AI has gotten good at writing. Here’s how experts say you can identify it.



It’s estimated that humans are producing the equivalent of 10 million Blu-ray Discs of data per day – and all and zero of those have to be stored somewhere.
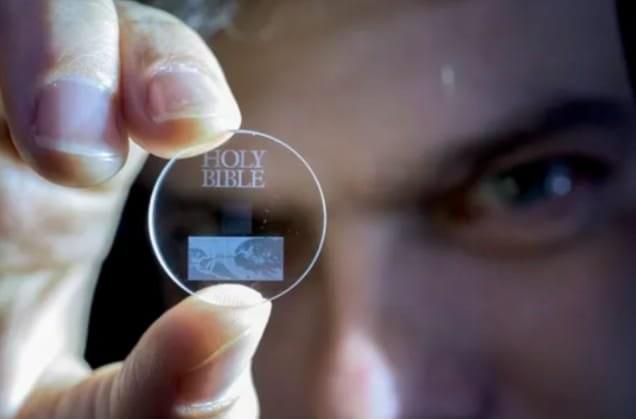
Now, UK researchers may have a solution: a five-dimensional (5D) digital data disc that can store 360 terabytes of data for about 13.8 billion years.
To create the data discs, scientists at the University of Southampton used a process called femtosecond laser writing, which creates tiny discs of glass using ultrafast lasers that generate short and intense pulses of light.
Brain tissue is one of the most intricate tissue specimens that scientists have arguably ever dealt with. Packed with an immeasurable amount of information, the human brain is the most sophisticated computational device with its network of around 86 billion neurons.
Understanding such complexity is a difficult task, and therefore making progress requires technologies to unravel the tiny, complex interactions taking place in the brain at microscopic scales. Imaging is therefore an enabling tool in neuroscience.
The new imaging and virtual reconstruction technology developed by Johann Danzl’s group, at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), is a big leap in imaging brain activity and is aptly named LIONESS—Live Information Optimized Nanoscopy Enabling Saturated Segmentation. Their work has been published in Nature Methods.
Summary: A novel study suggests that silence can indeed be ‘heard.’ Philosophers and psychologists, using auditory illusions, demonstrated how silence distorts our perception of time, much like sounds do.
The study indicates that the brain perceives and processes silence in a manner similar to sounds. The research establishes a novel method to study the perception of absence, broadening the scope for future exploration in the realm of sensory perception.

(NewsNation) — Astronomers have once again found a potential signal of life in the clouds of Venus.
The controversial observation of molecules of phosphine was first reported in 2020. Phosphine, comprised of hydrogen and phosphorus, is a gas on Earth that is only associated with life.
Three years later, “extensive additional detections” of the molecules were presented at the National Astronomy Meeting 2023 at Cardiff University in Wales, UK, according to a Forbes report.

– India’s First Odia AI News Anchor Launched By OTV
#otvnews.
OdishaTV is Odisha’s no 1 News Channel. OTV being the first private satellite TV channel in Odisha carries the onus of charting a course that behoves its pioneering efforts.
Accordingly its charter objectives are FREE, FAIR and UNBIASED. OTV delivers reliable information across all platforms: TV, Internet and Mobile.
Stay tuned for all the breaking news!
Visit Our Website https://odishatv.in/
Android App: bit.ly/OTVAndroidApp.
iOS App: http://bit.ly/OTViOSApp.
Watch Live: http://live.odishatv.in/
YouTube: https://goo.gl/Ehz6OP
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/otvnews.
OTV English Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/otvenglish.
Telegram @otvtelegram @otvkhabar.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/otvnews.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/otvnews/
#OTVNews #OdishaTV

This post is also available in:  עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
There are currently thousands of Starlink satellites that belong to SpaceX, and they are causing a lot of disputes in the science and astronomy communities. They are disrupting scientific research by causing streaks in deep space photos, and according to a new study are also dumping “unintended electromagnetic radiation” into space, which could be a major problem for Earth-bound astronauts.
The study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics states that the satellites in low Earth orbit could be muddling or even drowning out signals from deep space that radio astronomers search for.
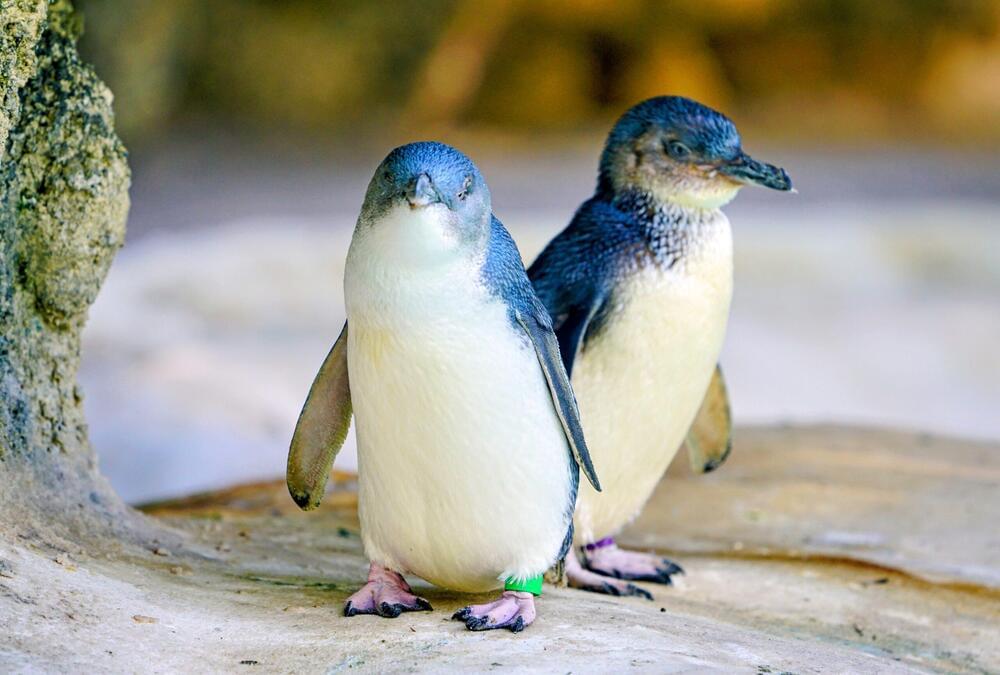

In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have identified a new extinct species of small penguins that lived in New Zealand three million years ago. These creatures, described as “ridiculously cute,” are ancestors of little penguins that continue to thrive today along the coasts of Australia, Tasmania, and New Zealand.
After careful examination of two fossilized skulls – one belonging to an adult, the other to a juvenile – the researchers named the new species Wilson’s little penguin. The study was published last month in the Journal of Paleontology.
According to Bob Yirka of Phys.org, the newly discovered species represents the oldest-known extinct little penguin. Given that the researchers have only the skulls of the extinct animals at their disposal – not their entire skeletons – certain details about the Wilson’s little penguins remain uncertain.