The discovery will help us understand more about the evolution of our galaxy and learn about fast-moving central stars.
For the function of many biomolecules, their three-dimensional structure is crucial. Researchers are therefore not only interested in the sequence of the individual building blocks of biomolecules, but also in their spatial structure. With the help of artificial intelligence (AI), bioinformaticians can already reliably predict the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence. For RNA molecules, however, this technology is still in its infancy. Researchers at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) describe a way to use AI to reliably predict the structure of certain RNA molecules from their nucleotide sequence in the journal PLOS Computational Biology on July 7, 2022.
For the work, the teams led by Vivian Brandenburg and Professor Franz Narberhaus from the RUB Chair of Biology of Microorganisms cooperated with Professor Axel Mosig from the Bioinformatics Competence Area of the Bochum Center for Protein Diagnostics.
Curiosity is important for human development and learning and encourages an exploration for new information. New research published in the Journal of Individual Differences found that high dispositional curiosity is related to greater general knowledge, but not necessarily related to fluid intelligence.
Curiosity is important for both crystallized intelligence (i.e., one’s general knowledge) and fluid intelligence (i.e., one’s ability to reason and use novel information). “Seeking out new environments, being more attentive, and exploring more and more comprehensively might, in turn, also increase the probability of gaining new information,” explain study author Freda-Marie Hartung and colleagues. “Thus, it is plausible to assume that interindividual differences in epistemic curiosity are related to interindividual differences in general knowledge.”
Thus, the researchers were interested in how dispositional curiosity influences one’s acquisition of knowledge and how fluid intelligence affects this relationship. Hartung and her colleagues recruited 100 participants during lectures at a German University to complete a self-report questionnaire on the relevant personality traits (i.e., curiosity, conscientiousness, social anxiety). They also completed measures assessing their general knowledge (i.e., geography, history, math, natural sciences) and fluid intelligence (i.e., reasoning and memory tasks).
Older people with underactive thyroid, which is formally called hypothyroidism, may be at increased risk of developing dementia, according to a new research study published in the July 6, 2022, online issue of Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. According to the find.
Deepmind enters into a partnership with the renowned British research institute “The Crick”. Together, the organizations aim to advance the use of artificial intelligence in biology and biomedicine.
Artificial intelligence is already having a direct impact on our everyday lives, for example in autonomous driving, through generative AI systems such as DALL-E 2 and Alphacode or hand tracking for VR headsets.
Beyond these direct application scenarios, AI can be a tool that accelerates science – indirectly impacting our future, but possibly on a much larger scale.
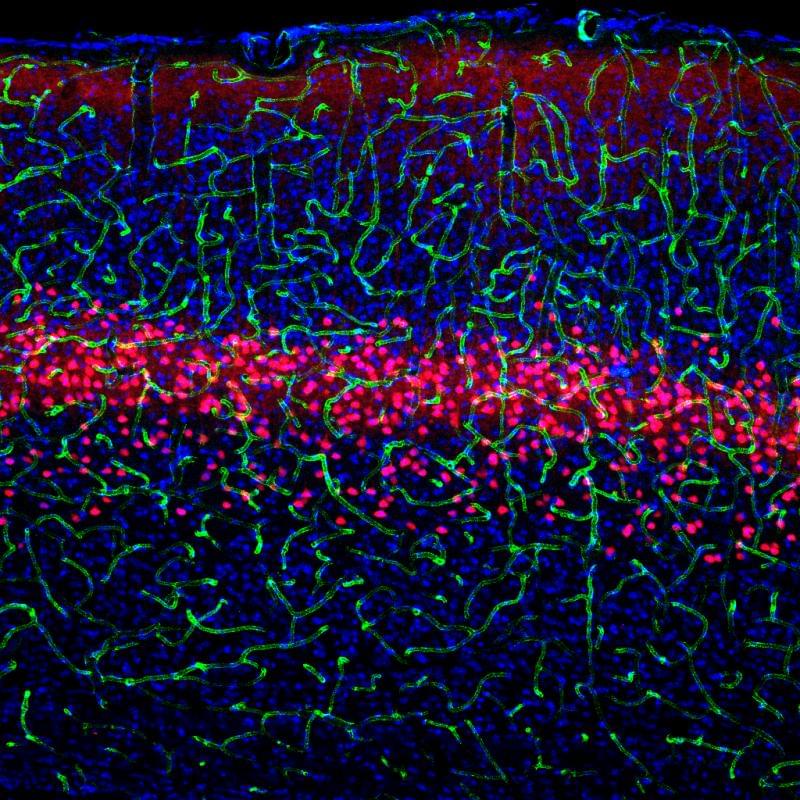
How the brain functions is still a black box: scientists aren’t even sure how many kinds of nerve cells exist in the brain. To know how the brain works, they need to know not only what types of nerve cells exist, but also how they work together. Researchers at the Salk Institute have gotten one step closer to unlocking this black box.
