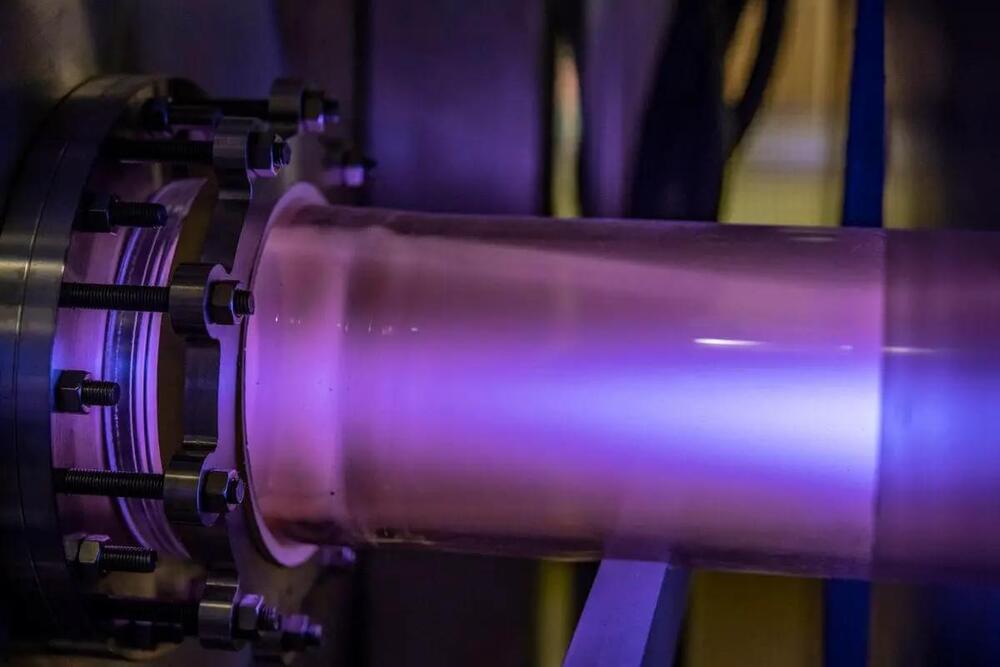
Physicists at West Virginia University have overcome a long-standing limitation of the first law of thermodynamics.
Paul Cassak, a professor and associate director of the Center for KINETIC Plasma Physics at West Virginia University, and Hasan Barbhuiya, a graduate research assistant in the Department of Physics and Astronomy, are investigating the conversion of energy in superheated plasmas in space. Funded by the National Science Foundation, their findings, published in the Physical Review Letters journal, are set to revolutionize the understanding of how plasmas in space and labs are heated and could have far-reaching implications in physics and other sciences.