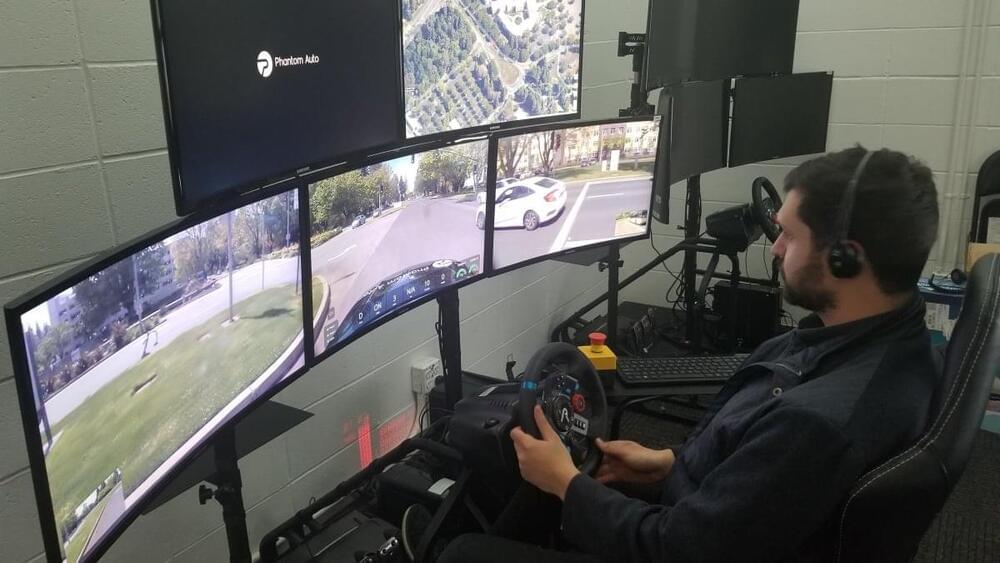
The exit ramp is a long, curving slope, and you have to make sure the 50-foot big rig you’re driving carefully navigates the bend and doesn’t fly out of control at a high speed.
But the thing is, you’re not actually there. You’re in a room in Silicon Valley, watching the ramp unfold in front of you on several screens. That heavy load you’re carrying is thousands of miles away in Florida.
Welcome to teleoperated driving, or remote-controlled driving with a human in front of a steering wheel, brake, and gas pedals, and a “windshield” plastered with monitors. It’s a method that allows autonomous vehicles to operate without anyone inside. Instead, there’s a watchful remote driver, or operator,… More.
Driving a truck is really hard, Seltz-Axmacher admits. Doing it through remote control is maybe just as difficult, until you’ve had enough training. After attempting to remotely back up a 50-foot long trailer between two parked trucks, for instance, he said he returned to the professional truckers with his tail between his legs. On the flip side, long-time truck drivers still require practice for remote control driving and go through one-week trainings to get used to operating a truck from in front of a monitor instead of the road.
Phantom operator McCarter finds remote driving similar to traditional driving, since both are high-focus tasks. In the case of teleoperating, McCarter is only monitoring the situation. He says his actual driving sessions are usually shorter, popping in to solve an “edge case” — like if an autonomous delivery robot encounters an unexpected construction crew fixing a pothole. Then McCarter, who has been monitoring the ride, is alerted and he can jump in, get around the construction site, and hand the reins back to the autonomous bot.
Remote-controlled vehicles might also help us get used to autonomy. A Capgemini study (opens in a new tab) on autonomous car perceptions from last month found that about half of consumers trust self-driving cars to run errands for them or pick up and drop off friends and family members. Just under 50 percent of more than 5,500 consumers surveyed said self-driving cars invoke “fear.” It’s comforting knowing there’s a human right there who can take over, even if they’re miles away.