In new work on graphs’ hidden structure, mathematicians probe the limits of randomness.


A man that wears a leopard print cowboy hat has a bold prediction: that AI will, in the next few years, replace up to 80 percent of jobs.

Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death worldwide and considered one of the most environmentally driven diseases. The role of DNA methylation in response to the individual exposure for the development and progression of CVD is still poorly understood and a synthesis of the evidence is lacking.
A systematic review of articles examining measurements of DNA cytosine methylation in CVD was conducted in accordance with PRISMA (preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses) guidelines. The search yielded 5,563 articles from PubMed and CENTRAL databases. From 99 studies with a total of 87,827 individuals eligible for analysis, a database was created combining all CpG-, gene-and study-related information. It contains 74,580 unique CpG sites, of which 1,452 CpG sites were mentioned in ≥ 2, and 441 CpG sites in ≥ 3 publications. Two sites were referenced in ≥ 6 publications: cg01656216 (near ZNF438) related to vascular disease and epigenetic age, and cg03636183 (near F2RL3) related to coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, smoking and air pollution. Of 19,127 mapped genes, 5,807 were reported in ≥ 2 studies.
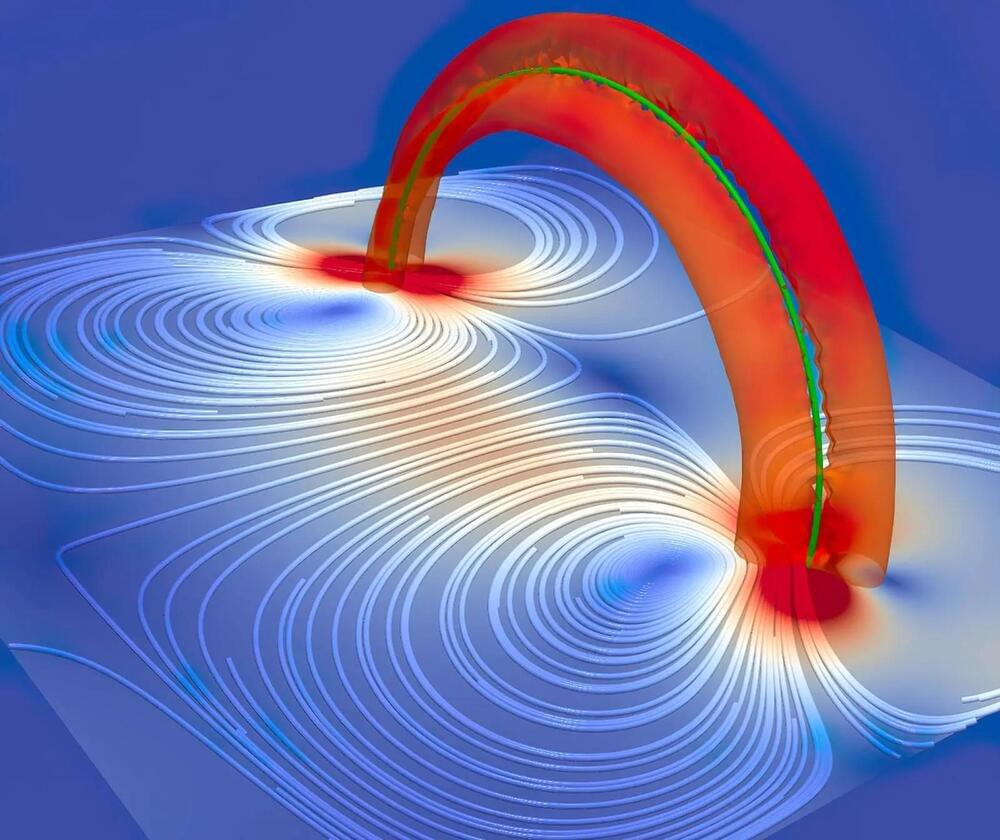
Explaining the interaction between quantized vortices and normal fluids.
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University, Florida State University.
Florida State University (Florida State or FSU) is a public space-grant and sea-grant research university in Tallahassee, Florida, United States that was established in 1851. The university comprises 16 separate colleges and more than 110 centers, facilities, labs, and institutes that offer more than 360 programs of study, including professional school programs.
Last spring, engineers in Barcelona packed up the sperm-injecting robot they’d designed and sent it by DHL to New York City. They followed it to a clinic there, called New Hope Fertility Center, where they put the instrument back together, assembling a microscope, a mechanized needle, a tiny petri dish, and a laptop.
Then one of the engineers, with no real experience in fertility medicine, used a Sony PlayStation 5 controller to position a robotic needle. Eyeing a human egg through a camera, it then moved forward on its own, penetrating the egg and dropping off a single sperm cell. Altogether, the robot was used to fertilize more than a dozen eggs.
The result of the procedures, say the… More.
Meet the startup companies trying to engineer a desktop fertility machine. If they succeed, it could make IVF cheaper and more widespread.

Harvard University plans to use an AI chatbot similar to ChatGPT as an instructor on its flagship coding course.
Students enrolled on the Computer Science 50: Introduction to Computer Science (CS50) programme will be encouraged to use the artificial intelligence tool when classes begin in September.
The AI teacher will likely be based on OpenAI’s GPT 3.5 or GPT 4 models, according to course instructors.
🤣😂 My how things have changed considering AI. #TotallyFunny

The technology could eventually revolutionize health care. We’ve seen CRISPR start to be used experimentally to treat children with cancer, for example. It is being explored for lots of genetic diseases. And last year, a company used CRISPR to try to treat a woman with dangerously high cholesterol.
But CRISPR could also transform farming, including aquaculture. This week, I wrote about researchers who inserted an alligator gene into catfish. The idea isn’t to make these fish more alligator-like, but to make them more resistant to disease. It turns out that alligators have a particular talent for fighting off infections.
These gene-edited fish, pigs, and other animals could soon be on the menu.
Understanding the basics of artificial intelligence in healthcare.
Healthcare spending simply isn’t keeping up. Healthcare systems will struggle to remain viable unless big structural and transformational changes are implemented. Automation, along with artificial intelligence (AI), has the potential to revolutionize healthcare.
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare is utilized to analyze and avoid illness treatment procedures. AI is employed in many fields of healthcare, including diagnosis, drug research, medication, patient monitoring care centers, and so on.