Whether sitting or hanging, the surface of a protein-containing droplet changes as the water escapes, an effect researchers link to the pull of gravity.


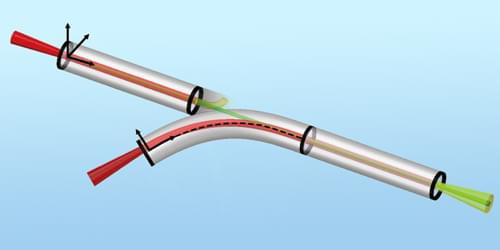
A curved “laser wakefield accelerator” could boost the acceleration potential of a multistage version of this device.
Laser wakefield accelerators (LWFAs) use laser-generated plasmas to accelerate electrons to high energies. The devices are significantly smaller than radio-frequency-based particle accelerators—centimeters versus hundreds of meters—making them less expensive, more efficient alternatives. But researchers still need to demonstrate that LWFAs can achieve particle energies that match those of their conventional counterparts. Now Xinzhe Zhu from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and colleagues have brought that goal a step closer, demonstrating a method for linking multiple LWFAs in a way that would boost their acceleration potential [1].
In an LWFA, charged particles reach relativistic speeds by surfing a wave of plasma created by a powerful laser. The particle energy achievable with a single LWFA is limited to a few GeV for two reasons: the particle bunch and the plasma wave quickly fall out of sync, and the laser energy dissipates with distance. Routing particles through multiple connected LWFAs would overcome these problems. But current techniques for combining LWFAs require refocusing the beam at each connection, lowering the efficiency of the process.
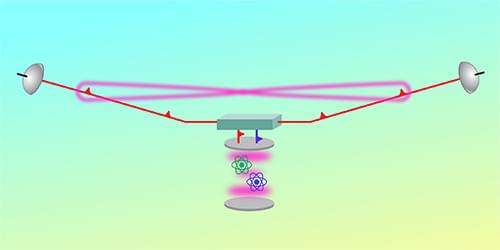
A quantum repeater based on trapped ions allows the transmission of entangled, telecom-wavelength photons over 50 km.
Communication networks have transformed our society over the past half century, and we can scarcely imagine our daily lives without them. Recent advances in the emergent field of quantum technologies have exhilarated scientists about the possibility of linking quantum devices in networks. Long-distance quantum communication portends functionality that is beyond the reach of classical networks [1]. To make full use of entanglement and other quantum effects, quantum networks exchange signals at the level of single photons. As a result, attenuation in fiber is the dominant source of error in these systems. Photon loss, however, can be remedied using a set of intermediate network nodes, called quantum repeaters, which create a direct entangled connection between distant network nodes [2].
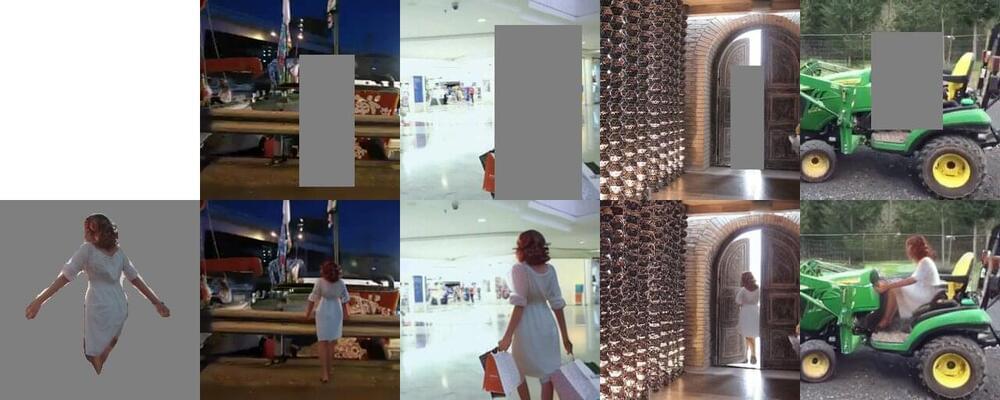

