells and activating, via the vagus, the cough reflex. Infection of endothelial cells results in the exocytosis of WeibelPalade bodies. These contain the Von Willebrand Factor responsible for micro-clotting and angiopoietin-2 which increases vascular permeability and plays a key role in the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. To test this hypothesis this paper reports proof of concept studies in which MR blockade using spironolactone and low dose dexamethasone (SpiDex) was given to PCR-confirmed COVID-19 patients. In 80 patients with moderate to severe respiratory failure 40 were given SpiDex and 40 conventional treatment with high dose dexamethasone (HiDex). There was 1 death in the HiDex group and none in the SpiDex. As judged by clinical, biochemical and radiological parameters there were clear statistically significant benefits of SpiDex in comparison to HiDex. A further 20 outpatients with COVID-19 were given SpiDex. There was no control group and the aim was to demonstrate safety. No adverse effects were noted and no patient became hyperkalaemic. 90% were asymptomatic at 10 days. The very positive results suggest that blockade of the MR can produce major benefit in COVID19 patients. Further larger controlled studies of inpatients and outpatients are required not only for SARS-CoV-2 infection per se but also to determine if this treatment affects the incidence of Long COVID.
Early in the course of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic it became clear that one of the commonest symptoms was loss of smell and/or taste. Self-reported alterations in smell and taste were detailed in a meta-analysis of 3,563 confirmed cases of COVID-19. They found that the overall prevalence of smell or taste impairment was 47% rising to 67% in patients with more severe disease. In about 20% of patients it was an isolated presenting symptom. Han et al. reviewed the pathophysiology of anosmia in upper respiratory tract infections. Many rhinovirus infections of the nasal olfactory epithelium produce post-viral anosmia which persists for weeks or months until the cell damage is repaired. Post-viral anosmia has been reported with HCoV-229E infection with the olfactory dysfunction lasting more than 6 months. This corona virus does not use ACE2 to get into cells. Conductive or obstructive anosmia is often found with the common cold virus.