A new backdoor has been discovered that borrows its features from the leaked CIA’s Hive malware suite.



@NatureNano is hiring!
If you are an expert in 2D materials, electronics, optoelectronics, nanophotonics, or electronic engineering and interested in a career in science publishing?
Apply by Jan 22nd 2023 and join the editorial team.
Associate or Senior Editor, Nature Nanotechnology, with Springer Nature. Apply Today.

A new test that ‘fishes’ for multiple respiratory viruses at once using single strands of DNA as ‘bait’, and gives highly accurate results in under an hour, has been developed by Cambridge researchers.
The test uses DNA ‘nanobait’ to detect the most common respiratory viruses – including influenza, rhinovirus, RSV and COVID-19 – at the same time. In comparison, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests, while highly specific and highly accurate, can only test for a single virus at a time and take several hours to return a result.
While many common respiratory viruses have similar symptoms, they require different treatments. By testing for multiple viruses at once, the researchers say their test will ensure patients get the right treatment quickly and could also reduce the unwarranted use of antibiotics.
The essence of the Turing Test revolves around whether a computer can successfully impersonate a human. The test is to be put into practice under a set of detailed conditions which rely on human judges being connected with test subjects (a computer and a person) solely via an instant messaging system or its equivalent. That is, the only information which will pass between the parties is text.
To pass the test, a computer would have to be capable of communicating via this medium at least as competently as a person. There is no restriction on the subject matter; anything within the scope of human experience in reality or imagination is fair game. This is a very broad canvas encompassing all of the possibilities of discussion about art, science, personal history, and social relationships. Exploring linkages between the realms is also fair game, allowing for unusual but illustrative analogies and metaphors. It is such a broad canvas, in my view, that it is impossible to foresee when, or even if, a machine intelligence will be able to paint a picture which can fool a human judge.
While it is possible to imagine a machine obtaining a perfect score on the SAT or winning Jeopardy—since these rely on retained facts and the ability to recall them—it seems far less possible that a machine can weave things together in new ways or to have true imagination in a way that matches everything people can do, especially if we have a full appreciation of the creativity people are capable of. This is often overlooked by those computer scientists who correctly point out that it is not impossible for computers to demonstrate creativity. Not impossible, yes. Likely enough to warrant belief in a computer can pass the Turing Test? In my opinion, no. Computers look relatively smarter in theory when those making the estimate judge people to be dumber and more limited than they are.
Experience the beauty of AI-generated creativity with “Fantasy Lost,” an original composition by Raymond Miller. Witness the power of Artificial Intelligence as it “humanizes” the performance, bringing a unique and compelling twist. Accompanied by artwork of beautiful Tolkienesque elven women rendered by Stable Diffusion 2.1 and a helpful scrolling score and lighted keyboard for anyone who wishes to play the piece, this video is a short jaunt through an otherworldly musical and visual odyssey. Join us at Creative AI channel and explore the endless possibilities of AI in art and music.

https://sc.mp/subscribe-youtube.
Russia announced on January 11, 2023, that it would send a rescue vessel to the International Space Station to bring home three astronauts. Roscosmos cosmonauts Sergei Prokopyev and Dmitry Petelin, along with NASA astronaut Frank Rubio have in effect been stranded since their original capsule was damaged. US and Russian space officials believe the Soyuz MS-22 started leaking in December 2022 after it was hit by a tiny meteoroid.
Related story:
Russia to send rescue mission to International Space Station https://sc.mp/f6jn.
Support us:
https://subscribe.scmp.com.
Follow us on:
Website: https://www.scmp.com.
Facebook: https://facebook.com/scmp.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/scmpnews.
Instagram: https://instagram.com/scmpnews.
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/south-china-morning-post/
#scmp #World #Space
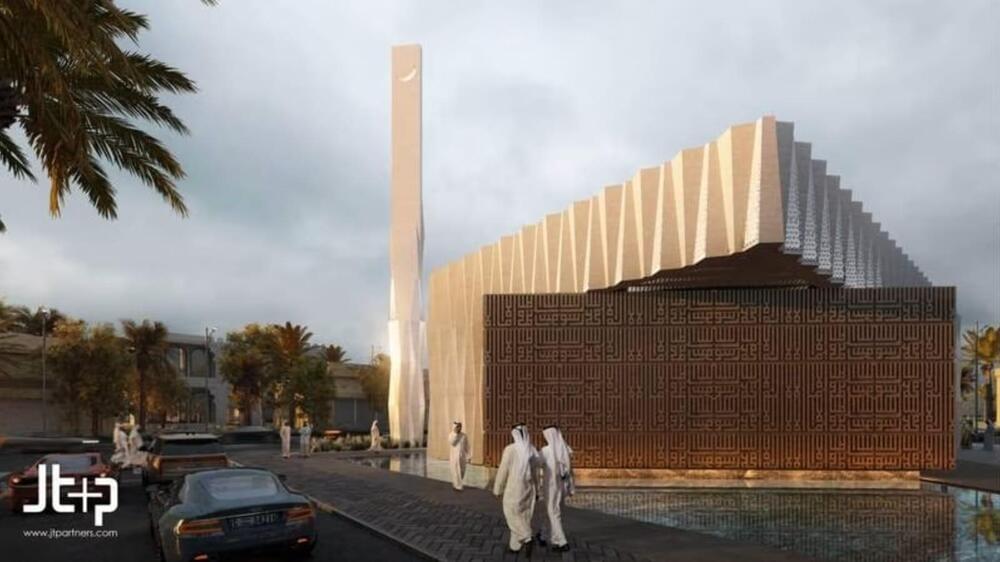

The Islamic Affairs and Charitable Activities Department in Dubai (IACAD) has announced its plans to build the world’s first 3D printed Mosque. The construction of the 2,000 square meter mosque, in Bur Dubai, is expected to start in October 2023, and have the capacity for 600 worshippers by early 2025.
HAL [Hybrid Assistive Limb] is the world’s first technology that improves, supports, enhances and regenerates the wearer’s physical functions. Made by Cyberdyne 2018.
In this video a woman in a wheelchair since childhood because of polio walks again.
Click visits the Cyberdyne company in Japan, who are manufacturing HAL (Hybrid Assisted Limb) exoskeleton’s.
Subscribe HERE http://bit.ly/1uNQEWR
Find us online at www.bbc.com/click.
Twitter: @bbcclick.
Facebook: www.facebook.com/BBCClick