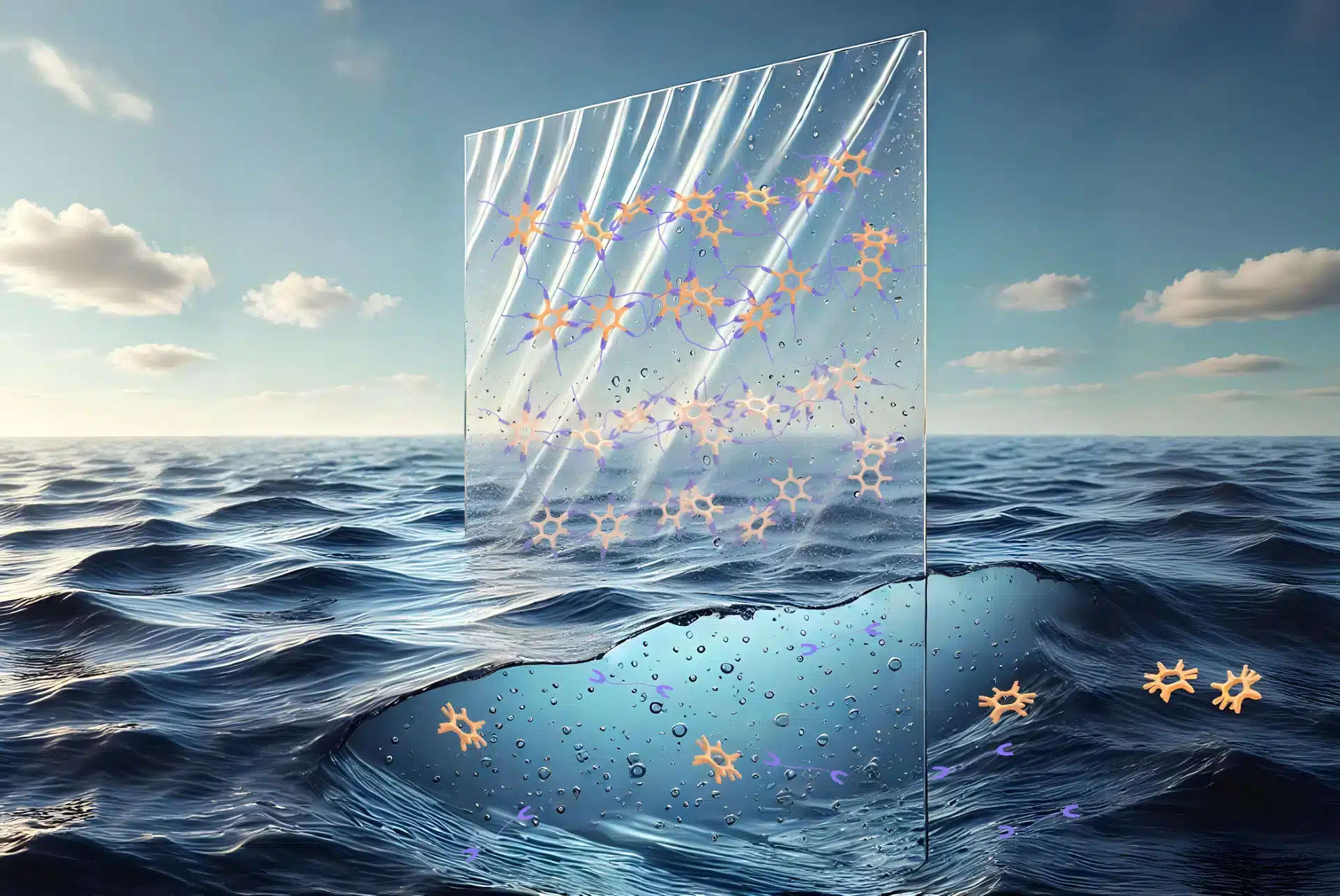
Tackling the problem of microplastics.
Summary: ChatGPT4 has demonstrated superiority in various student exams, revealing its potential to support academic learning and improve educational outcomes, particularly in test preparation. With its accessibility and affordability compared to traditional tutoring services, AI tutoring can help address the increasing demand for academic support, especially as universities begin to reinstate standardized testing requirements.
In 2023, OpenAI shook the foundation of the education system by releasing ChatGPT4. The previous model of ChatGPT had already disrupted classrooms K–12 and beyond by offering a free academic tool capable of writing essays and answering exam questions. Teachers struggled with the idea that widely accessible artificial intelligence (AI) technology could meet the demands of most traditional classroom work and academic skills. GPT3.5 was far from perfect, though, and lacked creativity, nuance, and reliability. However, reports showed that GPT4 could score better than 90 percent of participants on the bar exam, LSAT, SAT reading and writing and math, and several Advanced Placement (AP) exams. This showed a significant improvement from GPT3.5, which struggled to score as well as 50 percent of participants.
This marked a major shift in the role of AI, from it being an easy way out of busy work to a tool that could improve your chances of getting into college. The US Department of Education published a report noting several areas where AI could support teacher instruction and student learning. Among the top examples was intelligent tutoring systems. Early models of these systems showed that an AI tutor could not only recognize when a student was right or wrong in a mathematical problem but also identify the steps a student took and guide them through an explanation of the process.
