Chinese researchers have developed a novel method to efficiently engineer natural killer (NK) cells for cancer immunotherapy. NK cells are central to early antiviral and anticancer defense—among other immune system roles—making them well-suited for cancer immunotherapy. For example, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-NK therapy involves adding a lab-built receptor (a CAR) to an NK cell, enabling it to recognize a specific antigen on a cancer cell and attack it.
However, conventional CAR-NK immunotherapies rely primarily on mature NK cells isolated from human tissues, such as peripheral blood or cord blood, which poses multiple challenges, including high heterogeneity, low engineering efficiency, high handling costs, and time-intensive processing.
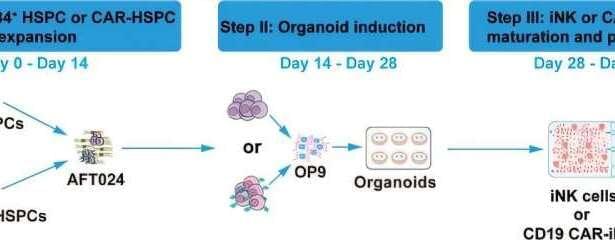
Now a research team led by Prof. Wang Jinyong from the Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a novel method to generate induced (that is, lab-generated) NK (iNK) cells and CAR-engineered iNK (CAR-iNK) cells from CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) derived from cord blood.