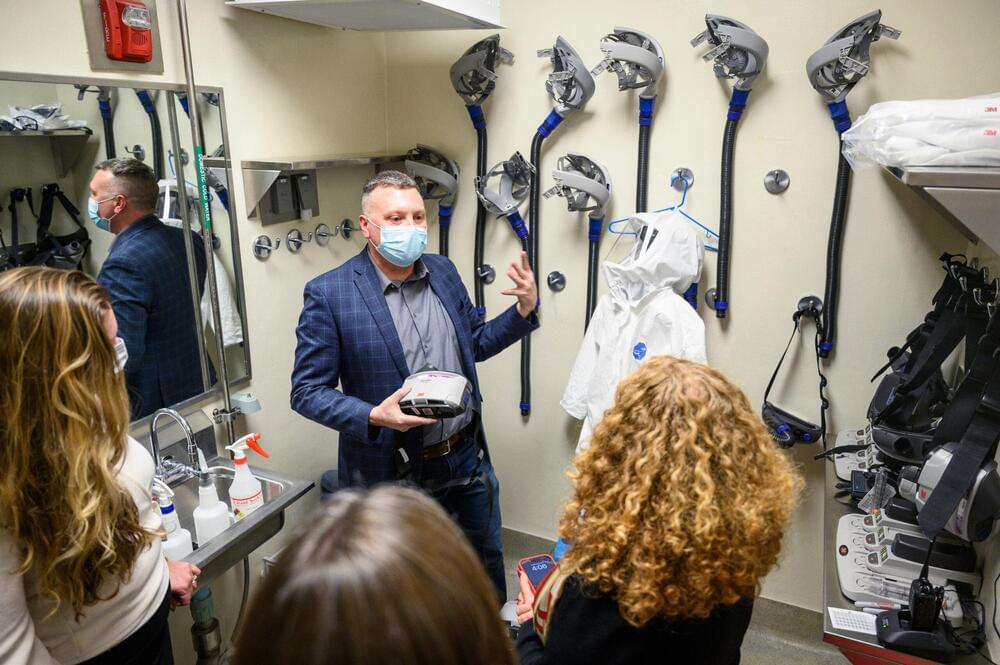
Scientists studying viruses at the University of Wisconsin-Madison recently opened their lab door for a tour, looking to shine a light on their work after being targeted by a Republican bill.
The legislation would have prohibited some of the research that has been done in the past in Madison…
The bill would have ended all so-called “gain-of-function” research at higher education institutions in the state, and cut funding from any university that continued such experiments.