Most galaxies seemed to be missing a huge proportion of the matter we expected them to have – now researchers may have found its hiding spot, but the discovery contradicts accepted models of galaxy formation.
By Leah Crane

Most galaxies seemed to be missing a huge proportion of the matter we expected them to have – now researchers may have found its hiding spot, but the discovery contradicts accepted models of galaxy formation.
By Leah Crane
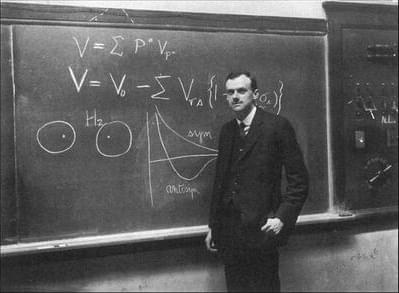

The cosmos is full of mysteries, one of which is the existence of supermassive black holes. Though much effort has been granted to these celestial mysteries, the evolution and formation of such supermassive black holes are quite hard to explain.
Supermassive Black Holes
According to Science Alert, these celestial objects are among the heaviest in the entire universe. In fact, their mass can be up to millions or billions of times that of the sun. They can have the mass of more than 10 billion suns, and this is not just in theory.
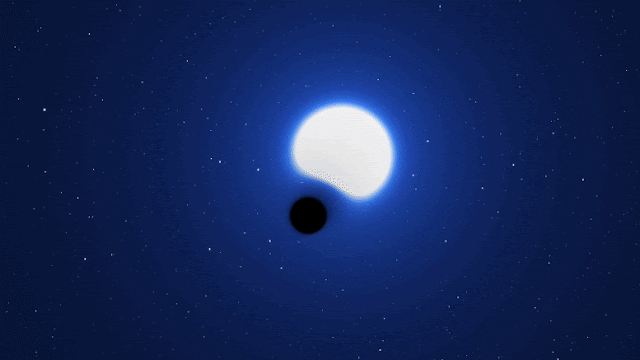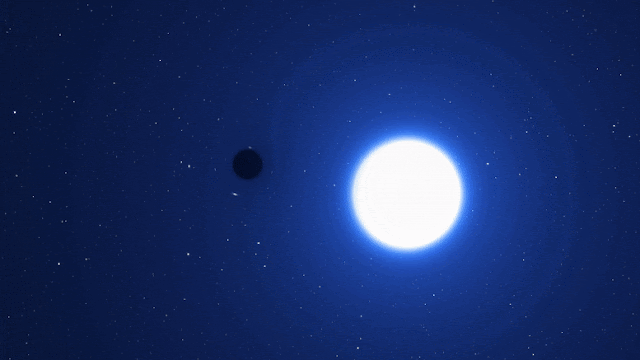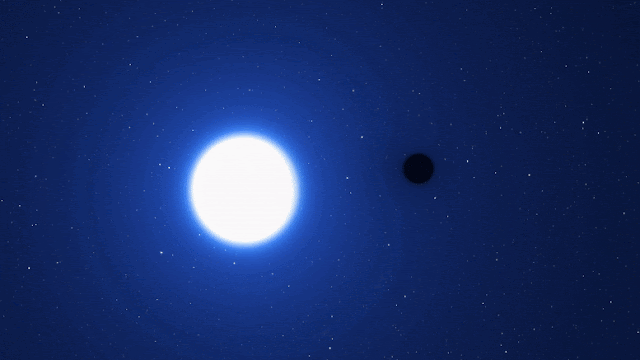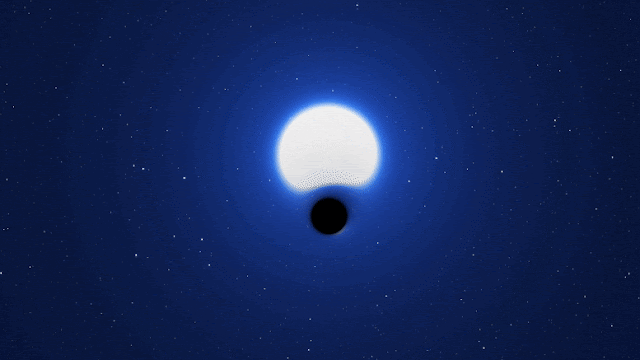
Astronomers have found what they are calling a “cosmic needle in a haystack” in a galaxy next to our Milky Way. It is a dormant black hole that seems to have formed without the explosion of a dead star.
Researchers said on Monday that this black hole is different from all the others that we know of because it is “X-ray quiet.” This means that it doesn’t make a lot of X-ray radiation, which would indicate that it is eating nearby matter with its huge gravitational pull, and that it didn’t form in a supernova.
Black holes are very dense things with so much gravity that not even light can get out.



