What does the ultimate civilization look like? Join us… and find out!
Subscribe for more from Unveiled ► https://wmojo.com/unveiled-subscribe.
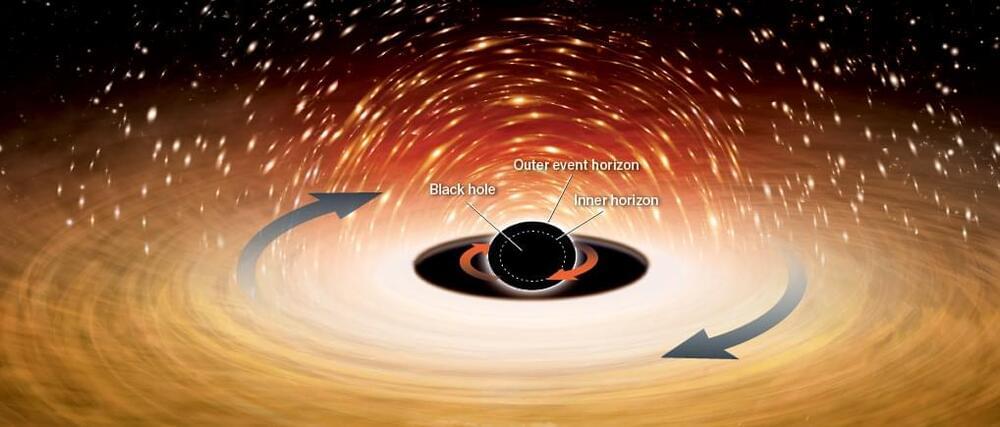
In this video, Unveiled travels to the highest possible point on all civilization scales combined… to reach the Omega level! Featuring the Kardashev Scale, John Barrow’s Scale of Microdimensional Mastery, a revised 2020 scale focussing on how well a society can merge with the environment, and more… this is the best of the best (of the best!)
This is Unveiled, giving you incredible answers to extraordinary questions!
Find more amazing videos for your curiosity here:
What If We’re the Remnants of a Type III Civilization? — https://youtu.be/tku2lTWNMMU
Are We the Creation of a Type V Civilization? — https://youtu.be/T_u4lGDs3dM
0:00 Start.