Ethical training database paves the way for AI systems to be pretrained in human values.
A robot avatar that mimics the motions of a human controller could take the place of workers in several dangerous jobs, such as tree trimming and construction, by the end of 2022.
The challenge: If a tree branch gets too close to a power line, it can cause electrical outages or, even worse, dangerous fires (as Californians know all too well). To avoid this, utility companies have to regularly trim trees near their lines.
But it’s dangerous work, as workers are dozens of feet above the ground, using sharp power tools to trim trees while power lives are still active — this puts them at risk of falls, cuts, and electrocution, all at once.
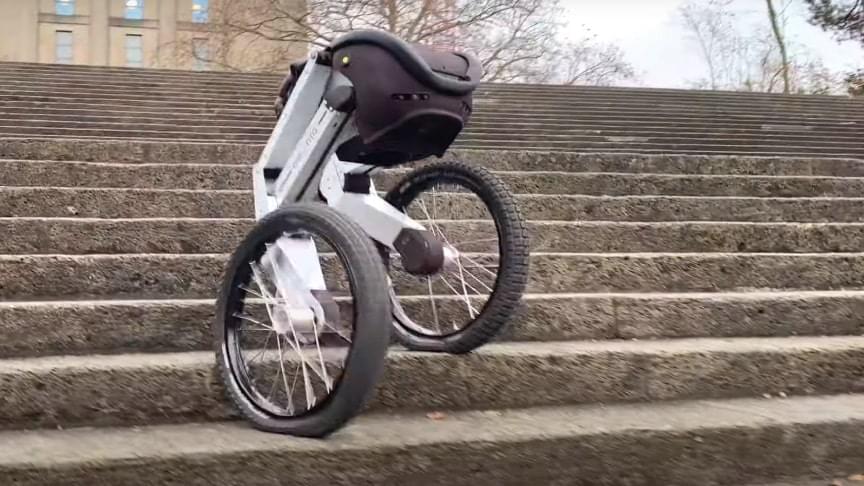
Bigger, faster, stronger: This is Ascento Pro! Our newest creation can climb full flights of stairs, drive at up to 12km/h and all this for up to 8h per battery charge. Oh and also it is now autonomous. Full autonomy is achieved through LiDAR, onboard cameras and LED headlights.
source/image(PrtSc): Ascento Robotics
In most cases, EVs have no problem outrunning gas cars at the strip, but this Audi is wildly potent. Can the Tesla Model 3 Performance prevail?
Facebook’s metaverse is far worse than you thought…
Support the channel here (all funds go back into the channel):
► Become a Patron: https://www.patreon.com/MoonReal.
► Follow my Twitter: https://twitter.com/MoonRealYT
The Metaverse will bring about a new age of crypto trading, business, NFT’s, and investing. But there is another side to the Metaverse. Because Mark Zuckerberg sees the Metaverse as a new business venture to extract the money out our depressed and lonely generation. Mark Zuckerberg wants the metaverse to make money from his users privacy and data which poses a major threat to our society. This video explains the metaverse and what it means for business and society. There is lots of money and wealth to be made. This is how Metaverse makes money because it’s business model relies on our sick society. So join me as I explain the truth behind Facebook’s meta rebranding and why Metaverse is the most evil business in the world.
