A talon-like claw with sharp ends and a softer middle helps this flying robot grasp onto thin perches just like a bird.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


Transparent ‘Grätzel’ solar cells achieve a new efficiency record
EPFL
According to a report by Euronews, researchers at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) have discovered a way to create transparent photosensitizers, molecules that can be activated by light and adsorb light across the entire visible light spectrum. Previous versions of DSCs were largely dependent on direct sunlight.
Billionaires are investing in brain-computer-interface systems. Here’s why
The technology has significantly progressed in the past 50 years.
Earlier this month, we reported that Bill Gates and Jeff Bezos-backed foundations (Gates Frontier and Bezos Expeditions) joined other companies.
A fifty year history.
1, 2, 3
Finally, Peter Thiel, a billionaire cofounder of PayPal, invested last year in an older BCI startup called Utah’s Blackrock Neurotech that has announced it hopes to apply for Food and Drug Administration approval soon. What is behind this popular rush to support BCI firms?

Virtual reality can work for those with one functional eye
Modern-day headsets and apps could be the key.
Virtual reality (VR) may soon be the way we use the internet. There are misconceptions about who can and cannot use the technology. Trying out headsets and apps is a great way to know if the technology suits your needs.
If you or someone you know only has one functional eye, and this has been keeping you away from exploring the world of virtual reality, then here’s a little surprise for you. VR experiences are not majorly affected if you do not use both of your eyes.
Thinkhubstudio/iStock.
We know this because users with two functional eyes have experimented with using VR with one eye and have found little that is different in their experience. There are many VR enthusiasts who vouch for this, and you can rest assured that you or a dear one can enjoy the experience too.

Ancient Mars did not have atmospheric oxygen, claims new research
That does not mean the planet did not have life.
A new experimental study conducted by Washington University in St. Louis is defeating any hope that scientists have had that atmospheric oxygen once existed on the Red Planet, according to a press release by the institution published on Thursday.
Instead, the scientists have found that under Mars-like conditions, manganese oxides can be readily formed without any presence of atmospheric oxygen.
Lubo Ivanko/iStock.
The new research is indicating that just because NASA’s Mars rovers found manganese oxides on Mars in 2014 does not mean that oxygen was actually present in the planet’s atmosphere.
Scientists can now “see” things without “looking” at them using a new quantum technique
“We also demonstrated that even very low-power microwave pulses can be detected efficiently using our protocol.”
A team of scientists has devised a means of using quantum mechanics to “view” objects indirectly. The new method could improve measurements for quantum computers and other systems. It brings together the quantum and classical worlds.
We “see” things via the complex interaction of light photons within specialized cells in the retina of our eyes. However, some scientists have speculated that a similar phenomenon could be replicated without photo-absorption or without any light.
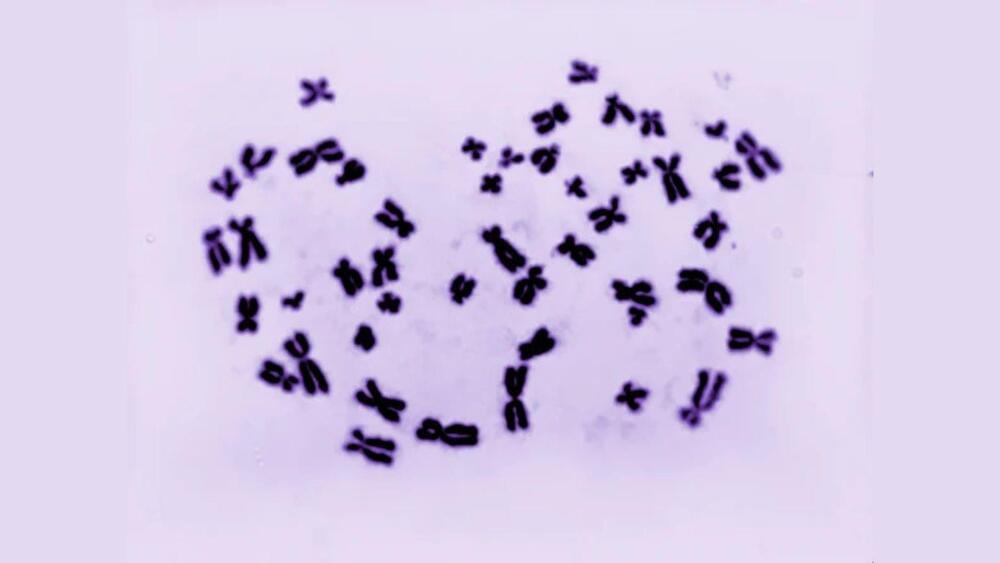
In a first, scientists produced male and female cells from a single person
It will provide a better understanding of how drugs affect men and women differently.
Scientists created male and female cells with the same genetic code from the same person for the first time. This unique set of cells could provide researchers with valuable insights into how sex chromosomes affect various diseases and their role in early development.
CDC/Dr. Laine.
The sex chromosome.
NASA’s Perseverance rover drops first sample on Mars, to return it to Earth one day
“Seeing our first sample on the ground is a great capstone to our prime mission period, which ends on Jan. 6.”
NASA’S Perseverance Mars rover has dropped its first rock sample on the Red Planet’s surface. A titanium tube containing a rock sample on December 21 that was deposited on the surface of Mars is likely to be the first sample that could return to Earth. The event marks a “historic” step in the Mars Sample Return campaign.
The first sample comprised a chalk-size core of igneous rock called “Malay”. This sample was collected on January 31, 2022, from a region in the Jezero Crater called “South Seitah”.
Currently, Perseverance has 17 other samples in its belly.
NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS

Gene therapy could save children from a rare genetic disease
This impressive achievement could potentially revolutionize how we treat cancer and immunity deficiencies.
Children born with Artemis-SCID face many challenges, from a missing repertoire of T and B cells to reduced resistance against chemotherapy used in bone marrow transplants. Additionally, malfunctioning DNA repair mechanisms increase the risk of developing graft-versus-host disease, where the donor’s immune system attacks host tissues.
That’s why researchers are trying everything to find an antidote for such a rare genetic disease and have now turned to gene therapy to treat Artemis-SCID. Gene therapy eliminates the need for donor cells.
Infant gene therapy – a breakthrough to save Artemis-SCID children
In a recent medical breakthrough, scientists have discovered how to use gene therapy to treat babies born with Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID), or “bubble boy syndrome,” without needing immune-suppressing drugs.
This new innovation has proven to be potentially life-changing for infants suffering from rare diseases, giving them an exponentially improved chance of leading a relatively healthy and normal life.