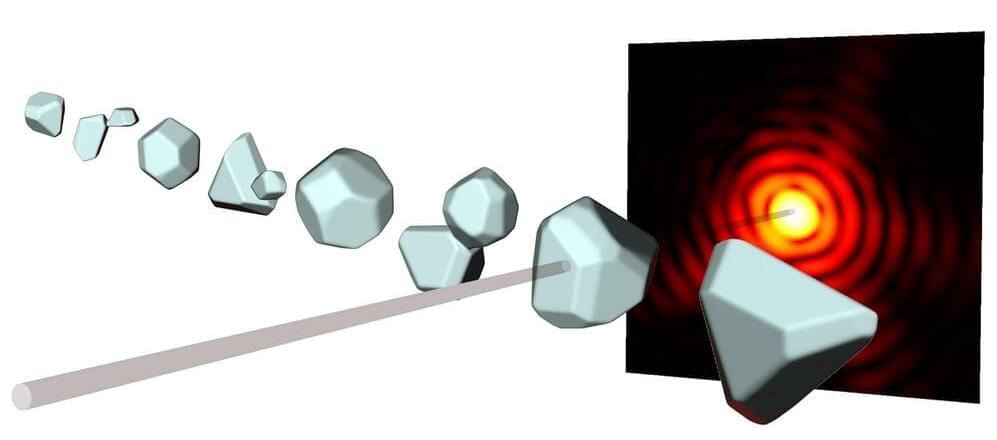
X-ray diffraction has been used for more than a hundred years to understand the structure of crystals or proteins—for instance, in 1952 the well-known double helix structure of the DNA that carries genetic information was discovered in this way. In this technique, the object under investigation is bombarded with short-wavelength X-ray beams. The diffracted beams then interfere and thus create characteristic diffraction patterns from which one can gain information about the shape of the object.
For several years now it has been possible to study even single nanoparticles in this way, using very short and extremely intense X-ray pulses. However, this typically only yields a two-dimensional image of the particle. A team of researchers led by ETH professor Daniela Rupp, together with colleagues at the universities of Rostock and Freiburg, the TU Berlin and DESY in Hamburg, have now found a way to also calculate the three-dimensional structure from a single diffraction pattern, so that one can “look” at the particle from all directions. In the future it should even be possible to make 3D-movies of the dynamics of nanostructures in this way. The results of this research have recently been published in the scientific journal Science Advances.
Daniela Rupp has been assistant professor at ETH Zurich since 2019, where she leads the research group “Nanostructures and ultra-fast X-ray science.” Together with her team she tries to better understand the interaction between very intense X-ray pulses and matter. As a model system they use nanoparticles, which they also investigate at the Paul Scherrer Institute. “For the future there are great opportunities at the new Maloja instrument, on which we were the first user group to make measurements at the beginning of last year. Right now our team there is activating the attosecond mode, with which we can even observe the dynamics of electrons,” says Rupp.
A method for turning male cells into egg cells in mice could one day be used to help men in a same-sex couple have children who are genetically related to them both.