This talks about the 2022 polio outbreak in NYC and it’s surrounding areas due to low vaccinations to the virus.
CDC public health news, press releases, government public health news, medical and disease news, story ideas, photos.


Were you unable to attend Transform 2022? Check out all of the summit sessions in our on-demand library now! Watch here.
We are on the cusp of a paradigm shift brought by generative AI — but it isn’t about making creativity “quick and easy.” Generative technology opens new heights of human expression and helps creators find their authentic voices.
How we create is changing. The blog you read earlier today may have been made with generative AI. Within 10 years, most creative content will be produced with generative technologies.
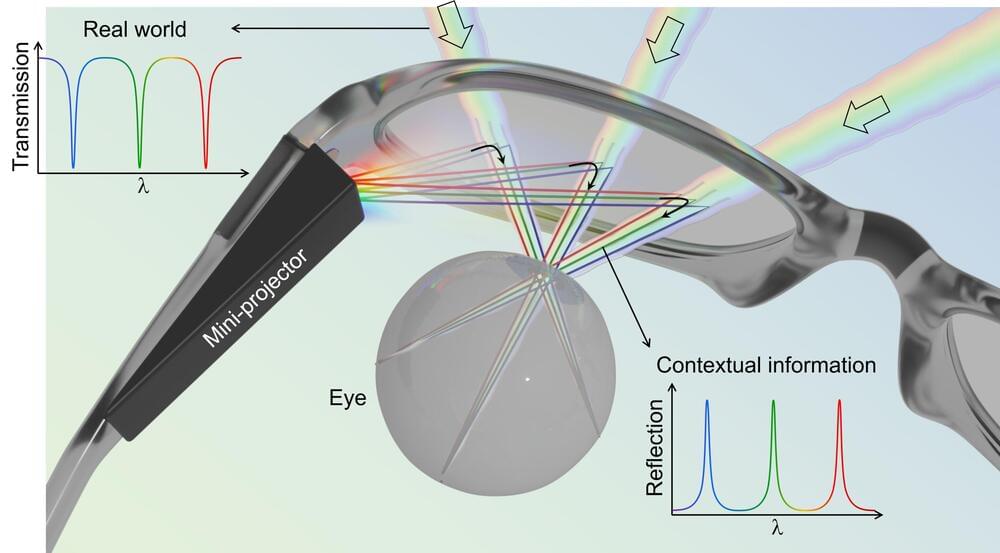
As anyone who has recently tried out an augmented reality headset knows, the technology is not yet ready to be part of our everyday lives. Researchers have been working to perfect high-performing augmented reality (AR) glasses, but there are a number of challenges. One major problem with conventional AR glasses is that there is a tradeoff in terms of quality and brightness between the external scene you actually see and the contextual information you also want to visualize.
Early solutions like Google Glass used multiple bulky optical components that were partially reflective and partially transmissive to mix the real-world and contextual scenes, with the result of a dimmed and distorted vision of both scenes.
More recent AR head-mounted-display eyeglasses have been patterned with diffractive gratings (fine grooves) with wavelength-sized spacing that deflect contextual information from a miniprojector beside the glasses to the viewer’s eye. But these eyeglasses still dim and distort the external scene because real-world light passing through the glass inevitably gets scattered and dispersed by the gratings. The distortions get worse when several sets of overlapping gratings must be used to handle multiple distinct colors from the miniprojector.
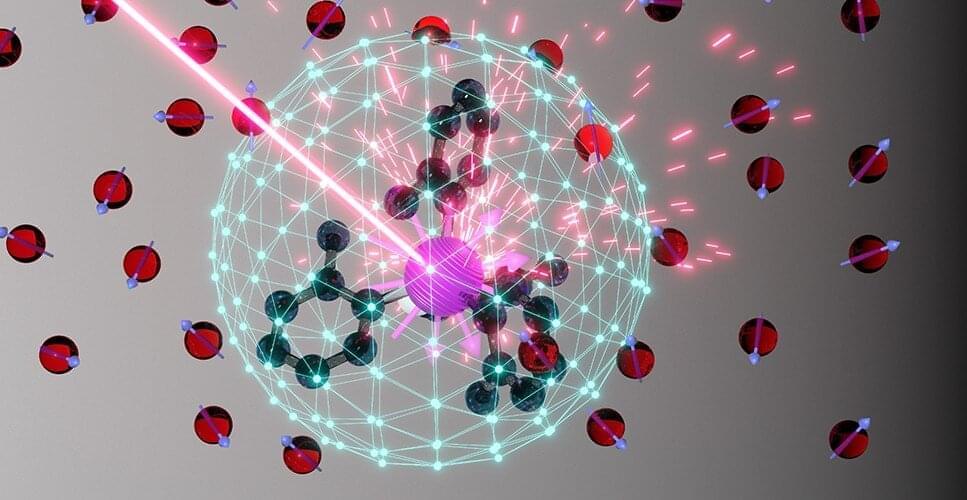
The concept of “symmetry” is essential to fundamental physics: a crucial element in everything from subatomic particles to macroscopic crystals. Accordingly, a lack of symmetry—or asymmetry—can drastically affect the properties of a given system.