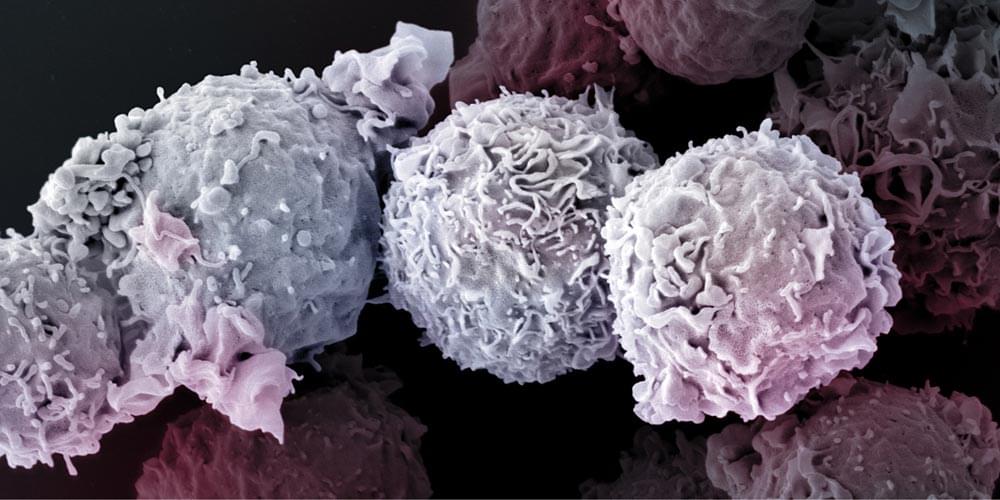
They are at the forefront in the fight against viruses, bacteria, and malignant cells: the T cells of our immune system. But the older we get, the fewer of them our body produces. Thus, how long we remain healthy also depends on how long the T cells survive. Researchers at the University of Basel have now uncovered a previously unknown signaling pathway essential for T cell viability.
Like human beings, every cell in our body tries to ward off death as long as it can. This is particular true for a specific type of immune cells, called T-lymphocytes, or T cells for short. These cells keep viruses, bacteria, parasites and cancerous cells at bay. While T cell production is an active process in infants, children and young adults, it comes to a gradual stop upon aging, meaning that in order to maintain adequate immunity up to an old age, your T cells should better live as long as you.
How T cells manage to survive for such a long time, up to several decades in humans, has long remained unclear. In collaboration with scientists at the Department of Biomedicine and sciCORE, the Center for Scientific Computing of the University of Basel, Professor Jean Pieters’ research group at the Biozentrum has now revealed the existence of a hitherto unrecognized pathway promoting long-term survival of T cells. In Science Signaling they report that this signaling pathway, regulated by the protein coronin 1, is responsible for suppressing T cell death.
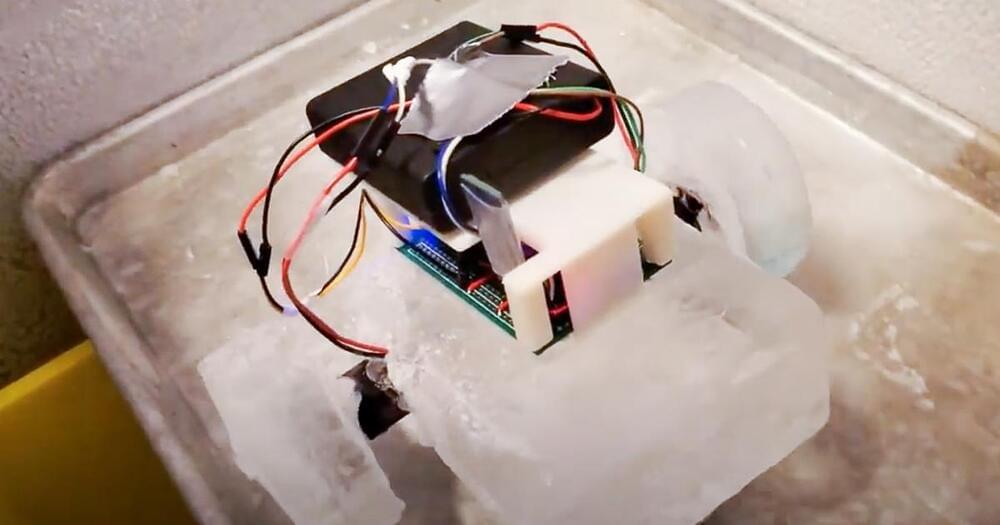
A team of researchers want to build robots out of ice and send them to space. The idea is that — lacking a local repair shop — the icy bots can use found materials to rebuild themselves.
Ice can be located all over the solar system, from the moon to the distant rings around Saturn. So researchers from the University of Pennsylvania are trying to figure out how to tap into that nearly unlimited resource for robotics.
NASA wants to send the robot dog, Spot, to space. The canine-bot can do many tricks — from herding sheep to helping the NYPD in a hostage situation — but it likely won’t be able to repair itself. Where could it find enough materials to do the job?
