Researchers have used a machine learning model to identify three compounds that could combat aging. They say their approach could be an effective way of identifying new drugs, especially for complex diseases.
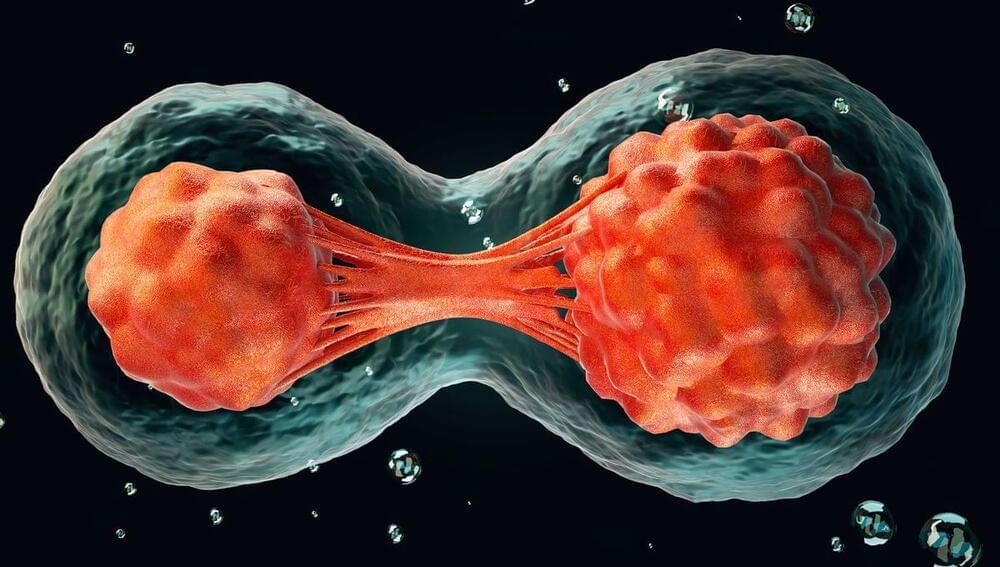
Cell division is necessary for our body to grow and for tissues to renew themselves. Cellular senescence describes the phenomenon where cells permanently stop dividing but remain in the body, causing tissue damage and aging across body organs and systems.
Ordinarily, senescent cells are cleared from the body by our immune system. But, as we age, our immune system is less effective at clearing out these cells and their number increases. An increase in senescent cells has been associated with diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s disease and the hallmarks of aging such as worsening eyesight and reduced mobility. Given the potentially deleterious effects on the body, there has been a push to develop effective senolytics, compounds that clear out senescent cells.