Using cutting-edge visualization and genetic techniques, the team uncovered a new subtype of nerve cell, or neuron, in the visual cortex. The group also detailed how the new cell and two similar neurons process images and connect to other parts of the brain. Learning how the brain analyzes visual information at such a detailed level may one day help doctors understand elements of disorders like schizophrenia and autism.
“Understanding these cell types contributes another piece to the puzzle uncovering neural circuits in the brain, circuits that will ultimately have implications for neurological disorders,” says Edward Callaway, Salk professor and senior author of the paper published December 6 in the journal Neuron.
Clinical studies have demonstrated a strong association between Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and delirium. A change to the Tau protein, which can lead to the formation of tangles in brain, is one of the hallmarks of AD pathology, and Tau phosphorylation at threonine 217 (Tau-PT217) and threonine 181 (Tau-PT181) are new plasma biomarkers that can detect early-stage AD. A clinical study led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has shown that plasma Tau-PT217 and Tau-PT181 are associated with incidence and severity of postoperative delirium. The findings are published in Annals of Surgery.
Early studies from the same research group at MGH have shown that the ratio of beta amyloid (which causes AD’s signature plaques) to Tau in cerebrospinal fluid is associated with postoperative delirium. Recent studies in other labs have reported that plasma Tau-PT181 concentration distinguishes AD dementia from other neurological disorders. Plasma levels of Tau-PT217 are associated with the changes in cerebrospinal fluid levels of Tau-PT217 and AD development.
In this current study, the team at MGH developed a novel method to measure Tau-PT217 and Tau-PT181 concentrations in plasma of patients, called nanoneedle technology, in collaboration with NanoMosaic (Woburn, MA). “The nanoneedle technology is ultrasensitive, requires a small volume, and can measure low concentrations of molecules, including Tau-PT217 and Tau-PT181,” says lead author Feng Liang, MD, Ph.D., in the Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine at MGH. “More than 20,000 nanoneedles are integrated on a silicon substrate assigned to detect one analyte. Each nanoneedle is a single molecule biosensor functionalized with antibodies,” says Liang.
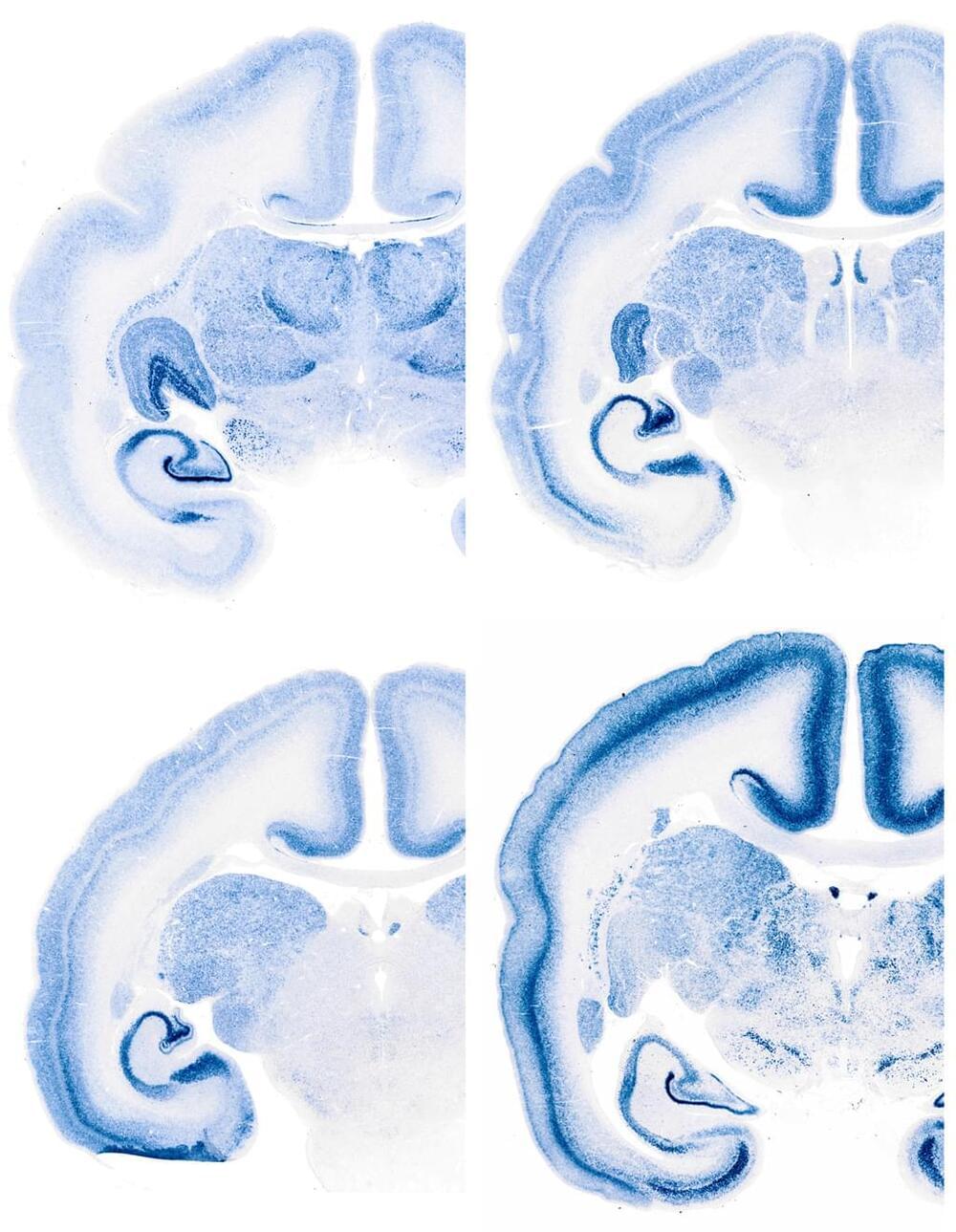
The human brain may be the most complex piece of organized matter in the known universe, but Allen Institute researchers have begun to unravel the genetic code underlying its function. Research published this month in Nature Neuroscience identified a surprisingly small set of molecular patterns that dominate gene expression in the human brain and appear to be common to all individuals, providing key insights into the core of the genetic code that makes our brains distinctly human.
