The thorny thought experiment has been turned into a real experiment — one that physicists use to probe the physics of information.



“Success is far from certain, but excitement is guaranteed.”
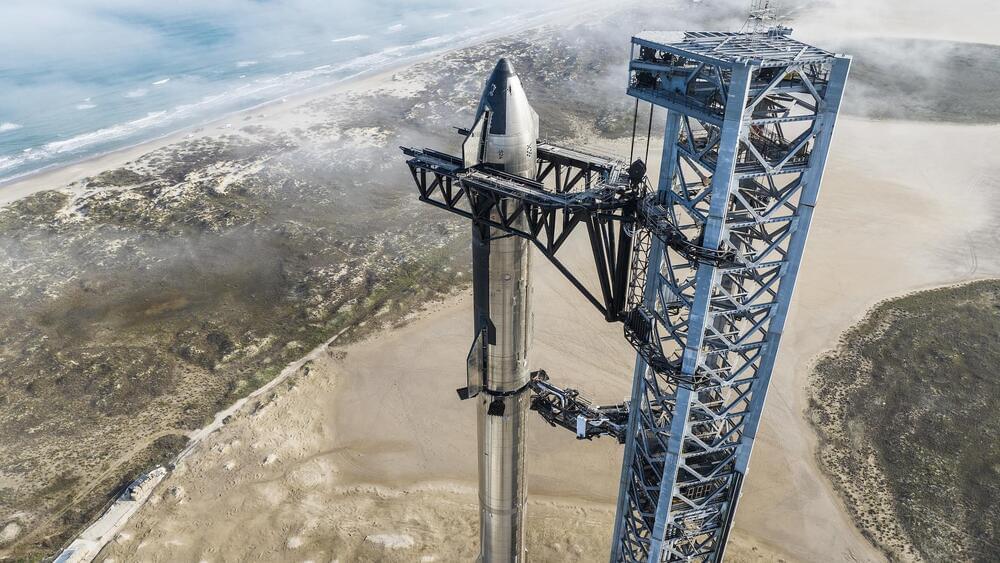
We may be just one month from seeing SpaceX attempt to fly Starship to orbit. SpaceX CEO Elon Musk confirmed the launch attempt is likely just around the corner over the weekend when he wrote on Twitter, “if remaining tests go well, we will attempt a Starship launch next month.”
SpaceX readies for massive Starship milestone.
SpaceX has been undergoing final preparations for the maiden orbital flight of its fully reusable Starship rocket for a few months, having recently carried out a full wet dress rehearsal.
SpaceX / Flickr.
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk confirmed the launch attempt is likely just around the corner over the weekend when he wrote on Twitter, “if remaining tests go well, we will attempt a Starship launch next month.”
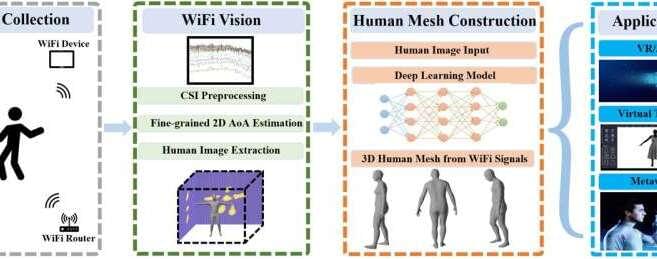
A 3D mesh is a three-dimensional object representation made of different vertices and polygons. These representations can be very useful for numerous technological applications, including computer vision, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) systems.
Researchers at Florida State University and Rutgers University have recently developed Wi-Mesh, a system that can create reliable 3D human meshes, representations of humans that can then be used by different computational models and applications. Their system was presented at the Twentieth ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems (ACM SenSys ‘22), a conference focusing on computer science research.
“Our research group specializes in cutting-edge wi-fi sensing research,” Professor Jie Yang at Florida State University, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Tech Xplore. “In previous work, we have developed systems that use wi-fi devices to sense a range of human activities and objects, including large-scale human body movements, small-scale finger movements, sleep monitoring, and daily objects. Our E-eyes and WiFinger systems were among the first to use wi-fi sensing to classify various types of daily activities and finger gestures, with a focus on predefined activities using a trained model.”

