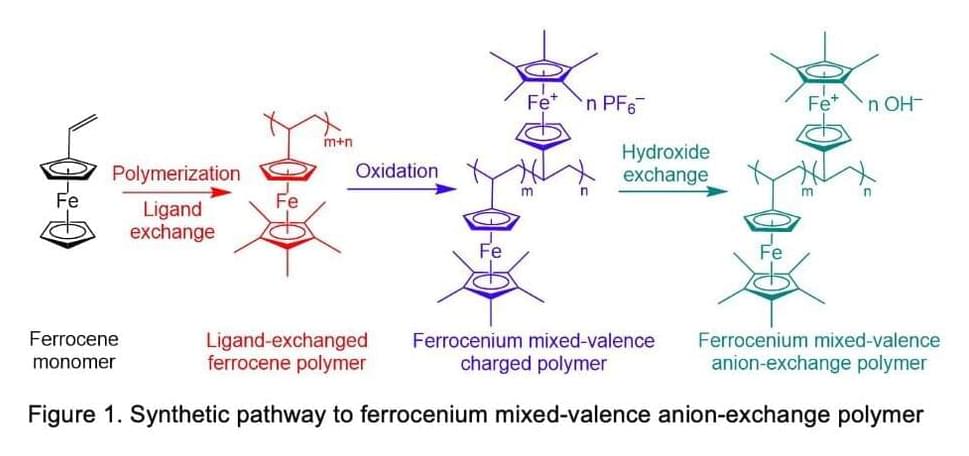
Anion exchange membranes (AEMs) are semipermeable fuel cell components that can conduct anions but reject cations and gases. This enables the partition of substances that could chemically react with one another, thus allowing the cells to operate properly.
A team of researchers at Tianjin University in China have recently developed new types of AEMs that are based on a newly designed ferrocenium material. Their membranes, presented in a paper published in Nature Energy, were found to achieve highly promising results in terms of power output, durability, and ohmic resistance.
“As the oriented mixed-valence ferrocenium material developed in our study is entirely new for the AEM field, we encountered many difficulties and frustrations along the way,” Michael D. Guiver, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “We spent a long research period and much effort, both experimentally and theoretically, to achieve these good outcomes. The whole process from initial conceptualization to final publication was convoluted, but fortunately successful.”