If you’ve ever sat waiting at the doctor’s office to give a blood sample, you might have wished there was a way to find the same information without needles.
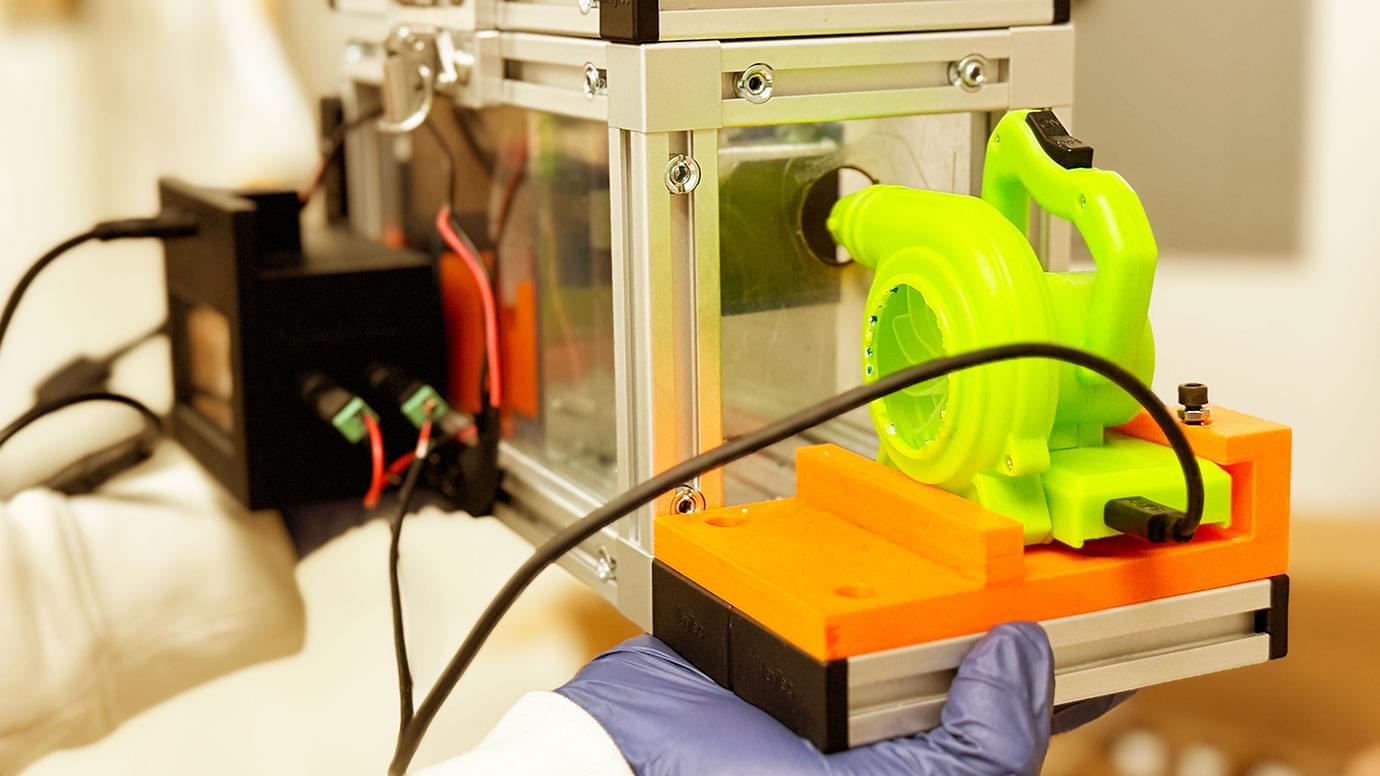
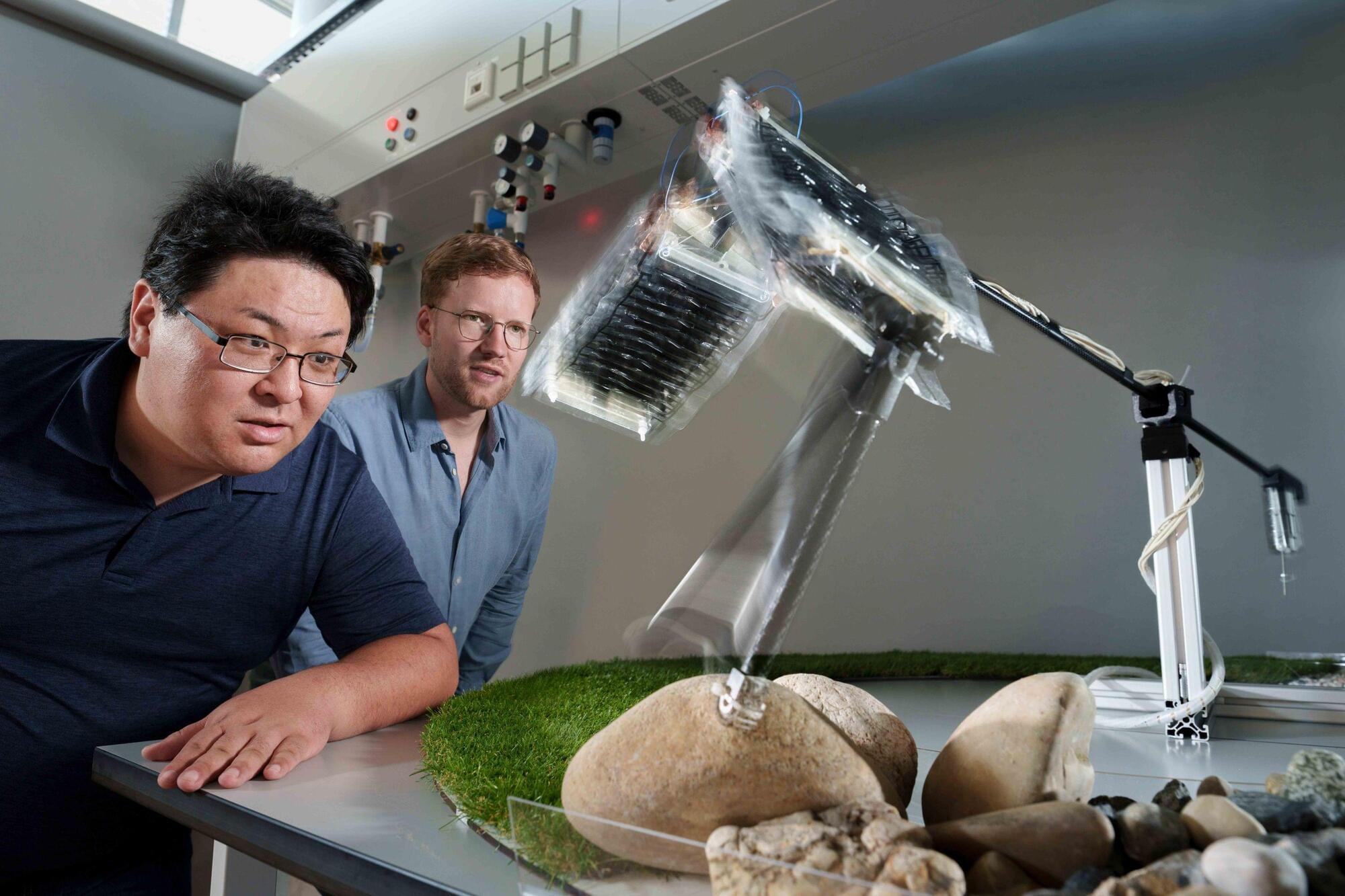
But for all the medical breakthroughs of the 20th century, the best way to detect molecules has remained through liquids, such as blood. New research from the University of Chicago, however, could someday put a pause on pinpricks. A group of scientists announced they have created a small, portable device that can collect and detect airborne molecules—a breakthrough that holds promise for many areas of medicine and public health.
The researchers envision the device, nicknamed ABLE, could detect airborne viruses or bacteria in hospital or public spaces, improve neonatal care or allow people with diabetes to read glucose levels from their breath. The entire device is just four by eight inches across.
Portable tech captures molecules in breath to aid medical care from diabetes to at-risk newborn development.