Biodegradable fibers spun from yeast protein avoid the resource use and pollution of cotton, wool, and polyester



About 68% of respondents said the pressure to publish their research is greater than it was two to three years ago and only 45% agreed that they have sufficient time for research (see ‘Researchers are feeling the pressure’). Another concern is uncertainty over funding — just 33% of respondents expect funding in their field to grow in the next 2–3 years. And that proportion fell to just 11% in North America, reflecting unprecedented cuts to US research funding this year.
“As a researcher based in Brazil, I strongly relate to the survey’s findings, particularly the growing pressure to publish despite limited time and resources,” says Claudia Suemoto, a gerontologist at the University of São Paulo Medical School. “The demand for productivity has indeed increased in recent years, yet opportunities for funding and access to qualified personnel remain constrained in Brazil and other low-and middle-income countries.”
Suemoto says this imbalance of high demands and restricted resources often forces researchers to do more with less, which could affect the quality and innovation of research. Comments researchers made as part of the survey indicate that the lack of time is down to factors including growing administrative and teaching demands and trying to identity and acquire funding.
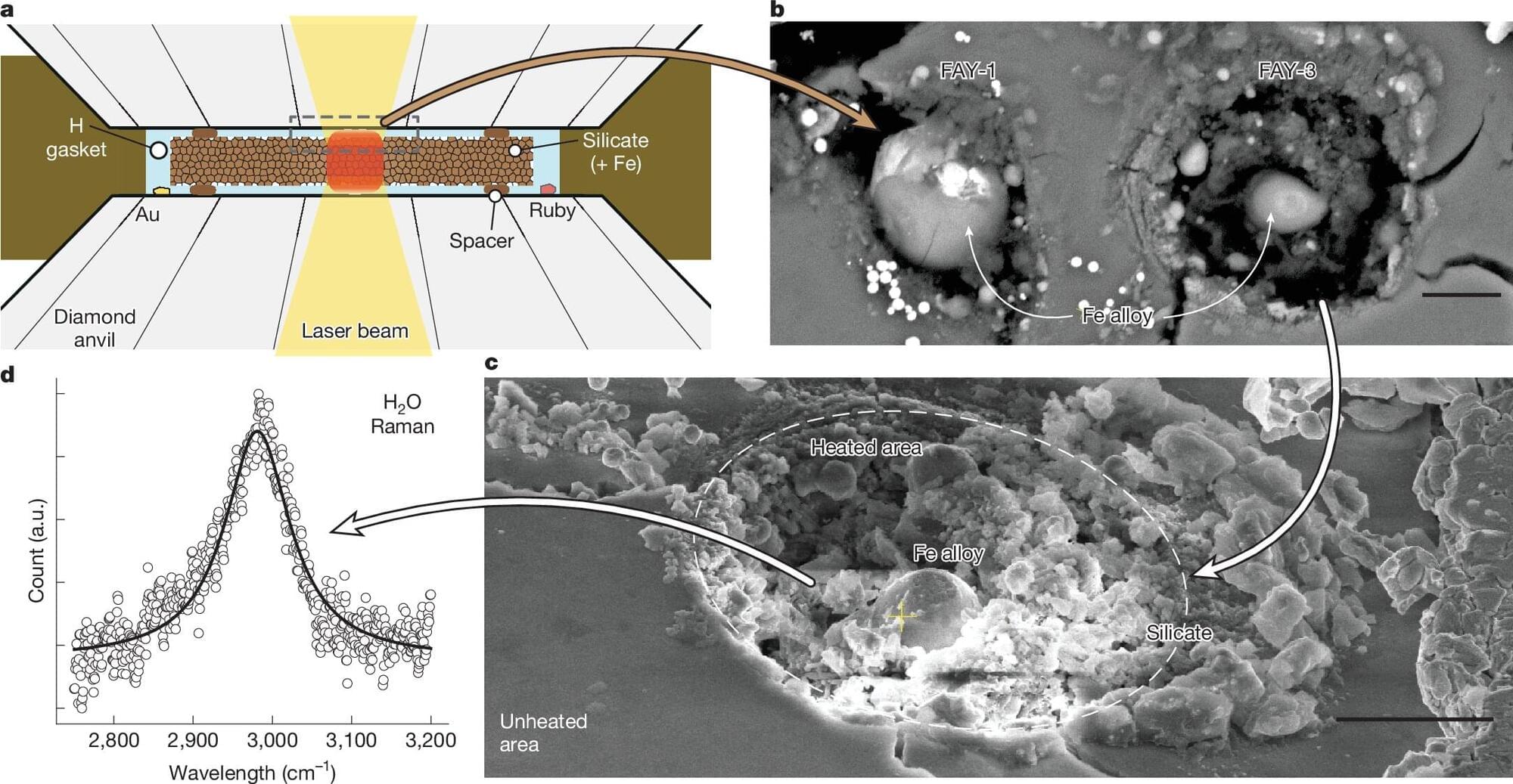
As more and more exoplanets are discovered throughout the galaxy, scientists find some that defy explanation—at least for awhile. A new study, published in Nature, describes a process that might explain why a large portion of exoplanets have water on their surface, even when it doesn’t make sense.