The recent advent of generative models, computational tools that can generate new texts or images based on the data they are trained on, opened interesting new possibilities for the creative industries. For example, they allow artists and digital content creators to easily produce realistic media content that integrates elements of different images or videos.
Inspired by these recent advances, researchers at Stanford University, UC Berkeley and Adobe Research have developed a new model that can realistically insert specific humans into different scenes, for instance showing them as they exercise in the gym, watch a sunset on the beach, and so on.
Their proposed architecture, which is based on a class of generative models known as diffusion models, was introduced in a paper pre-published on the arXiv server and set to be presented at the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2023 in Vancouver this June.
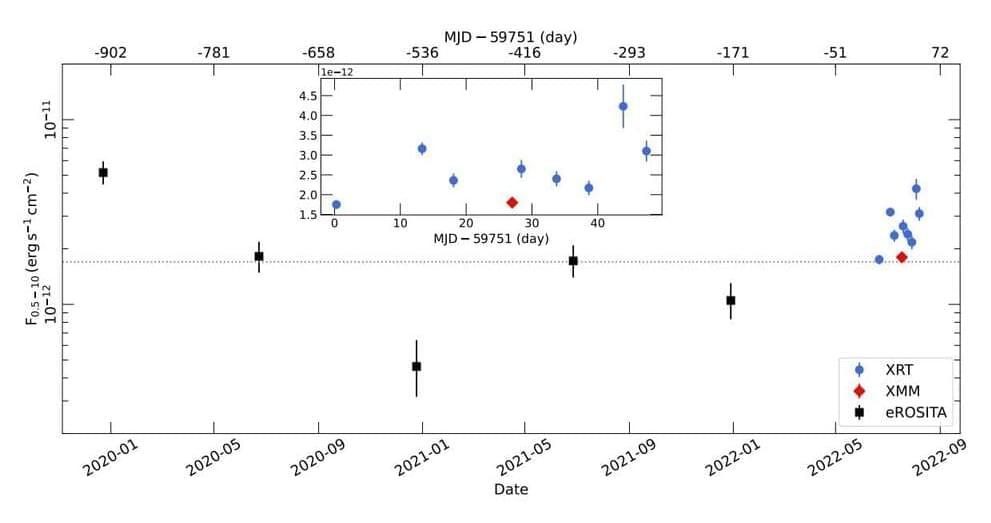
Using various space telescopes, an international team of astronomers have observed a recently detected luminous quasar known as SMSS J114447.77–430859.3, or J1144 for short. Results of the observational campaign, available in the July 2023 edition of Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, shed more light on the properties of this source.
Quasars, or quasi-stellar objects (QSOs) are active galactic nuclei (AGN) of very high luminosity, emitting electromagnetic radiation observable in radio, infrared, visible, ultraviolet and X-ray wavelengths. They are among the brightest and most distant objects in the known universe, and serve as fundamental tools for numerous studies in astrophysics as well as cosmology. For instance, quasars have been used to investigate the large-scale structure of the universe and the era of reionization. They also improved our understanding of the dynamics of supermassive black holes and the intergalactic medium.
J1144 was detected in June 2022 at a redshift of 0.83. It has a bolometric luminosity of about 470 quattuordecillion erg/s, which makes it the most luminous quasar over the last 9 billion years of cosmic history. It is also the optically brightest (unbeamed) quasar at a redshift greater than 0.4.

