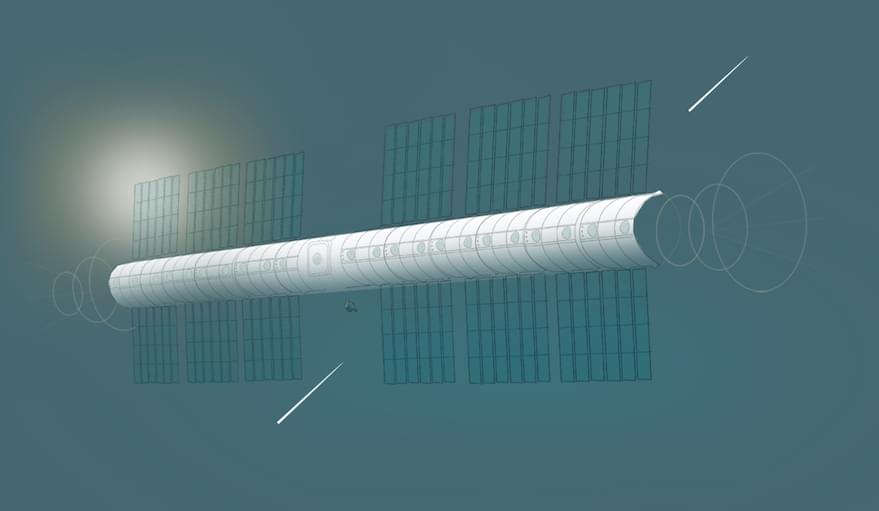
PARIS – Vast Space, a Southern California startup founded by cryptocurrency billionaire Jed McCaleb, plans to establish an artificial-gravity space station in low Earth orbit.
McCaleb envisions a future where millions of people are living throughout the solar system. Since other companies are helping to reduce launch costs, McCaleb thinks the next important step will be creating large structures where people can live and work in space.
“Earth has finite resources, but out in the solar system, there is an enormous untapped wealth, both in terms of energy and matter, that could support many ‘Earths,’” McCaleb told SpaceNews by email. “Likewise, mankind needs a frontier. Every prosperous civilization has had one to push off into – nevertheless, we haven’t had one for some time. Without a frontier, the world becomes a zero-sum game, which is detrimental to the psyche of a civilization. And in terms of the long-term future of humanity, we will need to live off of the Earth eventually.”