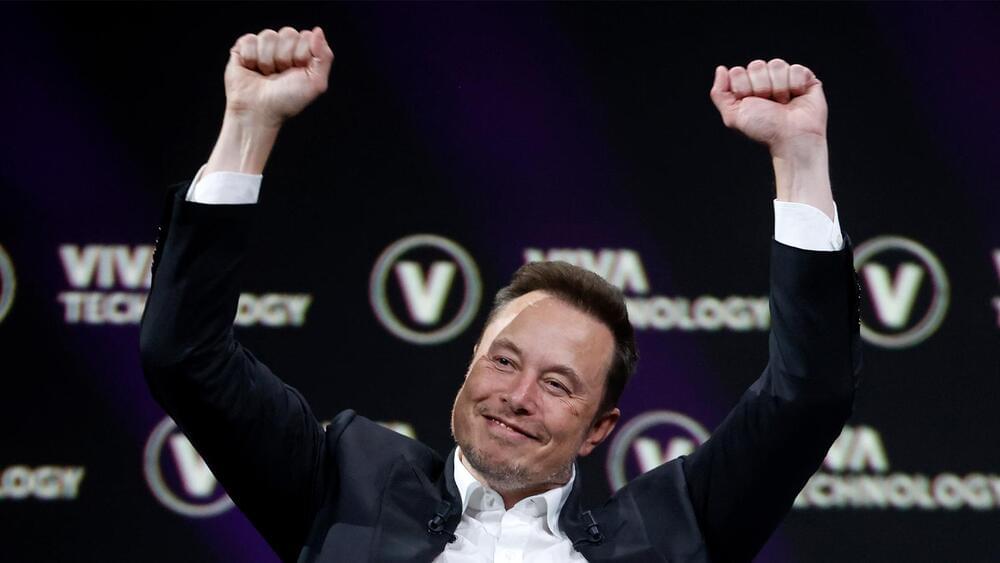
Shortly after resigning as CEO of Twitter, Musk is expected to assume the position of CEO once again, this time at a fresh AI startup.
The world’s richest person has announced a new startup called xAI. Elon Musk has assembled a team of highly experienced professionals in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI) to establish this enterprise. However, Musk’s Twitter statement merely offers limited information about the venture’s objectives, leaving its purpose ambiguous for the time being.
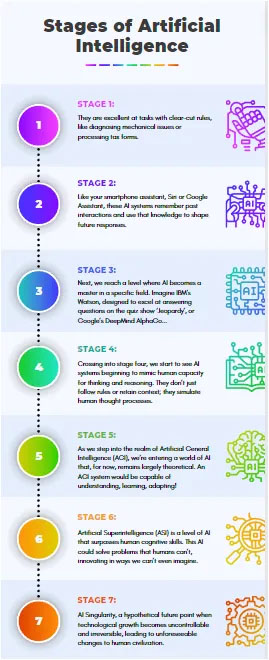
Musk’s recent foray into AI is not his initial involvement in the field. In 2015, he became an investor in OpenAI, a non-profit research laboratory dedicated to AI exploration. However, over time, Musk… More.
Getty Images.
Announcing formation of @xAI to understand reality— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) July 12, 2023