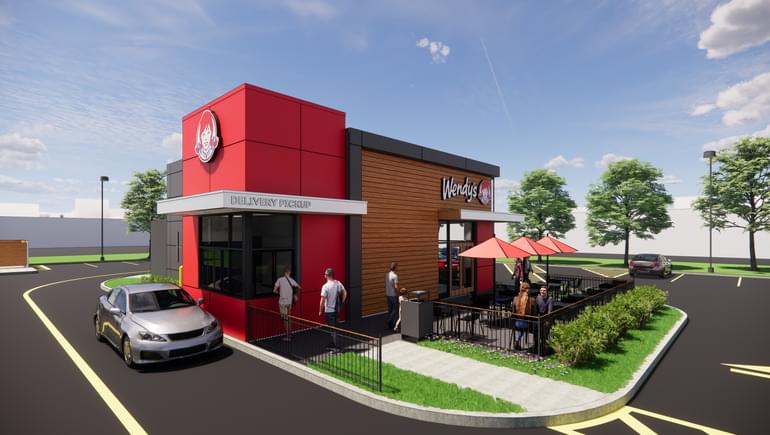
Customers will be ordering food from AI.
#Wendys #Google #yahoofinance.
Yahoo Finance culinary correspondent Brooke DiPalma joins the Live Show to discuss the partnership between Wendy’s and Google to revolutionize drive-thru orders with the use of AI technology, first premiering in Columbus.
Ohio in June of this year, and how AI is transforming the restaurant industry.
About Yahoo Finance:
At Yahoo Finance, you get free stock quotes, up-to-date news, portfolio management resources, international market data, social interaction and mortgage rates that help you manage your financial life.
Yahoo Finance Plus: With a subscription to Yahoo Finance Plus get the tools you need to invest with confidence. Discover new opportunities with expert research and investment ideas backed by technical and fundamental analysis. Optimize your trades with advanced portfolio insights, fundamental analysis, enhanced charting, and more.