University of Chicago physicists have finally engineered a way to create turbulence in a tank of water by using a ring of jets to blow loops until an isolated “ball” of turbulence forms and stays.

ABB
This is according to a press release by ABB published on Tuesday.

NASA recently announced its Wallops Visitor Center won’t be open for the mission and ‘there is no live stream planned for launch’.
Rocket Lab will launch a mission from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia within the next few days, but the company has not disclosed what it is lifting to orbit and it won’t stream the mission live.
NASA announced via Twitter on Tuesday, June 13, that its Wallops facility is “scheduled to support a Rocket Lab launch between June 15–20 in the evening.”

Vladimir Putin confirmed Russia has sent nuclear arms to its ally Belarus, which borders Ukraine. Putin has repeatedly warned that Russia, which has more nuclear weapons than any other country, will use all means to defend itself. Russia has a huge numerical superiority over the united states and the nato military alliance when it comes to tactical nuclear weapons. The united states believe Russia has around 2,000 such working tactical warheads. Reports say, the united states has around 200 tactical nuclear weapons, half of which are at bases in Europe. Remember, Belarus has borders with 3 nato members — Poland, Lithuania & Latvia. The treaty on the non-proliferation of nuclear weapons, signed by the soviet union, says no nuclear power can transfer nuclear weapons or tech to a non-nuclear power.
Those well-established conventional IT systems, however, can no longer be taken for granted. Companies are accelerating their digital transformation efforts, automating, optimizing, and reinventing their business processes. The pace of change continues to accelerate: Deloitte reports, for example, that 58% of organizations have stepped up their modernization plans due to the covid-19 pandemic.
Many ERP apps are now being moved to public cloud services, such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, while others are being replaced with SaaS-based alternatives, including Salesforce and Workday. The previously monolithic ERP platform is being deconstructed.
Enterprises now find themselves with a mixed-bag, hybrid cloud environment: some legacy core applications remain on premises, while new applications are cloud native and run in containers or as microservices.
Circa 2020
Imagine a dressing that releases antibiotics on demand and absorbs excessive wound exudate at the same time. Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology hope to achieve just that, by developing a smart coating that actively releases and absorbs multiple fluids, triggered by a radio signal. This material is not only beneficial for the health care industry, it is also very promising in the field of robotics or even virtual reality.
TU/e-researcher Danqing Liu, from the Institute of Complex Molecular Systems and the lead author of this paper, and her PhD student Yuanyuan Zhan are inspired by the skins of living creatures. Human skin secretes oil to defend against bacteria and sweats to regulate the body temperature. A fish secretes mucus from its skin to reduce friction from the water to swim faster. Liu now presents an artificial skin: a smart surface that can actively and repeatedly release and reabsorb substances under environmental stimuli, in this case radio waves. And that is special, as in the field of smart materials, most approaches are limited to passive release.
The potential applications are numerous. Dressings using this type of material could regulate drug delivery, to administer a drug on demand over a longer time and then ‘re-load’ with a different drug. Robots could use the layer of skin to ‘sweat’ for cooling themselves, which reduces the need for heavy ventilators inside their bodies. Machines could release lubricant to mechanical parts when needed. Or advanced controllers for virtual reality gaming could be made, that get wet or dry to enhance the human perception.
The basis of the material, the coating, is made of liquid-crystal molecules, well-known from LCD screens. These molecules have so-called responsive properties. Liu: “You could imagine this as a communication material. It communicates with its environment and reacts to stimuli.” With her team at the department of Chemical Engineering and Chemistry she discovered that the liquid-crystal molecules react to radio waves. When the waves are turned on, the molecules twist to orient with the waves’ direction of travel.
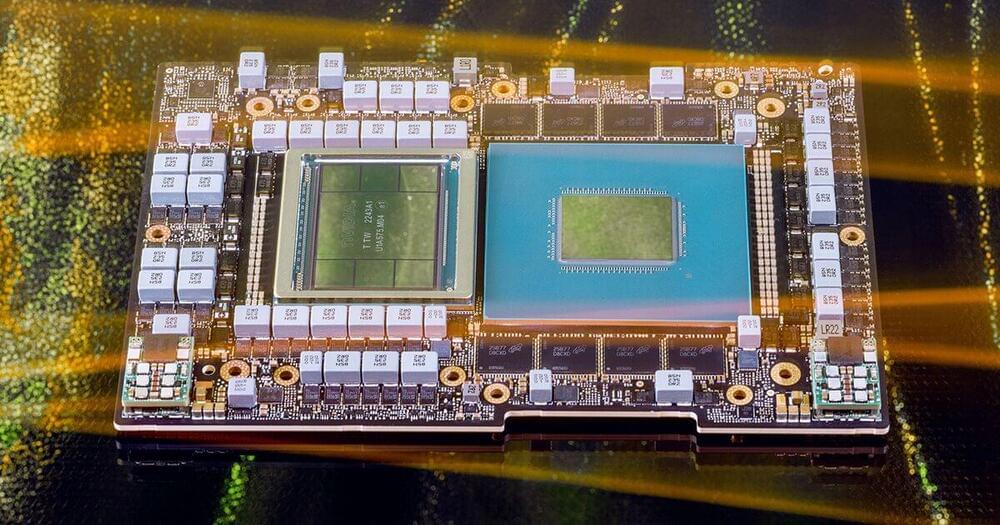

CEO Jensen Huang’s big bet on AI went from hand-delivering processors to Elon Musk and Sam Altman in 2016 to joining today’s alpha pack of Silicon Valley. He is worth close to $40 billion.
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy.

Nanoscientists have developed a wearable textile that can convert body movement into useable electricity and even store that energy. The fabric potentially has a wide range of applications from medical monitoring to assisting athletes and their coaches in tracking their performance, as well as smart displays on clothing.
The research team responsible for the textile describe how it works in a paper published in Nano Research Energy.
From smart watches to cordless headphones, people already have access to a wide range of wearable electronic devices. A range of health, sport and activity monitors are now integrated into smartphones.