“So much research focuses on the variations between individuals, but we turned that question on its head to ask, what makes us similar?” says Ed Lein, Ph.D., Investigator at the Allen Institute for Brain Science. “What is the conserved element among all of us that must give rise to our unique cognitive abilities and human traits?”
Researchers used data from the publicly available Allen Human Brain Atlas to investigate how gene expression varies across hundreds of functionally distinct brain regions in six human brains. They began by ranking genes by the consistency of their expression patterns across individuals, and then analyzed the relationship of these genes to one another and to brain function and association with disease.
Dramatic expansion of the human cerebral cortex, over the course of evolution, accommodated new areas for specialized cognitive function, including language. Understanding the genetic mechanisms underlying these changes, however, remains a challenge to neuroscientists.
A team of researchers in Japan has now elucidated the mechanisms of cortical evolution. They used molecular techniques to compare the gene expression patterns in mouse and monkey brains.
Using the technique called in situ hybridization to visualize the distribution of mRNA transcripts, Okano, Shimogori and their colleagues examined the expression patterns of genes that are known to regulate development of the mouse brain. They compared these patterns to those of the same genes in the brain of the common marmoset. They found that most of the genes had similar expression patterns in mice and marmosets, but that some had strikingly different patterns between the two species. Notably, some areas of the visual and prefrontal cortices showed expression patterns that were unique to marmosets.
Oxford researchers have identified the very first neurons in the human cerebral cortex, the part of the brain that sets us apart from all other animals.
Dr Irina Bystron and colleagues from the Department of Physiology, Anatomy and Genetics at the University of Oxford, together with Professor Pasko Rakic, a leading neuroscientist at Yale University, describe for the first time in Nature Neuroscience the very earliest nerve cells in the part of the developing human brain that becomes the cerebral cortex.
The cerebral cortex is largely responsible for human cognition, playing an essential role in perception, memory, thought, language, mental ability, intellect and consciousness. It is also responsible for our voluntary actions. As adults our cerebral cortex accounts for 40 per cent of the brain’s weight and is composed of about 20 billion neurons. The new findings show that its first neurons are in place much earlier than previously thought – approximately 31 days after fertilization, when the entire embryo is only about 4 mm long and shaped a bit like a comma, before the development of arms, legs or eyes.