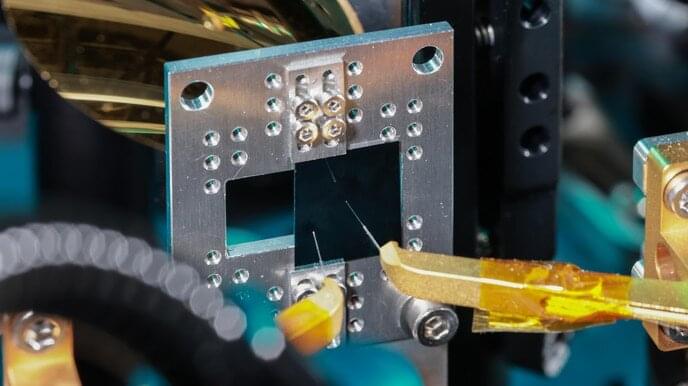
EPFL researchers have collaborated with colleagues at Harvard and ETH Zurich on a new thin-film circuit that, when connected to a laser beam, produces finely tailorable terahertz-frequency waves. The device opens up a world of potential applications in optics and telecommunications.
Researchers led by Cristina Benea-Chelmus in the Laboratory of Hybrid Photonics (HYLAB) in EPFL’s School of Engineering have taken a big step toward successfully exploiting the so-called terahertz gap, which lies between about 300 to 30,000 gigahertz (0.3 to 30 THz) on the electromagnetic spectrum. This range is currently something of a technological dead zone, describing frequencies that are too fast for today’s electronics and telecommunications devices, but too slow for optics and imaging applications.
Now, thanks to an extremely thin chip with an integrated photonic circuit made of lithium niobate, the HYLAB researchers and colleagues at ETH Zurich and Harvard University have succeeded not just in producing terahertz waves, but in engineering a solution for custom-tailoring their frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and phase.