Organic photovoltaics, solar energy devices based on organic semiconductors, have so far achieved very promising results in experimental settings, both in terms of efficiency and stability. However, engineers have not yet devised reliable strategies to fabricate these devices on a large-scale at a reasonable cost.
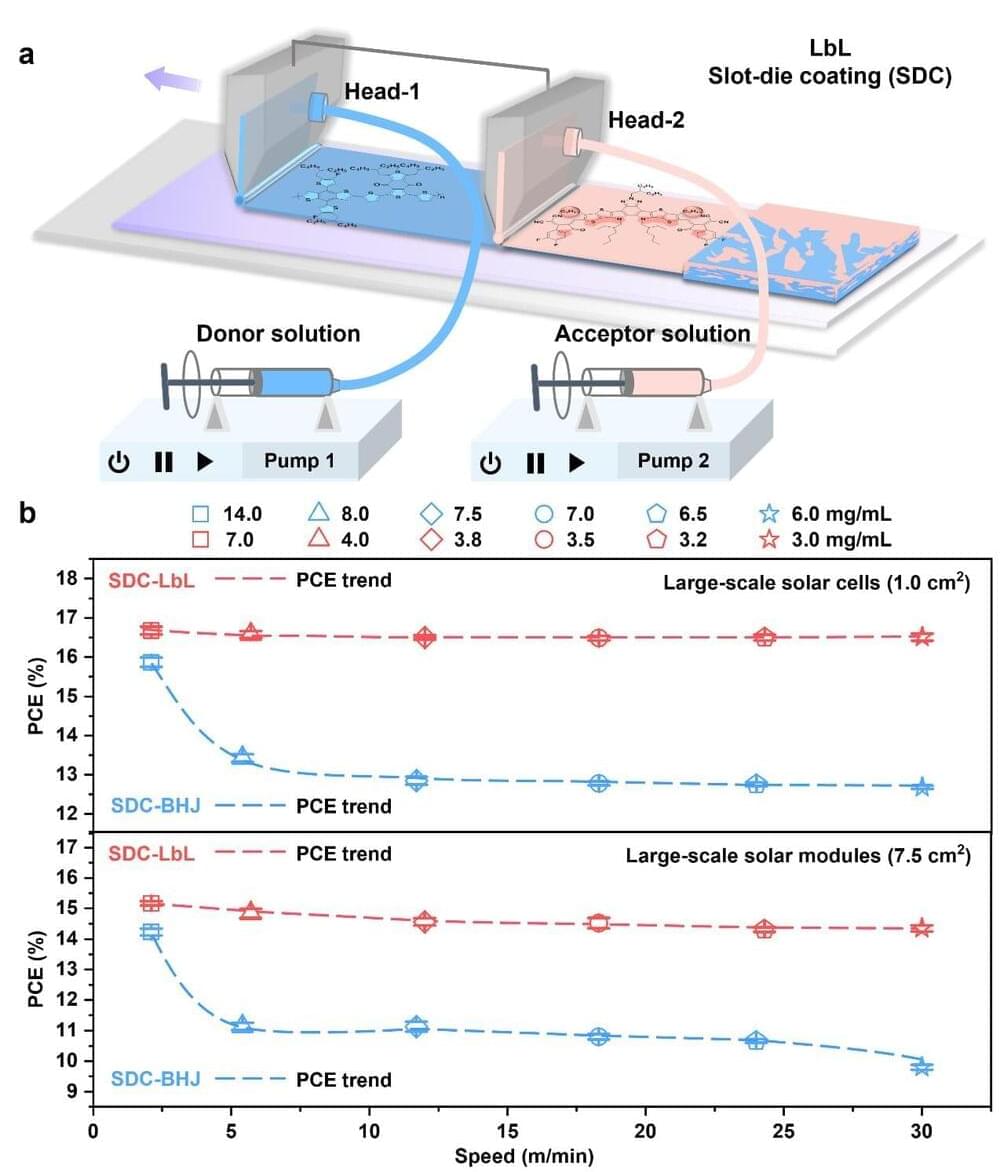
Researchers at Wuhan University in China have recently identified an approach that could facilitate the rapid fabrication of photoactive layers for organic solar cells, without compromising the cells’ efficiency and stability. Their proposed strategy, introduced in a paper published in Nature Energy, is based on sequential deposition, a method often used to deposit organic semiconductors and perovskite films on substrates.
“To realize the commercialization of organic photovoltaics (OPVs), the golden triangle of power conversion efficiency (PCE), stability, and cost should be considered simultaneously,” Jie Min, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore.