Protect your child from flu and its sometimes serious complications with a flu vaccine every fall. Flu vaccines can be life-saving for children.



Physicists at the University of Cincinnati have contributed to an international experiment on strange metals made from an alloy of ytterbium, a rare earth metal. The study involved firing radioactive gamma rays at the strange metal to observe its unusual electrical behavior. The experiment revealed unusual fluctuations in the strange metal’s electrical charge, furthering the understanding of the bizarre behavior of strange metals that operate outside the normal rules of electricity.
International team finds unusual electrical behavior in material that holds promise for new technology.
Physicists at the University of Cincinnati (UC) are learning more about the bizarre behavior of “strange metals,” which operate outside the normal rules of electricity.
Did peptides precede life on Earth? Should we be looking for their biosignatures on Mars?
If you think of DNA in correspondence terms, it writes instructions. RNA picks up the instructions and delivers them to a recipient in the cell. The instructions contain a recipe and what follows is the filling of it producing a protein molecule explicitly designed for the required task.
But before all of the above ever could have happened there had to be something with simpler chemistry. A research team at Rutgers University believes that what first emerged was probably a peptide containing the element nickel. They have named it Nickelback, not to be confused with a Canadian rock band of the same name. This Nickelback peptide consists of two bound nickel atoms which exhibit both stability and activity in terms of reacting with surrounding chemistry. Such a peptide is capable of redox reactions that transfer electrons from one chemical substance to another and is essential as the first stage on the way to life.
The Rutgers researchers believe that between 3.5 and 3.8 billion years ago, conditions in the water environment of early Earth led to the self-assembly of a pioneer peptide to become the precursor of proteins. With its emergence, metabolic processes began.
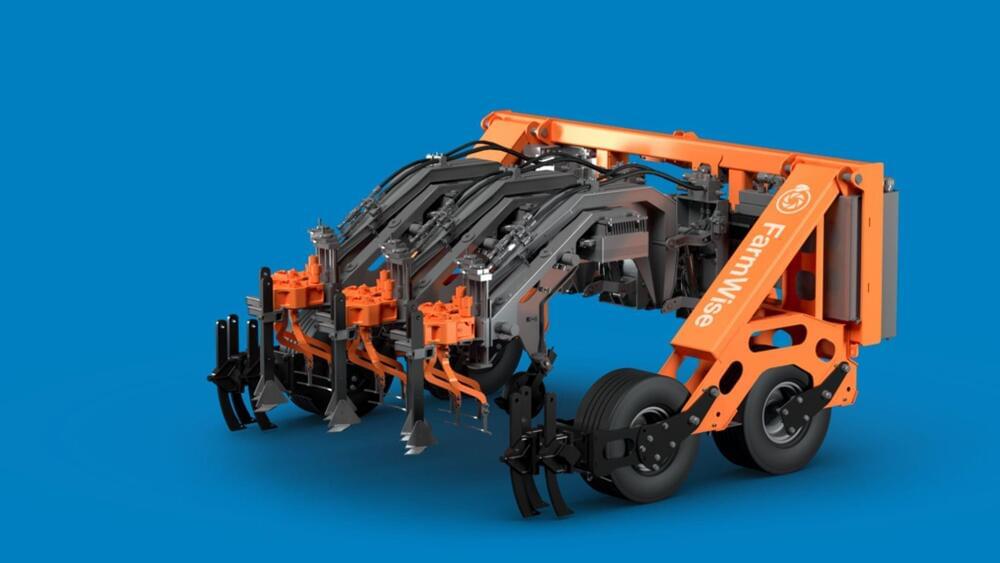

The machines could help to “drastically increase the efficiency of the farming industry.”
In farming, weeds can strangle crops and destroy yields. Unfortunately, spraying herbicides to deal with the intrusive plants pollutes the environment and harms human health and there simply aren’t enough workers to tackle all the weeds by hand.
A new startup called FarmWise has come up with a solution: autonomous weeding robots that use artificial intelligence to cut out weeds while leaving crops untouched, according to an MIT report published on Thursday.

It will be a free addition to the Grammarly service.
GrammarlyGO, a contextually aware assistant powered by generative artificial intelligence (AI), has been unveiled by Grammarly, a U.S. cloud-based typing assistant. GrammarlyGO will be increasing productivity by altering the way individuals and organizations communicate and complete work, according to a blog by the company published on Wednesday. “It uses generative AI to help people and businesses succeed with on-demand communication assistance, whether they are starting from scratch or revising an existing piece of writing,” said the press release.
ILexx/iStock.
“GrammarlyGO will address this problem by quickly generating highly relevant text with an understanding of personal voice and brand style, context, and intent — saving people and businesses time while accounting for their unique needs.”


ChatGPT is “going to be a tool, just like the cell phone in your pocket,” says OpenAI’s co-founder.
Greg Brockman, president and co-founder of OpenAI, has suggested that ChatGPT could help enhance the “interactive” entertainment experience.
“Imagine if you could ask your AI to make a new ending that goes a different way and maybe even put yourself in there as a main character or something,” he said during a panel discussion at the 2023 South by Southwest (SXSW) event on Friday.
Joel Carillet/iStock.
Brockman compared the technology to a team of “assistants” who aren’t flawless but are “eager and never sleep,” according to a report by The Hollywood Reporter (THR) on Friday.
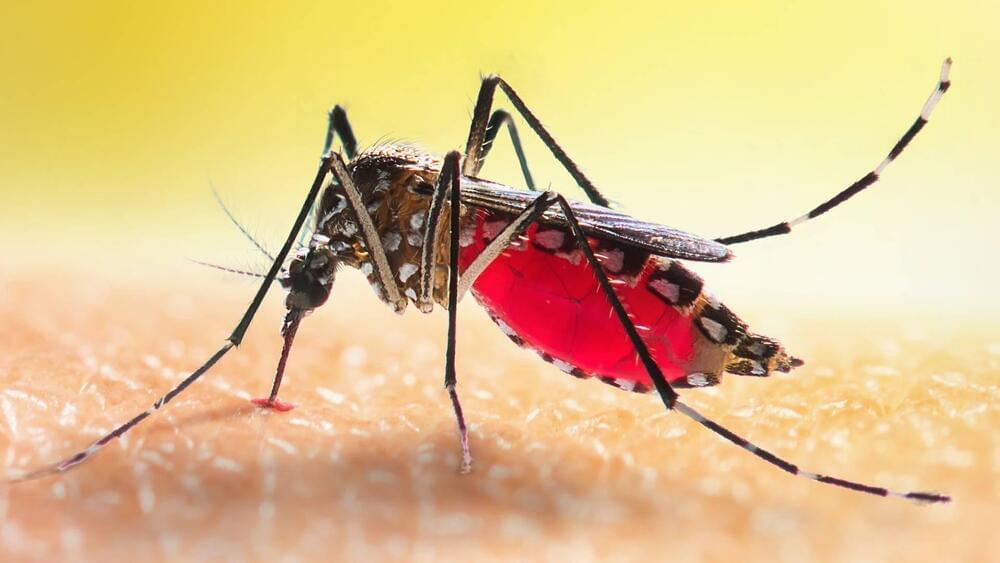

The research could be used to produce repellents for the insects.
Anyone who has ever been bitten by a mosquito has wondered why are these insects attracted to me? Now, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers may have an answer, according to a press release published last month.
“Understanding the molecular biology of mosquito odor-sensing is key to developing new ways to avoid bites and the burdensome diseases they cause,” said Christopher Potter, Ph.D.
Panom/iStock.
They claim they have mapped specialized receptors on the insects’ nerve cells that are able to fine-tune their ability to detect particularly “welcoming” odors in human skin.
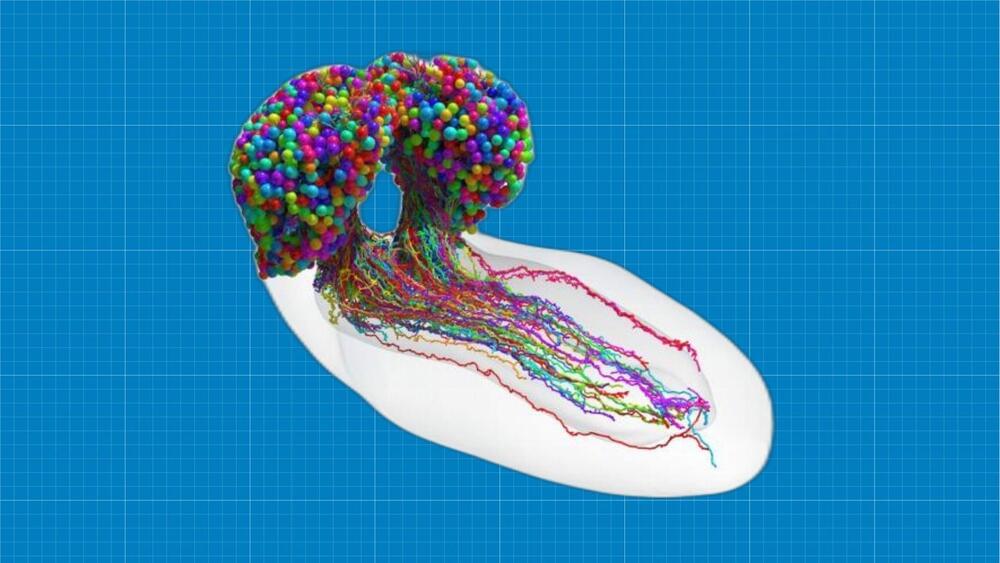

Perhaps, human consciousness can be fully understood one day.
Researchers from Johns Hopkins and Cambridge universities have created the first-ever map of the wiring patterns of every neuron in the fruit fly larval brain.
Neurons in an organism’s nervous system, including the brain, are linked to one another by synapses.
University of Cambridge.
The meticulously created connectome, which took 12 years to complete, depicts the locations of all 3,016 neurons in the fruit fly larval brain (Drosophila melanogaster). The 548,000 synapses that connect those brain cells allow the cells to communicate chemically with one another, which in turn causes electrical signals to be sent through the wiring of the cells.