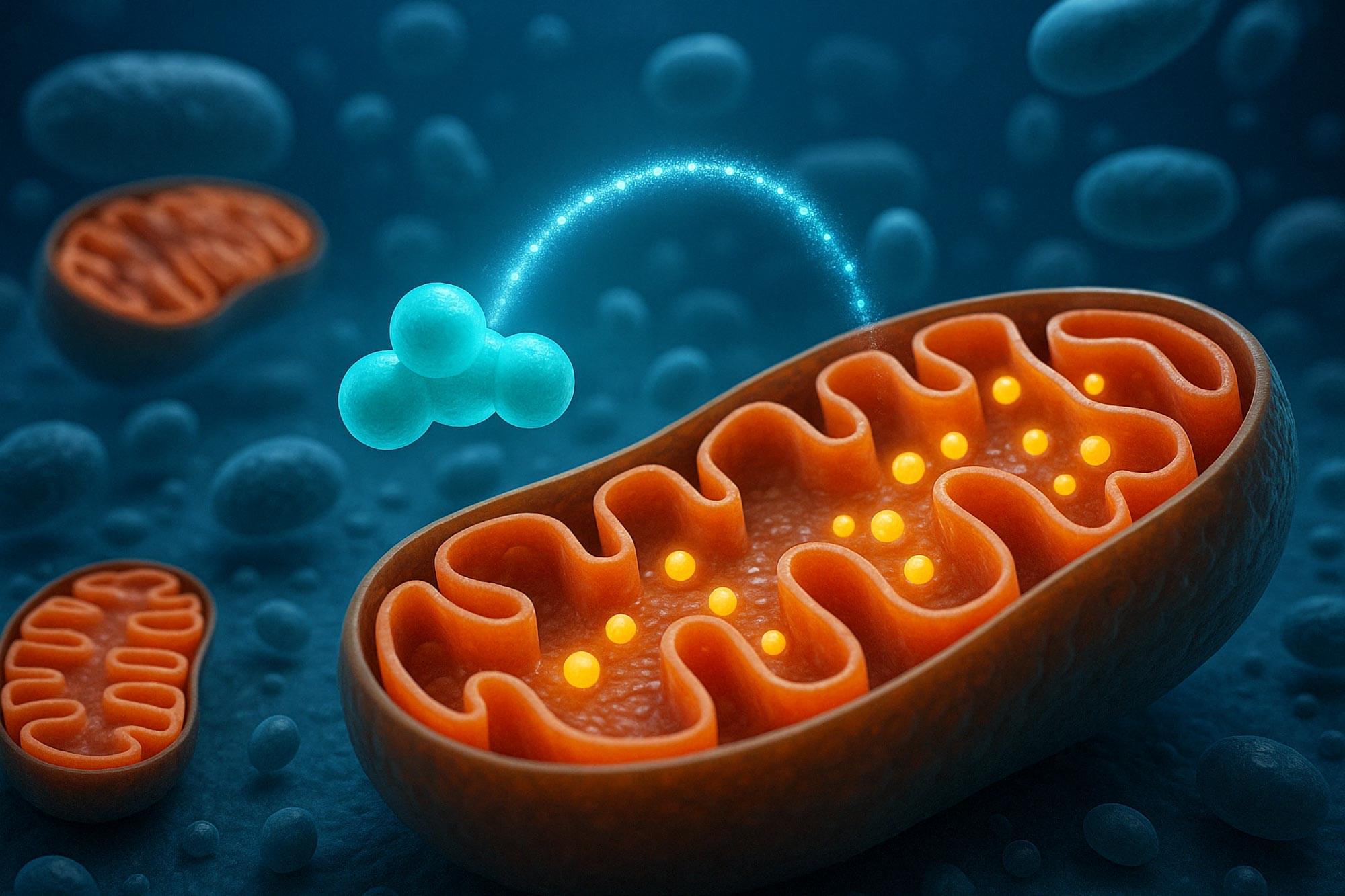
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier.
This microscopic gatekeeper controls how cells fuel themselves by transporting pyruvate, a key energy source, across mitochondrial membranes. Now visualized using cryo-electron microscopy, the carrier’s lock-like mechanism could be the key to tackling diseases like cancer, diabetes, and even hair loss. By blocking or modifying this gateway, researchers believe we could reroute how cells generate energy and develop powerful, targeted treatments.
Unlocking a Mitochondrial Mystery.