Future-architecture designs?


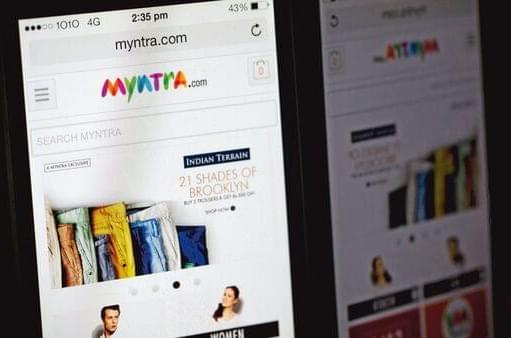
Customers can essentially look up curated looks on the app, say by typing keywords such as “airport looks”, and the system is designed to showcase a host of products including apparel, footwear, bags and sunglasses that consumers can choose from.
The move comes as the retailer is set to announce its bi-annual “end of reason sale” next month.
The feature is capable of discovering fashion ensembles at scale based on looks relevant to destinations, events, celebrity styling ideas or occasions, the retailer said.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links:
Oral Microbiome: https://www.bristlehealth.com/?ref=michaellustgarten.
Enter Code: ConquerAging.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
Use Code: ConquerAging At Checkout.
Green Tea: https://www.ochaandco.com/?ref=conqueraging.
Epigenetic Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1


Will truth and reason survive the evolution of artificial intelligence? AI researcher Gary Marcus says no, not if untrustworthy technology continues to be integrated into our lives at such dangerously high speeds. He advocates for an urgent reevaluation of whether we’re building reliable systems (or misinformation machines), explores the failures of today’s AI and calls for a global, nonprofit organization to regulate the tech for the sake of democracy and our collective future. (Followed by a Q&A with head of TED Chris Anderson)

Elon Musk has ruled out the possibility of a winter for artificial intelligence, and hinted that the current boom is just beginning.
“There will not be a winter for AI, quite the opposite,” the business mogul tweeted on Sunday.
Musk’s tweet was in response to comments from Adam D’Angelo, the CEO of Quora, who said he expects to see “continual progress” from where AI currently stands all the way to artificial general intelligence (AGI) – without a period of time that feels like a “winter,” or downturn.
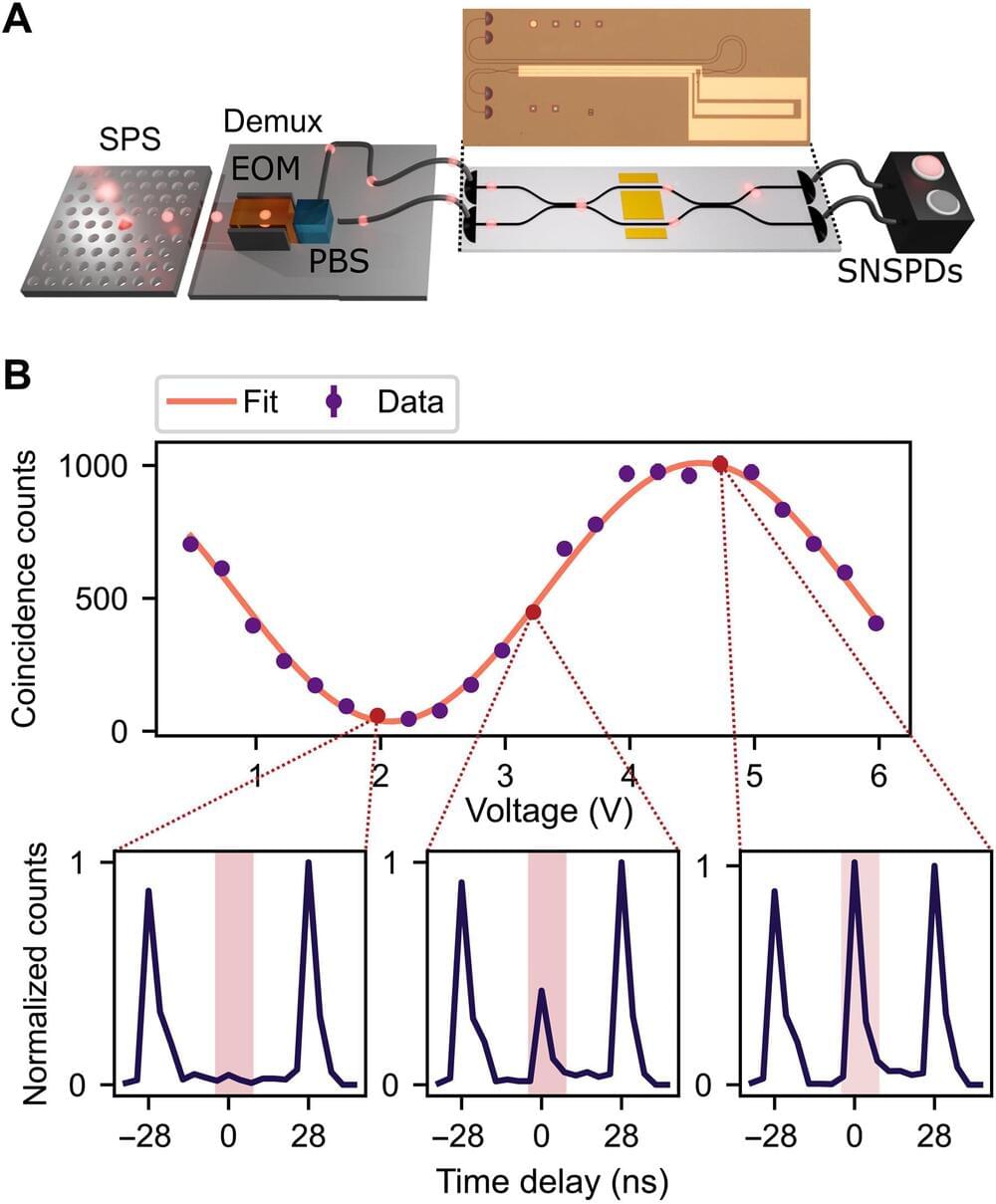
Scalable photonic quantum computing architectures require photonic processing devices. Such platforms rely on low-loss, high-speed, reconfigurable circuits and near-deterministic resource state generators. In a new report now published in Science Advances, Patrik Sund and a research team at the center of hybrid quantum networks at the University of Copenhagen, and the University of Münster developed an integrated photonic platform with thin-film lithium niobate. The scientists integrated the platform with deterministic solid-state single photon sources using quantum dots in nanophotonic waveguides.
They processed the generated photons within low-loss circuits at speeds of several gigahertz and experimentally realized a variety of key photonic quantum information processing functionalities on high-speed circuits; with inherent key features to develop a four-mode universal photonic circuit. The results illustrate a promising direction in the development of scalable quantum technologies by merging integrated photonics with solid-state deterministic photon sources.
Quantum technologies have progressively advanced in the past several years to enable quantum hardware to compete with and surpass the capabilities of classical supercomputers. However, it is challenging to regulate quantum systems at scale for a variety of practical applications and also to form fault-tolerant quantum technologies.


In a sequence of papers accepted for the 16th Annual Conference in Artificial General Intelligence in Stockholm, I pose a mechanistic explanation for these phenomena. They explain how we may build a machine that’s aware of itself, of others, of itself as perceived by others, and so on.
Intelligence and Intent
A lot of what we call intelligence boils down to making predictions about the world with incomplete information. The less information a machine needs to make accurate predictions, the more “intelligent” it is.