Oldest known animal killed and secrets of immortality.
Ming the ocean quahog lived peacefully for over 500 years off the coast of Iceland. So why did a team of researchers dredge it up and kill it?
Oldest known animal killed and secrets of immortality.
Ming the ocean quahog lived peacefully for over 500 years off the coast of Iceland. So why did a team of researchers dredge it up and kill it?
Iranian nation-state groups have now joined financially motivated actors in actively exploiting a critical flaw in PaperCut print management software, Microsoft said.
The tech giant’s threat intelligence team said it observed both Mango Sandstorm (Mercury) and Mint Sandstorm (Phosphorus) weaponizing CVE-2023–27350 in their operations to achieve initial access.
“This activity shows Mint Sandstorm’s continued ability to rapidly incorporate [proof-of-concept] exploits into their operations,” Microsoft said in a series of tweets.
Web3 is a “decentralized web ecosystem” in which users retain their data. Blockchain-based, it would usher in the era of the “token economy”, say experts.
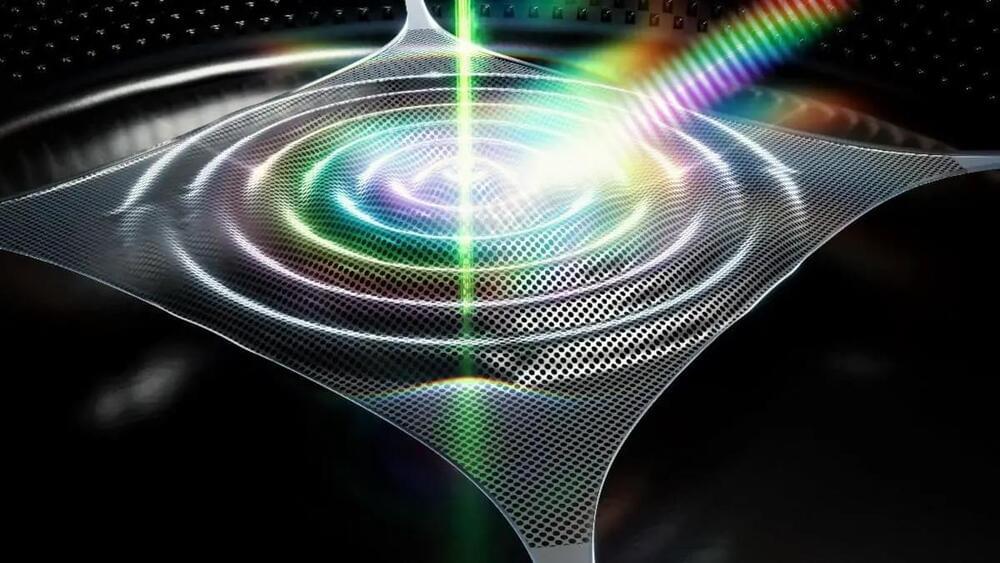
Physicists at Delft University of Technology have developed a new technology on a microchip by combining two Nobel Prize-winning methods for the first time. The microchip is capable of accurately measuring distances in materials, which could have applications in areas such as underwater measurement and medical imaging.
The new technology, which utilizes sound vibrations instead of light, could be useful for obtaining high-precision position measurements in materials that are opaque. This breakthrough could result in the development of new methods for monitoring the Earth’s climate and human health. The findings have been published in the journal Nature Communications.
<em>Nature Communications</em> is a peer-reviewed, open-access, multidisciplinary, scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio. It covers the natural sciences, including physics, biology, chemistry, medicine, and earth sciences. It began publishing in 2010 and has editorial offices in London, Berlin, New York City, and Shanghai.
Scientific work often involves sifting through enormous amounts of data, a task that’s overwhelmingly mundane for humans but a piece of cake for artificial intelligence. A new platform dubbed BacterAI can conduct as many as 10,000 experiments per day to teach itself – and us – more about bacteria.
The human body is home to trillions of microbes, covering almost every surface inside and out. Many of them are vital to specific bodily functions, while many others make you sick. Research continues to uncover how inextricably linked our overall health is to our microbiomes, but managing and exploring the data involved remains a daunting task.
“We know almost nothing about most of the bacteria that influence our health,” said Paul Jensen, corresponding author of the new study. “Understanding how bacteria grow is the first step toward reengineering our microbiome.”
