Microelectrode array for brain organoids.
Shared with Dropbox.


Ancient philosopher Anaximander’s discoveries about rain, wind and the cosmos may make him the true force behind modern science, argues physicist Carlo Rovelli in his newly republished first book.
By Simon Ings

Plants emit weak electric signals. Researchers have developed a device to read and send signals back — a type of “plant communication.”

In recent years, a group of Hungarian researchers have made headlines with a bold claim. They say they’ve discovered a new particle — dubbed X17 — that requires the existence of a fifth force of nature.
The researchers weren’t looking for the new particle, though. Instead, it popped up as an anomaly in their detector back in 2015 while they were searching for signs of dark matter. The oddity didn’t draw much attention at first. But eventually, a group of prominent particle physicists working at the University of California, Irvine, took a closer look and suggested that the Hungarians had stumbled onto a new type of particle — one that implies an entirely new force of nature.
Then, in late 2019, the Hungarian find hit the mainstream — including a story featured prominently on CNN — when they released new results suggesting that their signal hadn’t gone away. The anomaly persisted even after they changed the parameters of their experiment. They’ve now seen it pop up in the same way hundreds of times.
The very word ‘quantum’ makes people’s imaginations run wild. But chances are you’ve fallen for at least one of these myths.
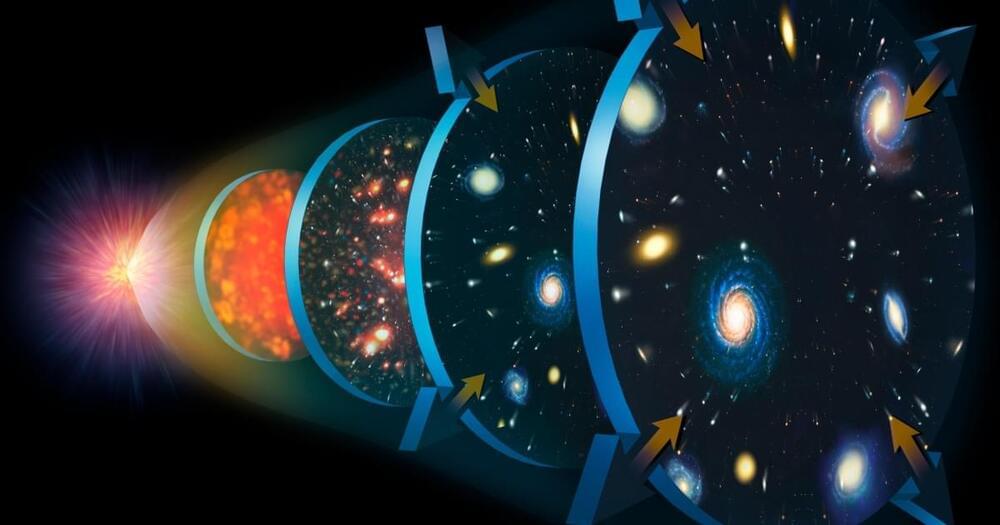
In this Big Think interview, theoretical physicist Sean Carroll discusses the concept of time and the mysteries surrounding its properties. He notes that while we use the word “time” frequently in everyday language, the real puzzles arise when we consider the properties of time, such as the past, present, and future, and the fact that we can affect the future but not the past.
Carroll also discusses the concept of entropy, which is a measure of how disorganized or random a system is, and the second law of thermodynamics, which states that there is a natural tendency for things in the Universe to go from a state of low entropy to high entropy — in other words, from less disorganized to more disorganized. He explains that the arrow of time, or the perceived difference between the past and the future, arises due to the influence of the Big Bang and the fact that the Universe began in a state of low entropy.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links:
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
Use Code: ConquerAging At Checkout.
Green Tea: https://www.ochaandco.com/?ref=conqueraging.
Oral Microbiome: https://www.bristlehealth.com/?ref=michaellustgarten.
Epigenetic Testing: https://bit.ly/3Rken0n.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING!
At-Home Blood Testing: https://getquantify.io/mlustgarten.