Po-Shen Loh (Carnegie Mellon University)https://simons.berkeley.edu/events/theoretically-speaking-bu…ation-chat…
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.



Peter Gabriel — We Do What We’re Told / Milgram’s 37 (Extended CubCut)
Mind control.
Peter Gabriel — We Do What We’re Told / Milgram’s 37
(Extended CubCut)
complete The Wave rearView:
German(Deutsch)
https://odysee.com/@derjapango:6/Die-Welle-_rearView_:a.
https://www.bitchute.com/video/F5iByojrFRxm/
English. Version.
https://odysee.com/@thelonewolfCub: d/The-Wave-_rearView_:0
Odysee INVITE link https://odysee.com/$/invite/@thelonewolfCLUB:1
(thanks for your support)
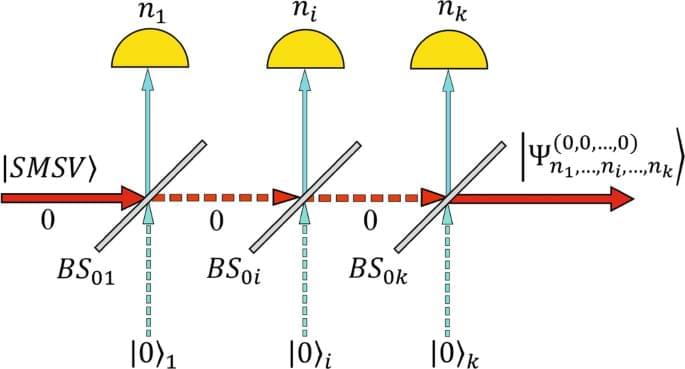
Algorithm of quantum engineering of large-amplitude high-fidelity Schrödinger cat states
We present an algorithm of quantum engineering of large-amplitude $$\ge 5$$ high-fidelity $$\ge 0.99$$ even/odd Schrödinger cat states (SCSs) using a single mode squeezed vacuum (SMSV) state as resource. Set of $$k$$ beam splitters (BSs) with arbitrary transmittance and reflectance coefficients sequentially following each other acts as a hub that redirects a multiphoton state into the measuring modes simultaneously measured by photon number resolving (PNR) detectors. We show that the multiphoton state splitting guarantees significant increase of the success probability of the SCSs generator compared to its implementation in a single PNR detector version and imposes less requirements on ideal PNR detectors.
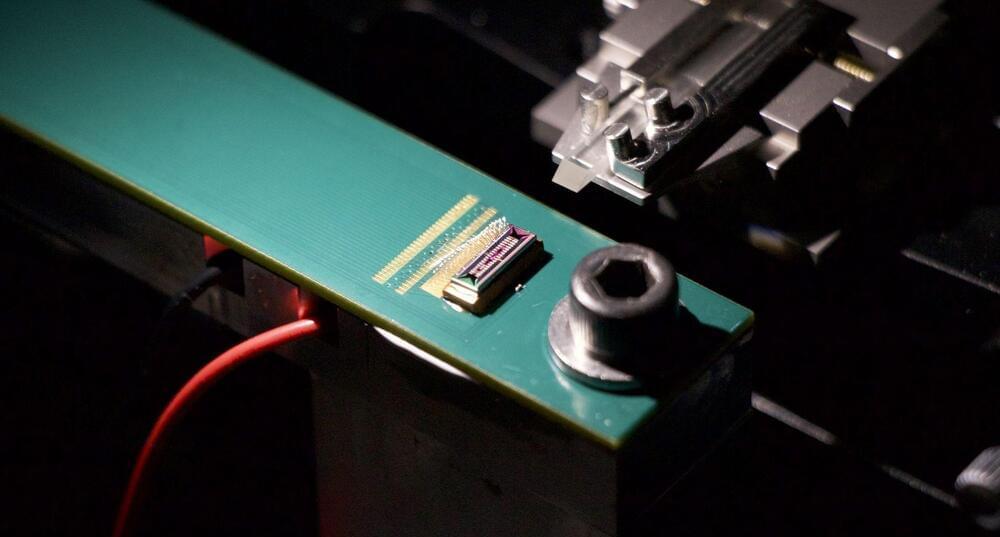
Stanford team shines light on cryptocurrency, designs photonic circuits to save energy
Cryptocurrency mining is only accessible to those with access to highly discounted energy. The newly-developed low-energy chips will make it possible for everyone to participate in mining profitably.
If you were to ask anyone their feelings about cryptocurrency in 2020, chances are they would respond along the lines of “to the moon”(Crypto investors often use the phrase when they believe that certain cryptocurrencies will rise significantly in price). However, a year later, those sentiments seemed to have jaded. A sense of negativity — FUD (fear, uncertainty, and doubt), as crypto-sympathizers would call it — seemed rife.
Stanford University.
A primary reason behind the fading support of the public, besides bad actors flooding the market with ponzi-like schemes and scams, seemed to be massive numbers of energy consumption floated by crypto and blockchain critics. The biggest question was “How is the world supposed to go greener and rely on these energy-hogging, power-hungry technologies?”
Researchers discover over 30,000 hidden viruses in the DNA of single-celled organisms
The research project was originally based on a new group of viruses that the study authors discovered in the water of the Gossenköllesee in Tyrol, Austria, in 2021.
During a comprehensive study of complex single-celled microbes, scientists from the University of Innsbruck’s Department of Ecology made a groundbreaking discovery. They discovered the DNA of more than 30,000 viruses that were previously unknown, integrated into the microbes’ genome.
The study revealed that some microbes contain a significant proportion of their DNA that is made up of hidden viruses, up to 10 percent.
Kontekbrothers/iStock.