It’s mini yet mighty.
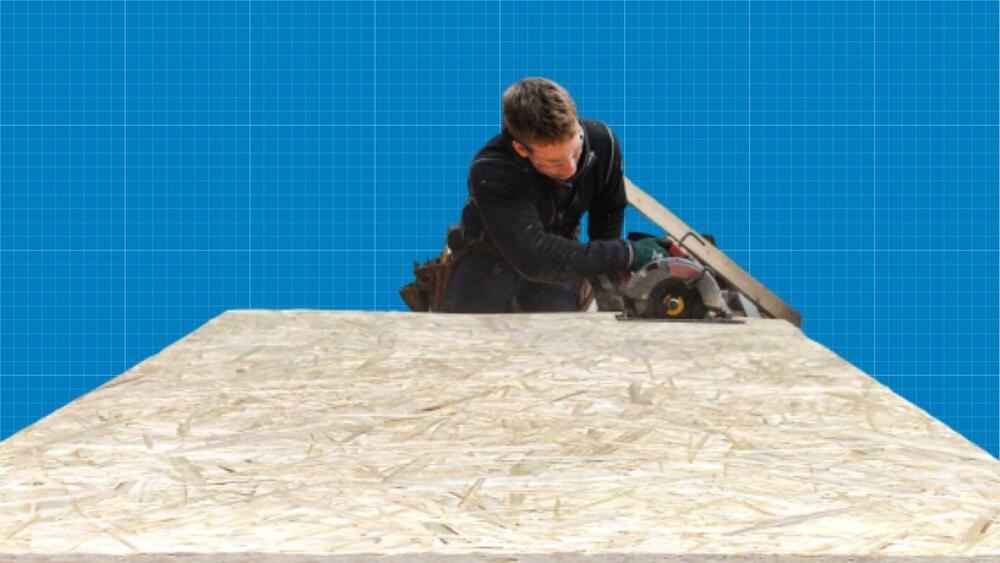
An autonomous ground robot was developed by researchers at Universidad Rey Juan Carlos and Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. It could help firefighters deal with situations in enclosed spaces.
Undoubtedly, firefighters would profit from the assistance of trustworthy mobile robots in their high-danger duties. Regarding this, researchers led a study called “HelpResponder” in 2021, which aims to reduce accident rates and mission times of intervention teams, as reported by Tech Xplore.
Fernandez Talavera et al.
This method could help firefighters plan interventions more effectively by paving safe access routes to the impacted areas and assisting them during evacuations.