Sorry if re-post…
A team of researchers affiliated with a large number of institutions in Japan has developed a vaccine that tricks the immune system into removing senescent cells. In their paper published in the journal Nature Aging, the group describes their vaccine, how it works and how effective it was when given to test mice.
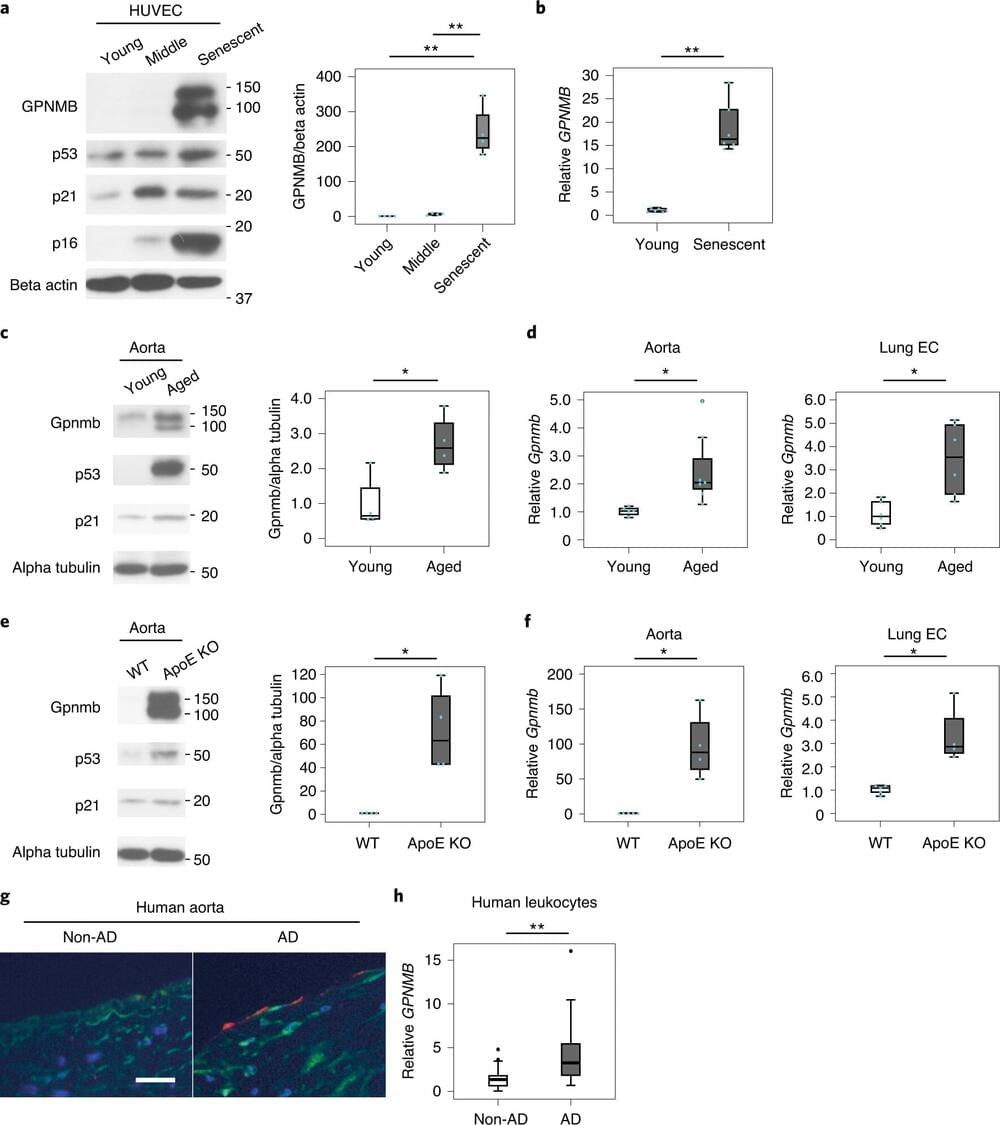
Prior research has shown that part of the aging process is the development of senescent cells —cells that outlive their usefulness but fail to die naturally. Instead, they produce chemicals that can lead to inflammation, aging and a host of other ailments. Prior research has shown that senescence occurs when cells stop dividing. Prior research has also shown that senescent cells can lead to tumor growth in some instances and tumor suppression in others. Senescence also plays a role in tissue repair, and its impacts on the body vary depending on factors such as overall health and age. It is suspected that senescence is related to telomere erosion, and in some cases, environmental factors that lead to cell damage. In this new effort, the researchers have developed a vaccine that creates antibodies that attach to senescent cells, marking them for removal by white blood cells.
The team was able to create the vaccine after identifying a protein made in senescent cells but not in healthy active cells. That allowed them to develop a type of vaccine based on the amino acids in the protein. When injected, the vaccine incites the body to produce antibodies that bind only to senescent cells, and that sets off an immune response that involves sending white blood cells to destroy the senescent cells.