Water where it shouldn’t be A particular category of exoplanets that are between the size of Earth and Neptune, referred to as “sub-Neptunes,” generally have a rocky core, which is surrounded by an envelope of either hydrogen or water. This makes sense if the planet forms farther away from its host planet, in a region where water can precipitate as ice. However, some of these planets are found much closer to their host stars, where it should be too hot to hold water at the surface.
While some planets may accumulate a certain amount of water from incoming comets and asteroids, that doesn’t work for these planets either. The amount of water that is typically found on their surfaces is too high for such explanations. Past experiments have also shown that hydrogen can reduce iron in silicates, producing water. However, they came to the conclusion that only small amounts of water would be produced at the kind of high pressures experienced at the surface of a sub-Neptune planet.
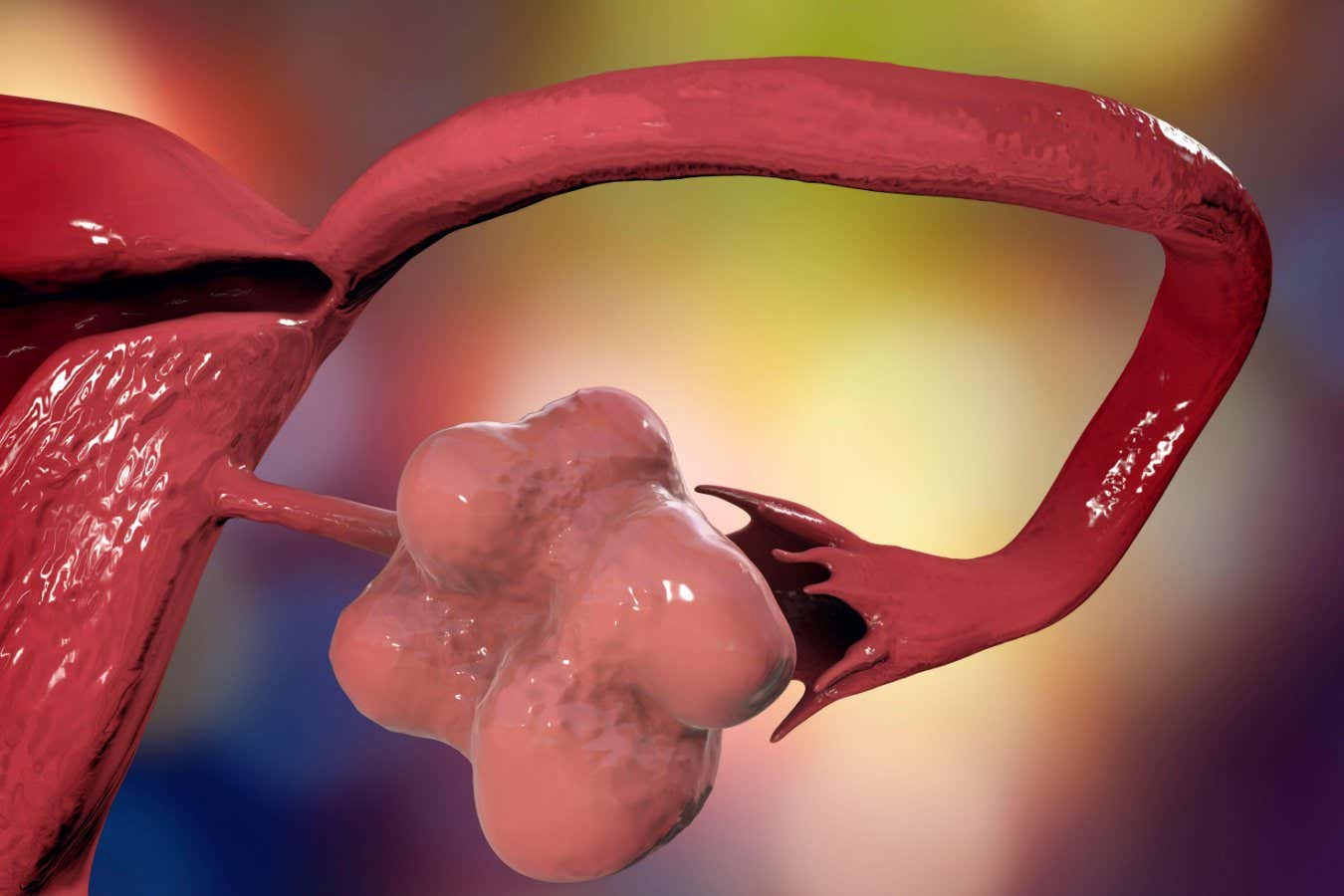

The human brain comprises hundreds of interconnected regions that drive our thoughts, emotions, and behaviours. Existing brain atlases can identify major structures in MRI scans – such as the hippocampus, which supports memory and learning – but their finer sub-regions remain hard to detect. These distinctions matter because sub-regions of areas like the hippocampus, for example, are affected differently during Alzheimer’s disease progression.
Examining the brain at the cellular level is achievable using microscopy (histology), but cannot be done in living individuals, limiting its potential for understanding how the human brain changes during development, ageing and disease.
Published in Nature, the new study introduces NextBrain, an atlas of the entire adult human brain that can be used to analyse MRI scans of living patients in a matter of minutes and at a level of detail not possible until now.
The creators of the atlas, which is freely available, hope it will ultimately help to accelerate discovery in brain science and its translation into better diagnosis and treatment of conditions such as Alzheimer’s.
