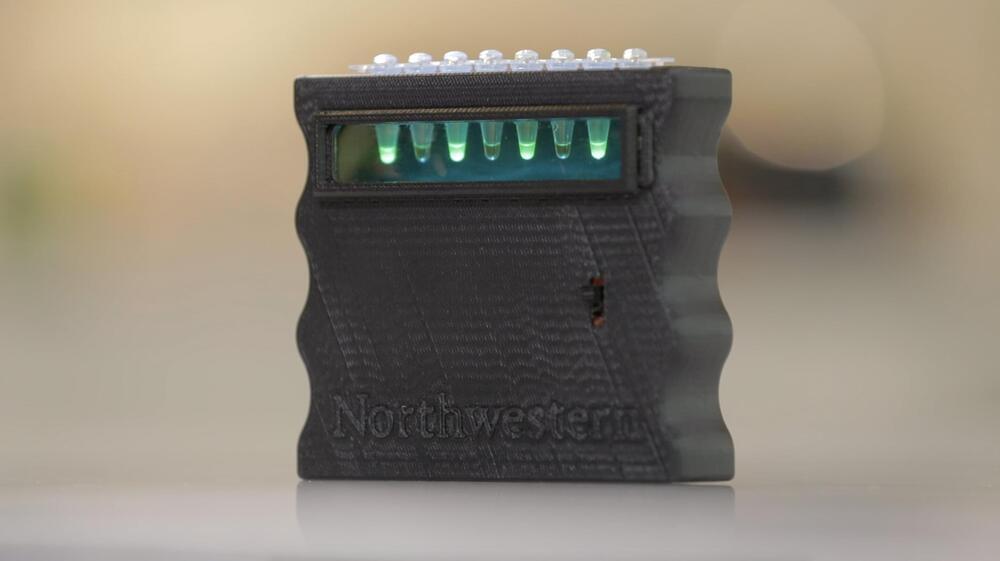
Northwestern University synthetic biologists have developed a low-cost, easy-to-use, hand-held device that can let users know—within mere minutes—if their water is safe to drink.
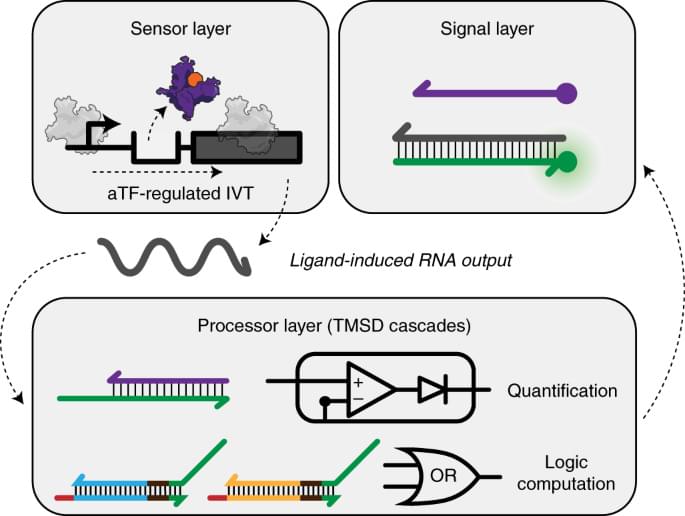
The new device works by using powerful and programmable genetic networks, which mimic electronic circuits, to perform a range of logic functions.
Among the DNA-based circuits, for example, the researchers engineered cell-free molecules into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), a ubiquitous circuit type found in nearly all electronic devices. In the water-quality device, the ADC circuit processes an analog input (contaminants) and generates a digital output (a visual signal to inform the user).