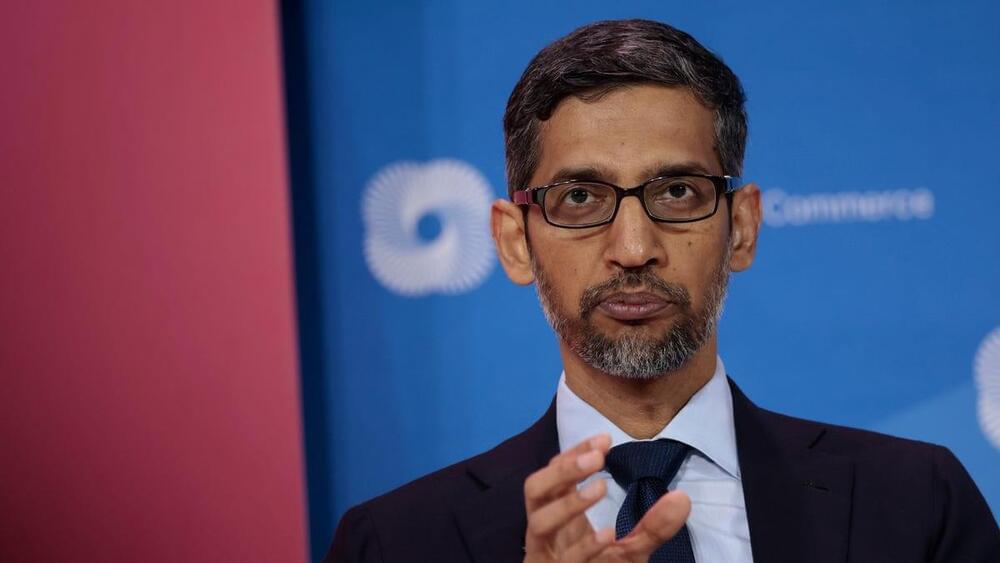
Business Insider reported based on a leaked company-wide email that Google is asking all of its employees to take two to four hours of their day to test Google’s “Bard” AI, the same system the company plans to integrate into its chat function. It’s unclear if all Googlers over the world have received the same ask. The company recently announced 12,000 job cuts to its global workforce, but Google, without its parent company Alphabet, still employs over 170,000 around the world.
In that memo, Google CEO Sundar Pichai said he would “appreciate” if all staff “contributed in a deeper way” and take two to four hours to pressure test Bard. Anybody who’s ever read a “suggestion” email from their boss knows that it’s more of a mandate than anything else. It’s unclear based on the email text if the two-to-four hour suggestion would be asked of them every day or spread over a longer period of time.