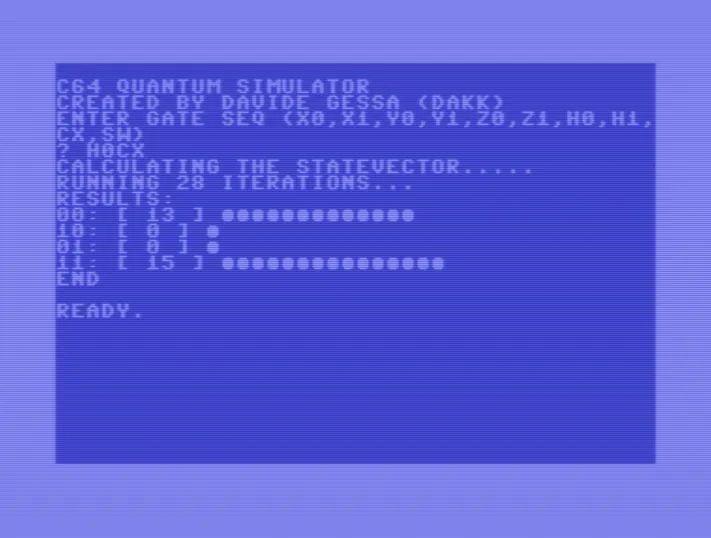
The term ‘quantum computer’ gets usually tossed around in the context of hyper-advanced, state-of-the-art computing devices, but much as how a 19th century mechanical computer, a discrete computer created from individual transistors, and a human being are all computers, the important quantifier is how fast and accurate the system is at the task, whether classical or quantum computing. This is demonstrated succinctly by [Davide ‘dakk’ Gessa] with 200 lines of BASIC code on a Commodore 64 (GitHub), implementing a range of quantum gates.
Much like a transistor in classical computing, the qubit forms the core of quantum computing, and we have known for a long time that a qubit can be simulated, even on something as mundane as an 8-bit MPU. Ergo [Davide]’s simulations of various quantum gates on a C64, ranging from Pauli-X, Pauli-Y, Pauli-Z, Hadamard, CNOT and SWAP, all using a two-qubit system running on a system that first saw the light of day in the early 1980s.
Naturally, the practical use of simulating a two-qubit system on a general-purpose MPU running at a blistering ~1 MHz is quite limited, but as a teaching tool it’s incredibly accessible and a fun way to introduce people to the world of quantum computing.