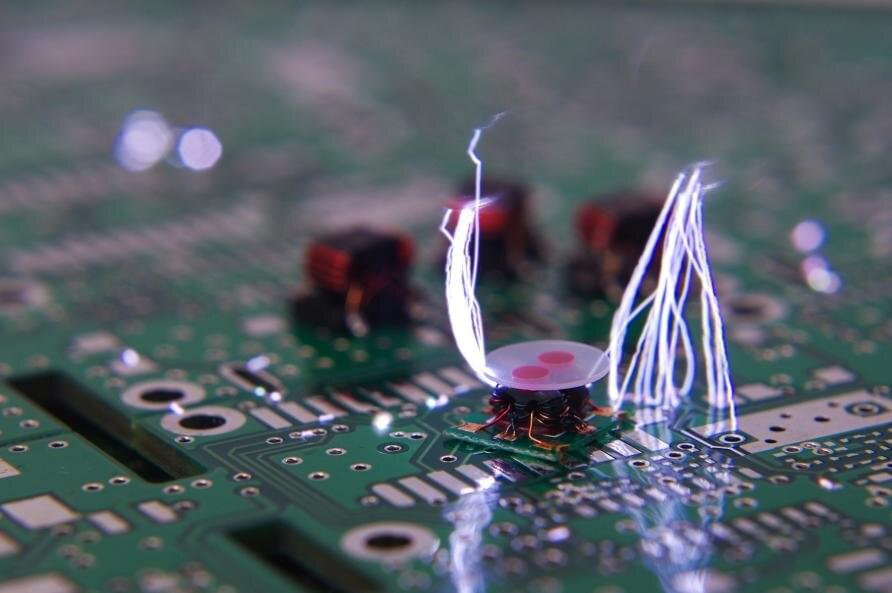
You may not have heard of piezoelectric materials, but odds are, you have benefitted from them.
Piezoelectric materials are solid materials —like crystals, bone or proteins—that produce an electric current when they are placed under mechanical stress.
Materials that harvest energy from their surroundings (through light, heat and motion) are finding their way into solar cells, wearable and implantable electronics and even onto spacecraft. They let us keep devices charged for longer, maybe even forever, without the need to connect them to a power supply.
I either think this has to do with some unknown physics problem like lack of some sorta gravity on spacetime fabric or it could be piloted by lifeforms as a black hole spaceship. Either way this could be addressed with a laser that could evaporate it back into light for instance a matter into light laser or put it back in place with a stasis field.
Supermassive black holes (SMBHs) lurk in the center of large galaxies like ours. From their commanding position in the galaxy’s heart, they feed on gas, dust, stars, and anything else that strays too close, growing more massive as time passes. But in rare circumstances, an SMBH can be forced out of its position and hurtle through space as a rogue SMBH.
In a new paper, researchers from Canada, Australia, and the U.S. present evidence of a rogue SMBH that’s tearing through space and interacting with the circumgalactic medium (CGM.) Along the way, the giant is creating shock waves and triggering star formation.
The paper is “A candidate runaway supermassive black hole identified by shocks and star formation in its wake.” The lead author is Pieter van Dokkum, Professor of Astronomy and Physics at Yale University. The paper is avaiable on the arXiv preprint server and hasn’t been peer-reviewed yet.
A time crystal, as originally proposed in 2012, is a new state of matter in which the particles are in continuous oscillatory motion. Time crystals break time-translation symmetry. Discrete time crystals do so by oscillating under the influence of a periodic external parametric force, and this type of time crystal has been demonstrated in trapped ions, atoms and spin systems.
Continuous time crystals are more interesting and arguably more important, as they exhibit continuous time-translation symmetry but can spontaneously enter a regime of periodic motion, induced by a vanishingly small perturbation. It is now understood that this state is only possible in an open system, and a continuous quantum-time-crystal state has recently been observed in a quantum system of ultracold atoms inside an optical cavity illuminated with light.
In a paper published in Nature Physics, researchers at University of Southampton in the U.K. showed that a classical metamaterial nanostructure can be driven to a state that exhibits the same key characteristics of a continuous time crystal.
