Nanotechnology is a field of science and engineering that focuses on the design and manufacture of extremely small devices and structures.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

New Superconducting Material Could Transform Electronics — If It Works
Superconductivity is an incredible property of certain materials with exciting consequences. Once reached, for example, said materials can conduct electricity without resistance, so no loss of energy. But most materials are superconductive at extremely low temperatures. The quest for a room-temperature superconductor is ongoing, and is not without a bit of scientific drama.
A few years ago, there was a claim of a room-temperature superconductor that became supercritical at a temperature of 15°C (59°F), but required a pressure of 2.5 million atmospheres. That’s on the order of the pressure you might find in the core of a rocky planet, and can be achieved by squeezing materials between two diamonds. Other scientists raised issues with the way the numbers were handled, including an accusation of the data used being fabricated.
The paper was retracted by the journal Nature last September, and the team claims they are ready to resubmit that work. They have also announced a brand-new material with even more extraordinary properties (if confirmed). The new substance is described as a nitrogen-doped lutetium hydride that becomes superconductive up to 20.5°C (69°F) and at a much lower pressure, roughly 10,000 atmospheres. Quite the improvement.
First nasal monoclonal antibody treatment for COVID-19 shows promise for treating virus, other diseases
A pilot trial by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, tested the nasal administration of the drug Foralumab, an anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody. Investigators found evidence that the drug dampened the inflammatory T cell response and decreased lung inflammation in patients with COVID-19. Further analysis showed the same gene expression modulation in patients with multiple sclerosis, who experienced decreased brain inflammation, suggesting that Foralumab could be used to treat other diseases. Their results are published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“We discovered a way to shut down inflammation not only seen in COVID-19, but also in a patient with multiple sclerosis as well as in healthy patients,” said lead author Thais Moreira, Ph.D., an assistant scientist at the Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases at BWH and an instructor in Neurology at Harvard Medical School. “This is very exciting because not only does our study suggest that this new monoclonal antibody drug is safe and can modulate the immune system without major side effects, but it can also decrease inflammation in multiple realms, so it may be useful for treating other diseases.”
“Inflammation is a major cause of many diseases,” said senior author Howard Weiner, MD, founder and director of the Brigham Multiple Sclerosis Center and co-director of the Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases. “Our center has spent decades looking for novel ways to treat disease where there is abnormal inflammation in a way that is safe and effective.”
How immune cells detect and respond to mutations in cancer cells
For the first time, a research team has identified and analyzed the steps by which immune cells “see” and respond to cancer cells, providing insights into reasons some treatments may be effective for certain patients but not others.
The UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center scientists leading the research believe their findings will lead to better, more personalized immunotherapies—even for patients whose immune systems currently do not appear to respond to treatment.
“This is an important step forward in our understanding of what the T-cell responses see in the tumor and how they change over time while they are in the tumor and in circulation in the blood, searching for new tumor cells to attack,” said Cristina Puig-Saus, Ph.D., a UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researcher, adjunct assistant professor of medicine at UCLA, and the first author of a study in Nature.

Bioinspired Neural Network Model Can Store Significantly More Memories
Researchers have developed a new model inspired by recent biological discoveries that shows enhanced memory performance. This was achieved by modifying a classical neural network.
Computer models play a crucial role in investigating the brain’s process of making and retaining memories and other intricate information. However, constructing such models is a delicate task. The intricate interplay of electrical and biochemical signals, as well as the web of connections between neurons and other cell types, creates the infrastructure for memories to be formed. Despite this, encoding the complex biology of the brain into a computer model for further study has proven to be a difficult task due to the limited understanding of the underlying biology of the brain.
Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have made improvements to a widely utilized computer model of memory, known as a Hopfield network, by incorporating insights from biology. The alteration has resulted in a network that not only better mirrors the way neurons and other cells are connected in the brain, but also has the capacity to store significantly more memories.
Microtubules are Biological Computers: searching for the mind of a cell
In episode 13 of the Quantum Consciousness series, Justin Riddle discusses how microtubules are the most likely candidate to be a universal quantum computer that acts as a single executive unit in cells. First off, computer scientists are trying to model human behavior using neural networks that treat individual neurons as the base unit. But unicellular organisms are able to do many of the things that we consider to be human behavior! How does a single-cell lifeform perform this complex behavior? As Stuart Hameroff puts it, “neuron doctrine is an insult to neurons,” referring to the complexity of a single cell. Let’s look inside a cell, what makes it tick? Many think the DNA holds some secret code or algorithm that is executing the decision-making process of the cell. However, the microscope reveals a different story where the microtubules are performing a vast array of complex behaviors: swimming towards food, away from predators, coordinating protein delivery and creation within the cell. This begs the question: how do microtubules work? Well, they are single proteins organized into helical cylinders. What is going on here? Typically, we think of a protein’s function as being determined by its structure but the function of a single protein repeated into tubes is tough to unravel. Stuart Hameroff proposed that perhaps these tubulin proteins are acting as bits of information and the whole tube is working as a universal computer that can be programmed to fit any situation. Given the limitations of digital computation, Roger Penrose was looking for a quantum computer in biology and Stuart Hameroff was looking for more than a digital computation explanation. Hence, the Hameroff-Penrose model of microtubules as quantum computers was born. If microtubules are quantum computers, then each cell would possess a central executive hub for rapidly integrating information from across the cell and to turn that information into a single action plan that could be quickly disseminated. Furthermore, the computation would get a “quantum” speed-up in that exponentially large search spaces could be tackled in a reasonable timeframe. If microtubules are indeed quantum computers, then modern science has greatly underestimated the processing power of a single cell, let alone the entire human brain.
