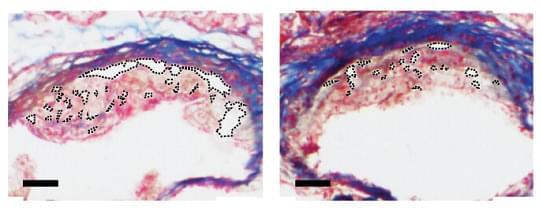
Atherosclerosis is a cardiac-based disease where plaque builds up inside the body’s arteries, the blood vessels responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood to the heart and other organs of the body. Plaque is made up of immune blood cells, known as macrophages, fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood.
As this plaque hardens it narrows the arteries, limiting the flow of oxygen-rich blood around the body. This, in turn, can lead to serious problems, including heart attack, stroke, or even death.
Now, a study from researchers led by Michigan State University engineers a nanoparticle capable of eating away, from the inside out, heart attack causing plaques. The team states their nanoparticle reduces and stabilizes plaque, providing a potential treatment for atherosclerosis, a leading cause of death in the United States. The study is published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.