Qubits, the quantum analog of computer bits for quantum computers, are extremely sensitive—the barest disturbance in a qubit system is enough for it to lose any quantum information it might have carried. Given this fragility, it seems intuitive that qubits would be most stable in a symmetric environment. However, for a certain type of qubit—a molecular qubit—the opposite is true.
Researchers from the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME), the University of Glasgow, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have found that molecular qubits are much more stable in an asymmetric environment, expanding the possible applications of such qubits, especially as biological quantum sensors.
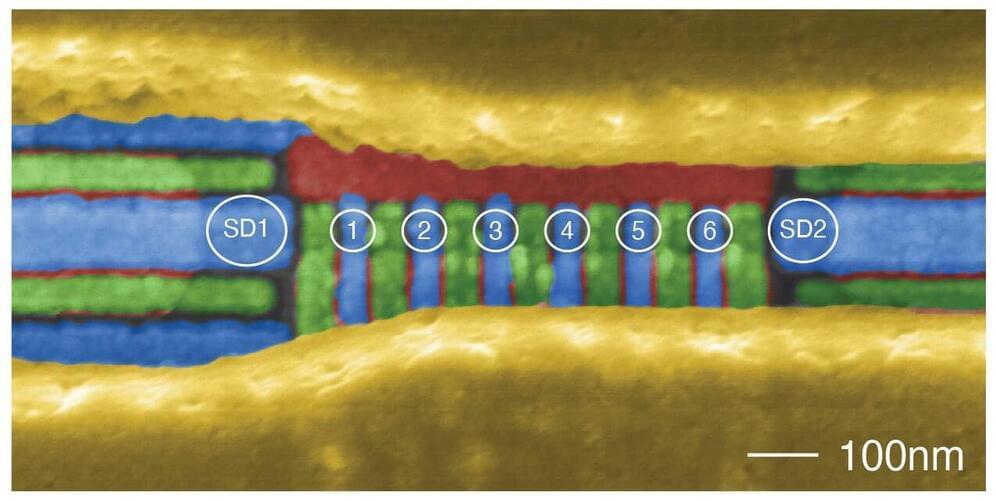
Researchers at QuTech—a collaboration between the Delft University of Technology and TNO—have engineered a record number of six, silicon-based, spin qubits in a fully interoperable array. Importantly, the qubits can be operated with a low error-rate that is achieved with a new chip design, an automated calibration procedure, and new methods for qubit initialization and readout. These advances will contribute to a scalable quantum computer based on silicon. The results are published in Nature today.
Different materials can be used to produce qubits, the quantum analog to the bit of the classical computer, but no one knows which material will turn out to be best to build a large-scale quantum computer. To date there have only been smaller demonstrations of silicon quantum chips with high quality qubit operations. Now, researchers from QuTech, led by Prof. Lieven Vandersypen, have produced a six qubit chip in silicon that operates with low error-rates. This is a major step towards a fault-tolerant quantum computer using silicon.
To make the qubits, individual electrons are placed in a linear array of six “quantum dots” spaced 90 nanometers apart. The array of quantum dots is made in a silicon chip with structures that closely resemble the transistor—a common component in every computer chip. A quantum mechanical property called spin is used to define a qubit with its orientation defining the 0 or 1 logical state. The team used finely-tuned microwave radiation, magnetic fields, and electric potentials to control and measure the spin of individual electrons and make them interact with each other.
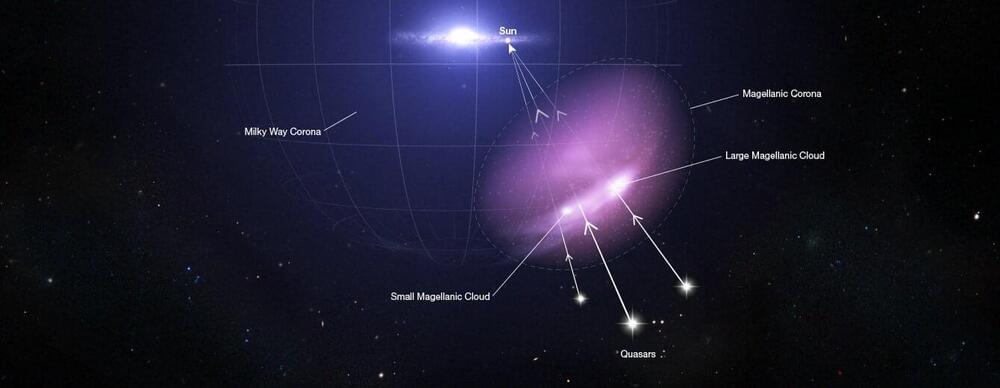
For billions of years, the Milky Way’s largest satellite galaxies—the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds—have followed a perilous journey. Orbiting one another as they are pulled in toward our home galaxy, they have begun to unravel, leaving behind trails of gaseous debris. And yet—to the puzzlement of astronomers—these dwarf galaxies remain intact, with ongoing vigorous star formation.
