It isn’t just your refrigerator that has magnets on it. The Earth, the stars, galaxies, and the space between galaxies are all magnetized, too. The more places scientists have looked for magnetic fields across the universe, the more they’ve found them. But the question of why that is the case and where those magnetic fields originate from has remained a mystery and a subject of ongoing scientific inquiry.
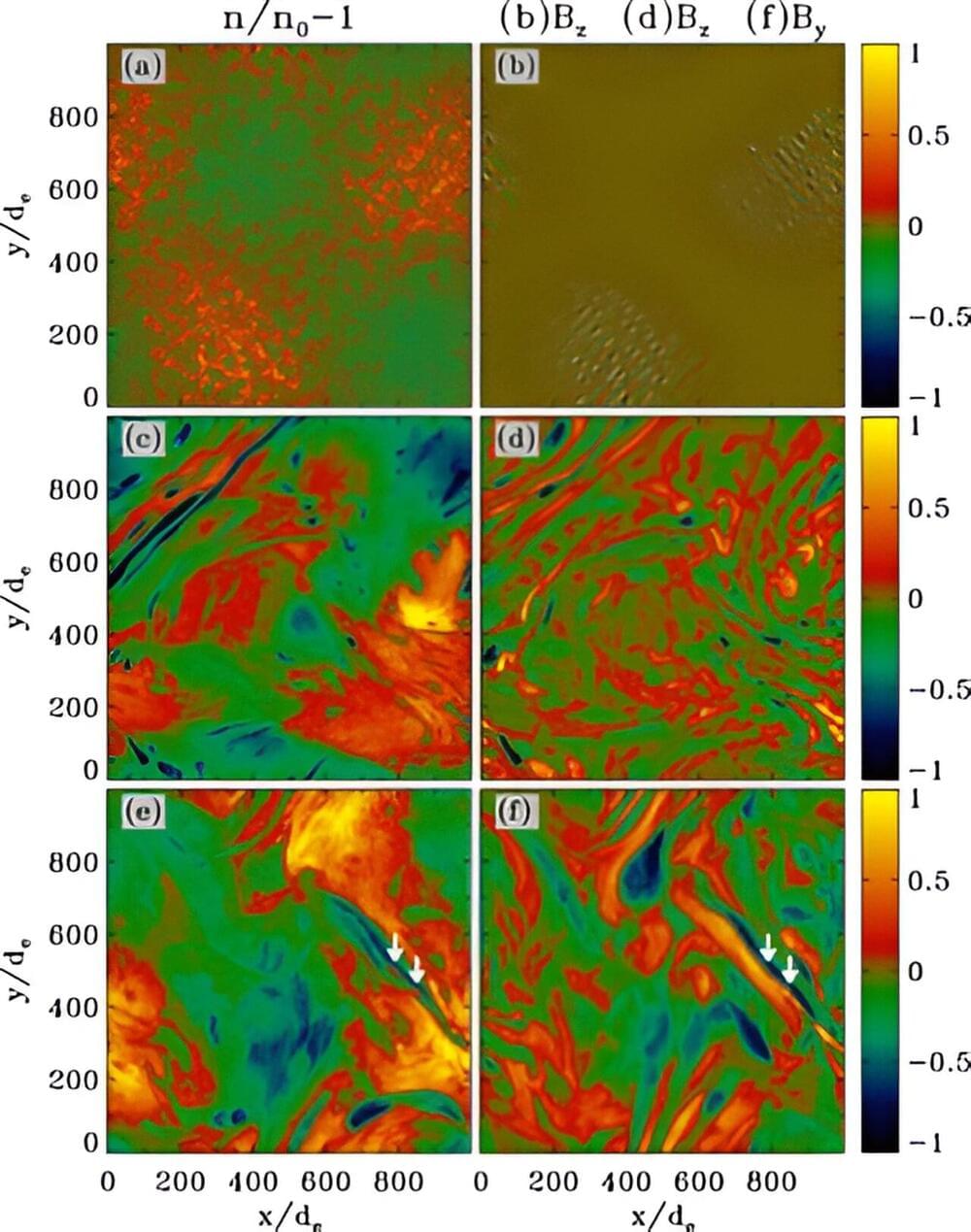
Published in the journal Physical Review Letters, a new paper by Columbia researchers offers insight into the source of these fields. The team used models to show that magnetic fields may spontaneously arise in turbulent plasma. Plasma is a kind of matter often found in ultra-hot environments like that near the surface of the sun, but plasma is also scattered across the universe in low-density environments, like the expansive space between galaxies; the team’s research focused on those low-density environments.
Their simulations showed that, in addition to generating new magnetic fields, the turbulence of those plasmas can also amplify magnetic fields once they’ve been generated, which helps explain how magnetic fields that originate on small scales can sometimes eventually reach to stretch across vast distances.