~~~ Timestamps ~~~
0:00 Introduction.
3:08 “Neuron doctrine is an insult to neurons”
8:23 DNA vs Microtubules.
14:20 Diffusion vs Central Hub.
17:50 Microtubules as Universal Computers.
23:40 Penrose’s Quantum Computation update.
29:48 Quantum search in a cell.
33:25 Stable microtubules in neurons.
35:18 Finding the self in biology.
#quantum.
#consciousness.
#microtubules.
Website: www.justinriddlepodcast.com.
Email: [email protected].
Twitter: @JRiddlePodcast.
Music licensed from and created by Baylor Odabashian. BandCamp: @UnscrewablePooch.
Painting behind me by Paul Seli. IG: @Paul. Seli.art
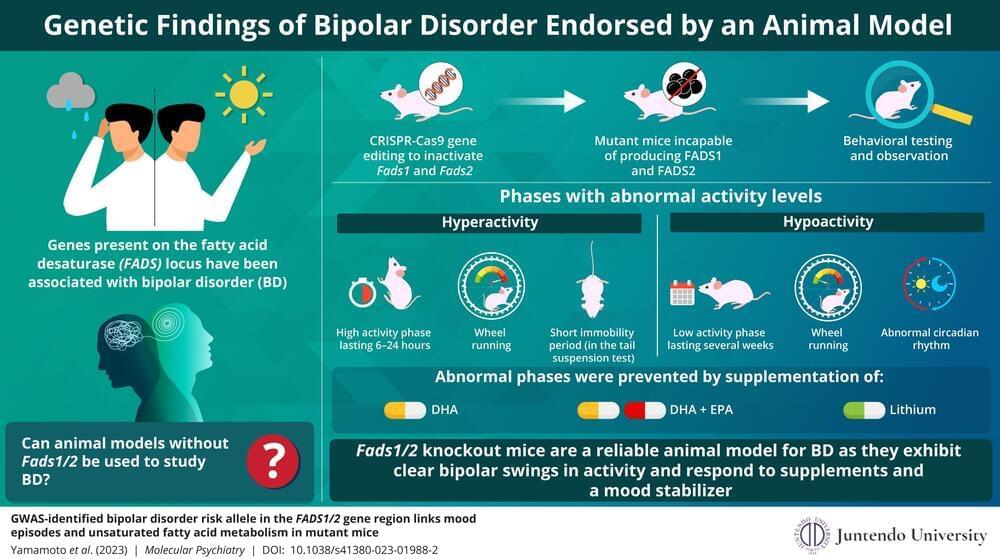
Researchers create mutant mice to study bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a debilitating condition characterized by alternating states of depression (known as depressive episodes) and abnormal excitement or irritability (known as manic episodes). Large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have revealed that variations in the genes present on the fatty acid desaturase (FADS) locus are linked to an increased risk of BD.
Enzymes coded by FADS genes—FADS1 and FADS2—convert or “biosynthesize” omega-3 fatty acids into the different forms required by the human body. Omega-3 fatty acids like eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are crucial for the brain to function, and a reduction in the synthesizing activity of these molecules seems to increase susceptibility to bipolar mood swings.
Research on most diseases involves establishment of an animal model of the disease. So, keeping this knowledge in mind, a team of researchers including Dr. Takaoki Kasahara and Hirona Yamamoto from RIKEN Brain Science Institute and Dr. Tadafumi Kato from Juntendo University in Japan, used CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing to create mutant mice that lack both Fads1 and Fads2 genes.

SpaceX Crew-5 astronauts hope to leave space station March 9 as NASA watches weather
“NASA and SpaceX continue to evaluate the weather for the return of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 mission from the International Space Station,” NASA wrote. “Teams conducted a weather briefing overnight and decided to waive off the initial undocking opportunity for early Thursday, March 9, due to high winds at the splashdown sites. Teams are currently targeting undocking for no earlier than Thursday evening, pending weather.”
It’s the latest in a series of interesting events for Crew-5.
“The universe started throwing curveballs our way, and then it got really crazy,” NASA astronaut Josh Cassada said during a livestreamed in-orbit farewell today (March 8) reflecting on Crew-5’s six-month mission. During their time aboard the orbital lab, two spacecraft docked at the ISS experienced coolant leaks (a Soyuz crew capsule and a Progress cargo vessel, both Russian) and the orbiting complex had to dodge space debris a few times. Nevertheless, all has been righted in time for Crew-5’s departure.

The Future of Consciousness: How Singularity Could Change the Way We Experience Life
Technological Singularity is expected to trigger profound changes in both social and technogenic structures. The introduction of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), that can be both disembodied and embodied as smart robots, will bring about a multitude of issues, including human unemployment or underemployment, ethical considerations regarding the treatment of robots, the challenge of managing their runaway superintelligence, and most importantly, harnessing the potential of human-machine convergence.