The country’s government recently announced a €2 billion fund aimed at tackling its severe drought problem.
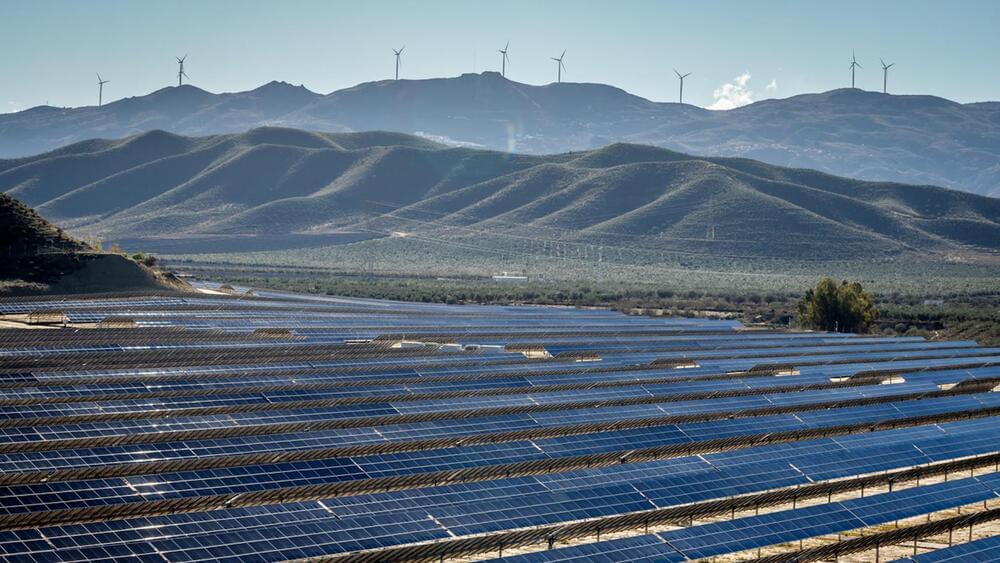
Spain hit an impressive renewable energy milestone last week when it was powered solely by renewables for nine hours straight.
Energy generated by solar panels, wind turbines, and hydro energy was able to power mainland Spain from 10 am to 7 pm local time (CEST) on Tuesday, May 16, a report from Spanish newspaper El País reveals.