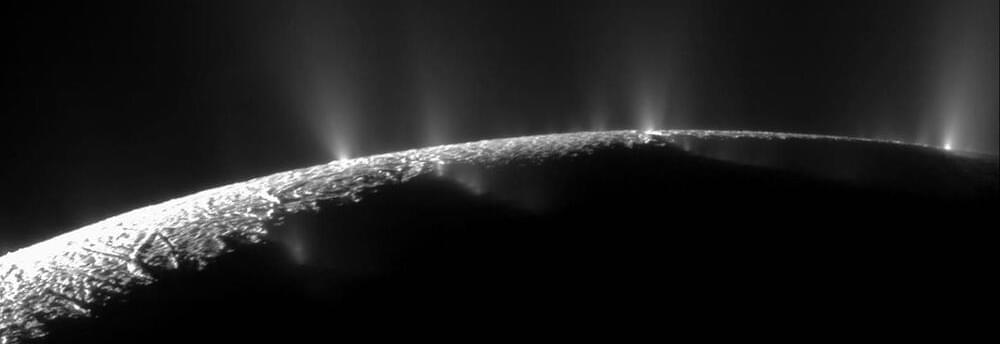
“Enceladus is giving us free samples of what’s hidden deep below.”
Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus shoots particles of frozen silica into space, and scientists might finally know why. Scientists have long known that Enceladus spewed out icy silica that eventually made its way into Saturn’s E ring, but they didn’t have a good explanation as to why this was happening.
Now, a new study by a team at the University of California Los Angeles might provide the answer. Their research shows that tidal heating in Encealadus’ rocky core creates currents that push the silica to the surface. Once there, it’s likely released into space by deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
NASA / jpl-caltech / space science institute.
Scientists have long known that Enceladus spewed out icy silica that eventually made its way into Saturn’s E ring, but they didn’t have a good explanation as to why this was happening.