A talk on “Diverse Intelligence: understanding and relating to unconventional biological, engineered, and hybrid agents” by Michael Levin.
The power to turn invisible, which has long been a hallmark of science fiction and fantasy, would be a revolutionary technical breakthrough. Check out how scientists are making an invisibility cloak into reality.
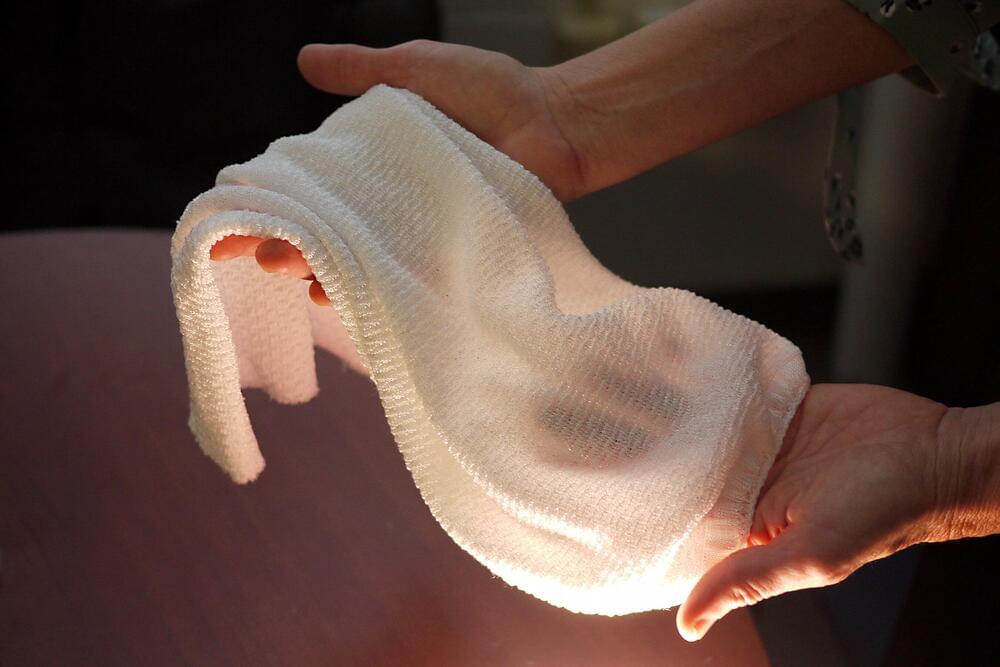

Despite decades of innovation in fabrics with high-tech thermal properties that keep marathon runners cool or alpine hikers warm, there has never been a material that changes its insulating properties in response to the environment. Until now.
University of Maryland researchers have created a fabric that can automatically regulate the amount of heat that passes through it. When conditions are warm and moist, such as those near a sweating body, the fabric allows infrared radiation (heat) to pass through. When conditions become cooler and drier, the fabric reduces the heat that escapes. The development was reported in the February 8, 2019 issue of the journal Science.
The researchers created the fabric from specially engineered yarn coated with a conductive metal. Under hot, humid conditions, the strands of yarn compact and activate the coating, which changes the way the fabric interacts with infrared radiation. They refer to the action as “gating” of infrared radiation, which acts as a tunable blind to transmit or block heat.

A Quebec hospital adopts a novel use of VR to help patients with anxiety, phobias and pain.
In a newswire release today, the Fondation de l’Hôtel-Dieu d’Alma (the Alma Hospital Foundation) announced the launch of a virtual reality (VR) project aimed at improving the mental health of those experiencing increasing anxiety. The Alma Hospital is a regional health centre for the area of Lac St. Jean and the Saguenay River valley to the north of Quebec City.
Jean Lamoureux, the hospital’s Executive Director states, “The number of requests for mental-health consultations is estimated to have increased by 30 to 40 percent during the pandemic. These needs are urgent…and, thanks to the innovation of Paperplane Therapeutics and TELUS, we will transform the way health services are delivered, while having a significant positive impact on patient well-being through technology.”