AI agents need two things to succeed in this space: infinite scalability and the ability to connect agents from different blockchains. Without the former, agents do not have infrastructure with sufficient capacity to transact. Without the latter, agents would be off on their own island blockchains, unable to truly connect with each other. As agent actions become more complex on chain, more of their data will also have to live on the ledger, making optimizing for both of these factors important right now.
Because of all of this, I believe the next frontier of AI agents on blockchains is in gaming, where their training in immersive worlds will inevitably lead to more agentic behavior crossing over to non-gaming consumer spaces.
If the future of autonomous consumer AI agents sounds scary, it is because we have not yet had a way to independently verify LLM training models or the actions of AI agents so far. Blockchain provides the necessary transparency and transaction security so that this inevitable phenomenon can operate on safer rails. I believe the final home for these AI agents will be Web3.
Ultrasonic standing waves can be used to manipulate the position and control the movement of levitated objects through acoustic radiation forces. Within this co
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects approximately 1% of people over the age of 60 and 5% of those over the age of 85. Current drugs for Parkinson’s disease mainly affect the symptoms and cannot stop its progression. Nanotechnology provides a solution to address some challenges in therapy, such as overcoming the blood-brain barrier (BBB), adverse pharmacokinetics, and the limited bioavailability of therapeutics. The reformulation of drugs into nanoparticles (NPs) can improve their biodistribution, protect them from degradation, reduce the required dose, and ensure target accumulation. Furthermore, appropriately designed nanoparticles enable the combination of diagnosis and therapy with a single nanoagent.
In recent years, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have been studied with increasing interest due to their intrinsic nanozyme activity. They can mimic the action of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase. The use of 13-nm gold nanoparticles (CNM-Au8®) in bicarbonate solution is being studied as a potential treatment for Parkinson’s disease and other neurological illnesses. CNM-Au8® improves remyelination and motor functions in experimental animals.
Among the many techniques for nanoparticle synthesis, green synthesis is increasingly used due to its simplicity and therapeutic potential. Green synthesis relies on natural and environmentally friendly materials, such as plant extracts, to reduce metal ions and form nanoparticles. Moreover, the presence of bioactive plant compounds on their surface increases the therapeutic potential of these nanoparticles. The present article reviews the possibilities of nanoparticles obtained by green synthesis to combine the therapeutic effects of plant components with gold.
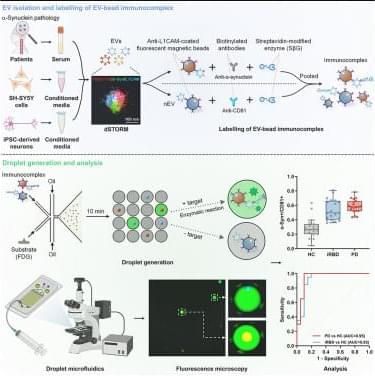
Single extracellular vesicle detection assay identifies membrane-associated α-synuclein as an early-stage biomarker in Parkinson’s disease
Posted in biotech/medical | Leave a Comment on Single extracellular vesicle detection assay identifies membrane-associated α-synuclein as an early-stage biomarker in Parkinson’s disease
Biomarker for Parkinson’s disease using single extracellular vesicle detection assay.
Detecting minute amounts of neuronally derived biomarkers in the massive protein excess of easily accessible biofluids such as blood is challenging.
The researchers develop a droplet-based microfluidic immunoassay for multiplexed quantification of membrane associated proteins at single extracellular-vesicle (EV) resolution.
They identify membrane-associated a-synuclein on the surface of neuronal EVs and demonstrate that it is increased under pathological conditions and in individuals at risk of or with Parkinson’s disease. https://sciencemission.com/Single-extracellular-vesicle-detection-assay
Yan et al. develop a droplet-based microfluidic immunoassay for multiplexed quantification of membrane-associated proteins at single-extracellular-vesicle (EV) resolution. They identify membrane-associated α-synuclein on the surface of neuronal EVs and demonstrate that it is increased under pathological conditions and in individuals at risk of or with Parkinson’s disease.
🚀 Imagine a future where living to 150 is possible—but only if you give up sugar, take ice-cold showers, and inject custom-engineered bacteria. Would you do it? In this deep dive into longevity science, we uncover the shocking truth about genetics, lifestyle, biohacking, and whether living longer actually makes life better. Plus, the real reason happiness might be the ultimate anti-aging hack! 🤯💡
#Longevity #AntiAging #Biohacking #LiveLonger #Science #Health #Wellness #LongevitySecrets #HealthyAging #LifeExtension
An extensive report on the future of AI research indicated that there’s skepticism about current approaches to AGI.
Cases of the fungal infection Candida auris are rising rapidly and coming from more sources too, a new US study reveals.
C. auris was first reported in the US in 2016 and is considered an “urgent antimicrobial resistance threat” in hospitals, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Focusing on a large health system in Miami, Florida, the new research found that reported clinical cases had risen from 5 in 2019 to 115 in 2023 – a considerable jump of 2,200 percent in four years.
A bioelectric capsule tricks the brain into feeling full by activating the stomach’s stretch receptors.