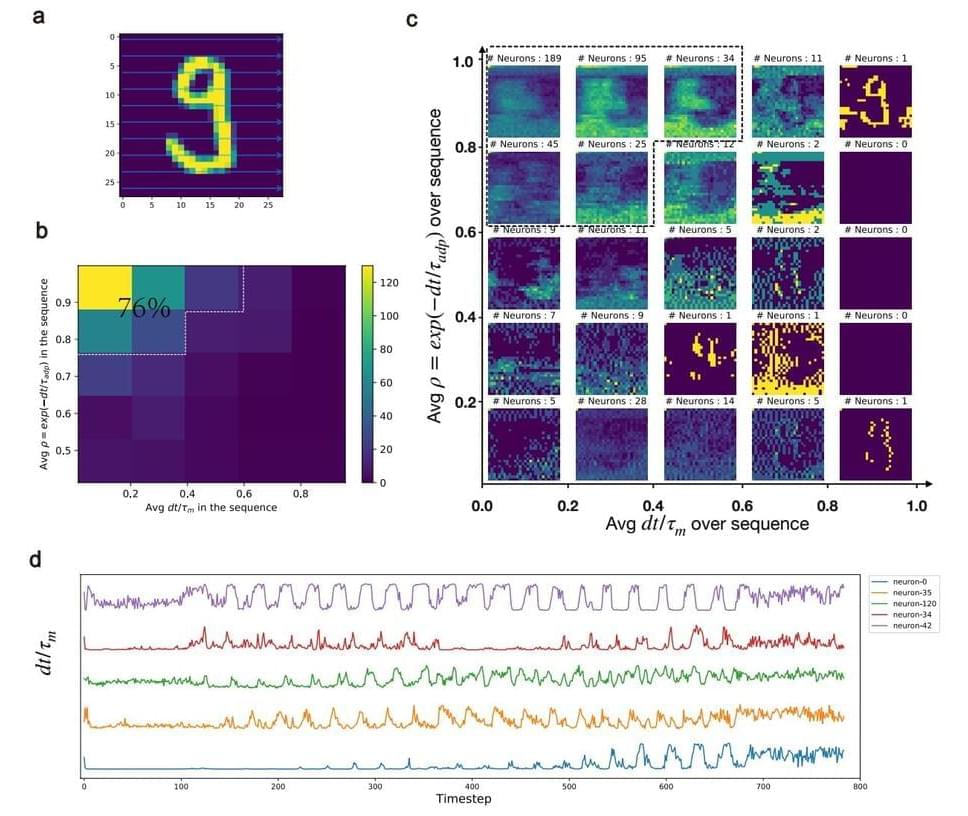
In a new study in Nature Machine Intelligence, researchers Bojian Yin and Sander Bohté from the HBP partner Dutch National Research Institute for Mathematics and Computer Science (CWI) demonstrate a significant step towards artificial intelligence that can be used in local devices like smartphones and in VR-like applications, while protecting privacy.
They show how brain-like neurons combined with novel learning methods enable training fast and energy-efficient spiking neural networks on a large scale. Potential applications range from wearable AI to speech recognition and Augmented Reality.
While modern artificial neural networks are the backbone of the current AI revolution, they are only loosely inspired by networks of real, biological neurons such as our brain. The brain however is a much larger network, much more energy-efficient, and can respond ultra-fast when triggered by external events. Spiking neural networks are special types of neural networks that more closely mimic the working of biological neurons: the neurons of our nervous system communicate by exchanging electrical pulses, and they do so only sparingly.

Year 2013 😗😁
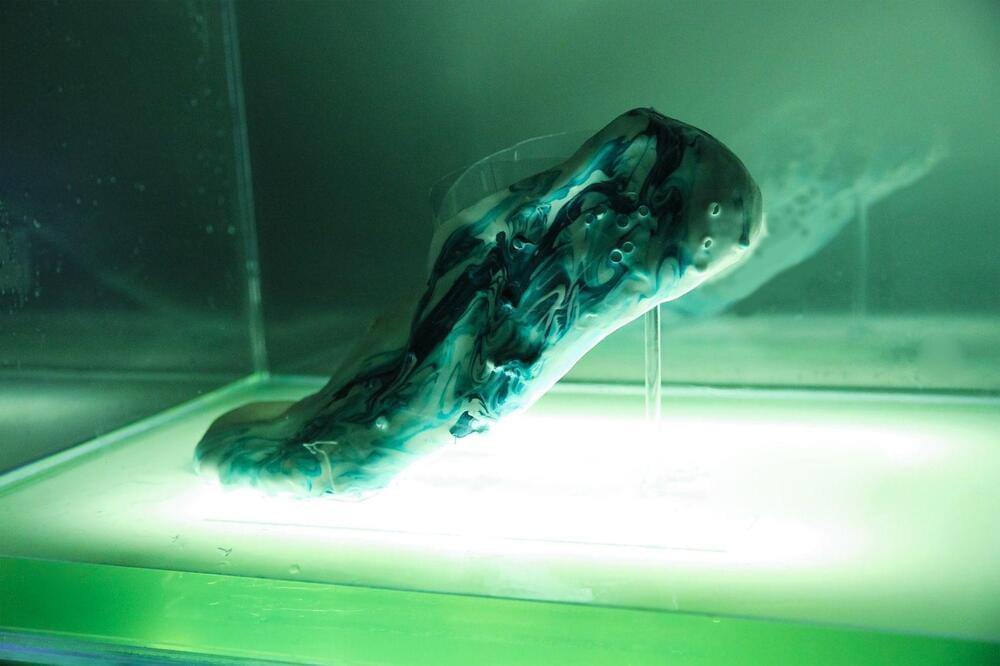
Shamees Aden, a British designer and scientist, has come up with a concept for a pair of self-repairing shoes of synthetic protocell materials.
Protocells are molecules that on their own are not alive, but when used with other types of protocells can mimic the properties of living organisms. They react to heat, light and pressure like live cells.
Aden’s concept for the shoes is that they could be 3D printed to the exact size of the wearer and when worn the shoes would react to heat and pressure to grow and expand in pressure points where more cushioning is needed. They would be kept in protocell fluid overnight to regenerate.