&
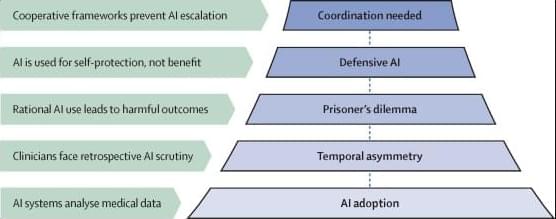
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can analyse medical images, records, and claims are becoming accessible to everyone. Although these systems outperform physicians at specific tasks, such as detecting cancer on CT scans, they are still imperfect. But as AI performance progresses from occasionally correct to reliably superior, there will be increasing pressure to conform to algorithmic outputs.

face_with_colon_three fungi is even better than current medicines and frankly better for you. We can also ingest fungi that can help be a natural food medicine to help prevent worse diseases.
While all attention is on the pandemic right now, the SARS-CoV-2 virus isn’t the only microbial threat we face.
While we’re all rightly focused on the COVID-19 pandemic at the moment, the SARS-CoV-2 virus isn’t the only microbial threat we face.
Back in 2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) warned that within a decade, antibiotic-resistant bacteria could make routine surgery, organ transplantation and cancer treatment life-threateningly risky — and spell the end of modern medicine as we know it.
face_with_colon_three Fungi can save all life on earth. This lecture teaches that mushrooms are outperforming even age old medicines.
Watch my 15 minute speech at the United Nations General Assembly’s AUDACITY 100 Disruptors Summit was a powerful reminder of how interconnected we all are.
I spoke about how fungal mycelium can help heal ecosystems, strengthen food systems, and strengthens the health.
of the residents of the planet. Mycelium supports our collective immunity.
When Mycelium Running: How Mushrooms Can Help Save the World was published in 2005, it foretold the mycelial revolution that continues to sweep the planet. This book is as relevant today as it was then. What has happened since? The scientific community continues to verify that mycelium is essential for our collective health, whether as nutritional supplements, or as the core fabric of our food webs.