“A lot of people were struggling to explain how these streams of material could be there,” said Dhanesh Krishnarao, assistant professor at Colorado College. “If this gas was removed from these galaxies, how are they still forming stars?”
With the help of data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and a retired satellite called the Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE), a team of astronomers led by Krishnarao has finally found the answer: the Magellanic system is surrounded by a corona, a protective shield of hot supercharged gas. This cocoons the two galaxies, preventing their gas supplies from being siphoned off by the Milky Way, and therefore allowing them to continue forming new stars.
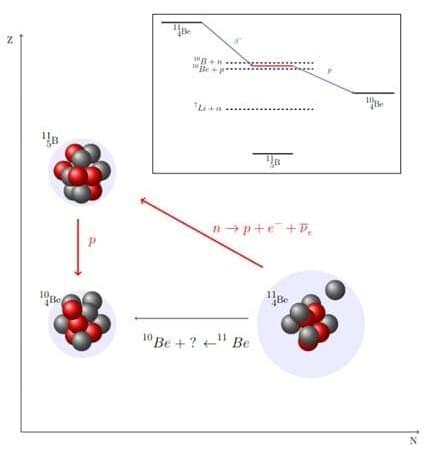
Most mass in everyday matter around us resides in protons and neutrons inside the atomic nucleus. However, the lifetime of a free neutron—one not bounded to a nucleus—is unstable, decaying by a process called beta decay. For neutrons, beta decay involves the emission of a proton, an electron, and an anti-neutrino. Beta decay is a common process.
However, scientists have some significant uncertainties about the neutron lifetime and about the neutron decaying inside a nucleus that leads to a proton emission. This is called beta-delayed proton emission. There are only a few neutron-rich nuclei for which beta-delayed proton emission is energetically allowed. The radioactive nucleus beryllium-11 (11 Be), an isotope that consists of 4 protons and 7 neutrons, with its last neutron very weakly bound, is among those rare cases. Scientists recently observed a surprising large beta-delayed proton decay rate for 11 Be. Their work is published in Physical Review Letters.
The discovery of an exotic near-threshold resonance that favors proton decay is a key for explaining the beta-delayed proton decay of 11 Be. The discovery is also a remarkable and not fully understood manifestation of quantum many-body physics. Many-body physics involves interacting subatomic particles. While scientists may know the physics that apply to each particle, the complete system can be too complex to understand.
A team of physicists has created a new way to self-assemble particles—an advance that offers new promise for building complex and innovative materials at the microscopic level.
Self-assembly, introduced in the early 2000s, gives scientists a means to “pre-program” particles, allowing for the building of materials without further human intervention—the microscopic equivalent of Ikea furniture that can assemble itself.
The breakthrough, reported in the journal Nature, centers on emulsions—droplets of oil immersed in water—and their use in the self-assembly of foldamers, which are unique shapes that can be theoretically predicted from the sequence of droplet interactions.
Have you ever been faced with a problem where you had to find an optimal solution out of many possible options, such as finding the quickest route to a certain place, considering both distance and traffic?
If so, the problem you were dealing with is what is formally known as a “combinatorial optimization problem.” While mathematically formulated, these problems are common in the real world and spring up across several fields, including logistics, network routing, machine learning, and materials science.
However, large-scale combinatorial optimization problems are very computationally intensive to solve using standard computers, making researchers turn to other approaches. One such approach is based on the “Ising model,” which mathematically represents the magnetic orientation of atoms, or “spins,” in a ferromagnetic material.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), a term first coined at a Dartmouth workshop in 1956, has seen several boom and bust cycles over the last 66 years. Is the current boom different?
The most exciting advance in the field since 2017 has been the development of “Large Language Models,” giant neural networks trained on massive databases of text on the web. Still highly experimental, Large Language Models haven’t yet been deployed at scale in any consumer product — smart/voice assistants like Alexa, Siri, Cortana, or the Google Assistant are still based on earlier, more scripted approaches.
Large Language Models do far better at routine tasks involving language processing than their predecessors. Although not always reliable, they can give a strong impression of really understanding us and holding up their end of an open-ended dialog. Unlike previous forms of AI, which could only perform specific jobs involving rote perception, classification, or judgment, Large Language Models seem to be capable of a lot more — including possibly passing the Turing Test, named after computing pioneer Alan Turing’s thought experiment that posits when an AI in a chat can’t be distinguished reliably from a human, it will have achieved general intelligence.
But can Large Language Models really understand anything, or are they just mimicking the superficial “form” of language? What can we say about our progress toward creating real intelligence in a machine? What do “intelligence” and “understanding” even mean? Blaise Agüera y Arcas, a Fellow at Google Research, and Melanie Mitchell, the Davis Professor of Complexity at the Santa Fe Institute, take on these thorny questions in a wide-ranging presentation and discussion.