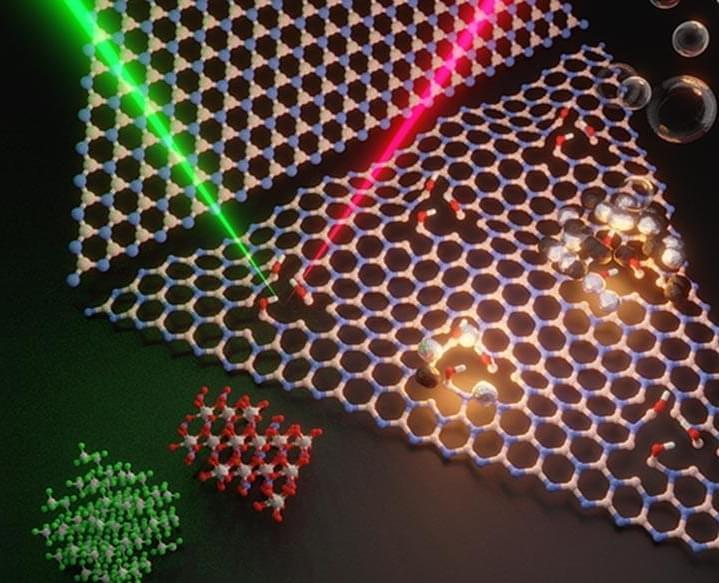
Demonstrating that a material thought to be always chemically inert, hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), can be turned chemically active holds potential for a new class of catalysts with a wide range of applications, according to an international team of researchers.
HBN is a layered material and monolayers can be exfoliated like in graphene 0, another two-dimensional material. However, there is a key difference between the two.
“While hBN shares similar structure as graphene, the strong polar bonds between the boron and nitride atoms makes hBN unlike graphene in that it is chemically inert and thermally stable at high temperature,” said Yu Lei, postdoctoral scholar in physics at Penn State and first co-author in the study published in Materials Today.
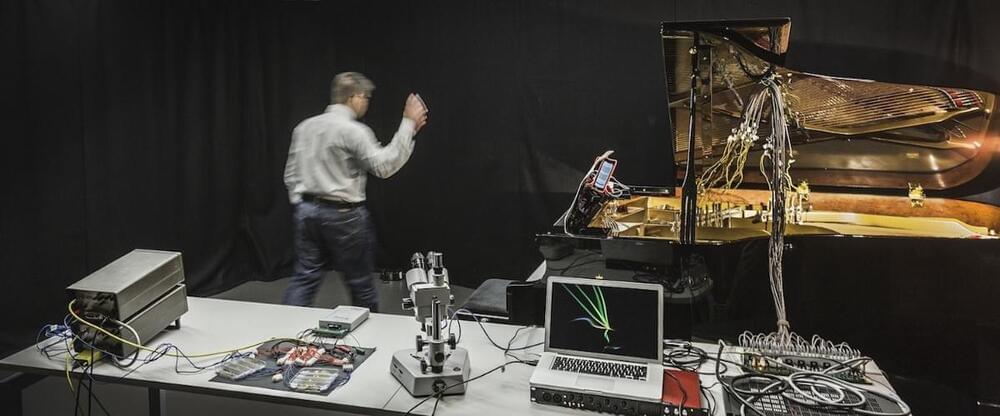
By Sieglinde Pfaendler, Omar Costa Hamido, Eduardo Reck Miranda
Science and the arts have increasingly inspired each other. In the 20th century, this has led to new innovations in music composition, new musical instruments, and changes to the way that the music industry does business to day. In turn, art has helped scientists think in new ways, and make advances of their own.
An emerging community leveraging quantum computing in music and the music industry has inspired us to organize the “1st International Symposium on Quantum Computing and Musical Creativity.” This symposium will bring together pioneering individuals from academia, industry, and music. They will present research, new works, share ideas, and learn new tools for incorporating quantum computation into music and the music industry. This symposium was made possible through the funding of the QuTune Project kindly provided by the United Kingdom National Quantum Technologies Programme’s Quantum Computing and Simulation Hub (QCS Hub).
Newsweek spoke to planetary scientist Dr. Amy Mainzer about the “Don’t Look Up” science and coaching Leonardo DiCaprio and Jennifer Lawrence for the movie.