Background: Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers and the leading cause of death from cancer among women worldwide. The genetic predisposition to breast cancer may be associated with a mutation in particular genes such as gene BRCA1/2. Patients who carry a germline pathogenic mutation in BRCA1/2 genes have a significantly increased risk of developing breast cancer and might benefit from targeted therapy. However, genetic testing is time consuming and costly. This study aims to predict the risk of gBRCA mutation by using the whole-slide pathology features of breast cancer H&E stains and the patients’ gBRCA mutation status.
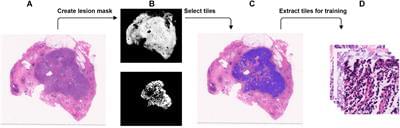
Methods: In this study, we trained a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) of ResNet on whole-slide images (WSIs) to predict the gBRCA mutation in breast cancer. Since the dimensions are too large for slide-based training, we divided WSI into smaller tiles with the original resolution. The tile-based classification was then combined by adding the positive classification result to generate the combined slide-based accuracy. Models were trained based on the annotated tumor location and gBRCA mutation status labeled by a designated breast cancer pathologist. Four models were trained on tiles cropped at 5×, 10×, 20×, and 40× magnification, assuming that low magnification and high magnification may provide different levels of information for classification.
Results: A trained model was validated through an external dataset that contains 17 mutants and 47 wilds. In the external validation dataset, AUCs (95% CI) of DL models that used 40×, 20×, 10×, and 5× magnification tiles among all cases were 0.766 (0.763–0.769), 0.763 (0.758–0.769), 0.750 (0.738–0.761), and 0.551 (0.526–0.575), respectively, while the corresponding magnification slides among all cases were 0.774 (0.642–0.905), 0.804 (0.676–0.931), 0.828 (0.691–0.966), and 0.635 (0.471–0.798), respectively. The study also identified the influence of histological grade to the accuracy of the prediction.