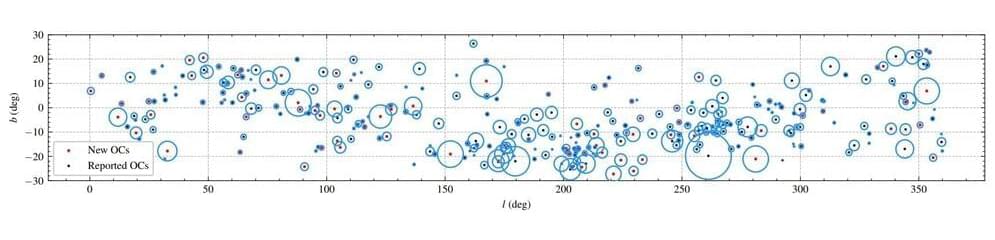
By analyzing the data from ESA’s Gaia satellite, astronomers from the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory (SHAO) in China have detected 101 new open clusters in the Milky Way galaxy. The discovery was presented in a paper published December 21 on the arXiv pre-print repository.
Open clusters (OCs), formed from the same giant molecular cloud, are groups of stars loosely gravitationally bound to each other. So far, more than 1,000 of them have been discovered in the Milky Way, and scientists are still looking for more, hoping to find a variety of these stellar groupings. Studying them in detail could be crucial for improving our understanding of the formation and evolution of our galaxy.
Now, a team of astronomers led by SHAO’s Qin Songmei reports the finding of 101 new OCs in the solar neighborhood. The discovery is a result of utilizing clustering algorithms pyUPMASK and HDSBSCAN on the data from Gaia’s Data Release 3 (DR3).