I had an amazing experience at the Foresight Institute’s Whole-Brain Emulation (WBE) Workshop at a venue near Oxford! For more information and a list of participants, see: https://foresight.org/whole-brain-emulation-workshop-2023/ I had the opportunity to work within a group of some of the most brilliant, ambitious, and visionary people I’ve ever encountered on the quest for recreating the human brain in a computer. We also discussed in depth the existential risks of upcoming artificial superintelligence and how to mitigate these risks, perhaps with the aid of WBE.
My subgroup focused on exploring the challenge of human connectomics (mapping all of the neurons and synapses in the brain).
WBE is a potential technology to generate software intelligence that is human-aligned simply by being based directly on human brains. Generally past discussions have assumed a fairly long timeline to WBE, while past AGI timelines had broad uncertainty. There were also concerns that the neuroscience of WBE might boost AGI capability development without helping safety, although no consensus did develop. Recently many people have updated their AGI timelines towards earlier development, raising safety concerns. That has led some people to consider whether WBE development could be significantly speeded up, producing a differential technology development re-ordering of technology arrival that might lessen the risk of unaligned AGI by the presence of aligned software intelligence.

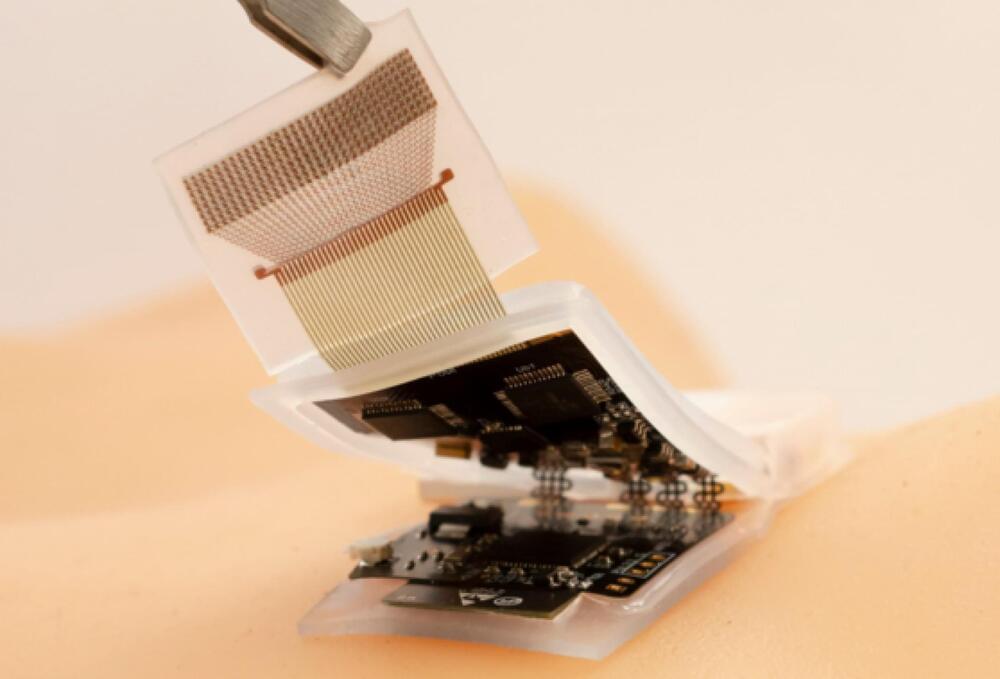
The device can track body signals from tissues as deep as 164 mm for up to twelve hours at a time.
A team of researchers and scientists from the University of California San Diego have developed a stick-on ultrasound patch, also called an ultrasonic system-on-patch (USoP), which a person can wear on the go as the device gives insight on the blood pressure, heart rate, and other physiological signs of the subject wearing it.
As per the press release, the USoP tracks these body signals from tissues as deep as 164 mm for up to twelve hours at a time.
Lin et al.
As per the press release, the USoP tracks these body signals from tissues as deep as 164 mm for up to twelve hours at a time.

Citizens are concerned about whether implemented rules are sufficient to protect them.
A recently reported scam in China that used ‘deep fake’ technology has raised concerns about the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in conducting fraudulent activities in the country. Discussion on the social media website Weibo about the explosion in the number of AI-powered scans gained more than 120 million views in a day, Reuters.
Over the years, the term ‘deep fakes’ has mainly been associated with celebrities, but as AI tech becomes more mainstream, it has also sparked fears of affecting the commoner.
Kentoh/iStock.