Angel_nt/iStock.
Today we will learn all there is to know about tractor beams’ past, present, and future.
Angel_nt/iStock.
Today we will learn all there is to know about tractor beams’ past, present, and future.


Summary: Music engages a multitude of brain areas, showcasing a complex interplay between auditory processing, emotion, and memory centers. It elicits emotions through the release of dopamine, our brain’s pleasure molecule, explaining the joy we often find in a favorite tune.
Moreover, music’s power to evoke vivid memories highlights its connection to the hippocampus, our memory storage center.
This broad influence of music on our brain mechanisms is also harnessed in therapeutic contexts, such as treating neurological disorders or improving mental health.


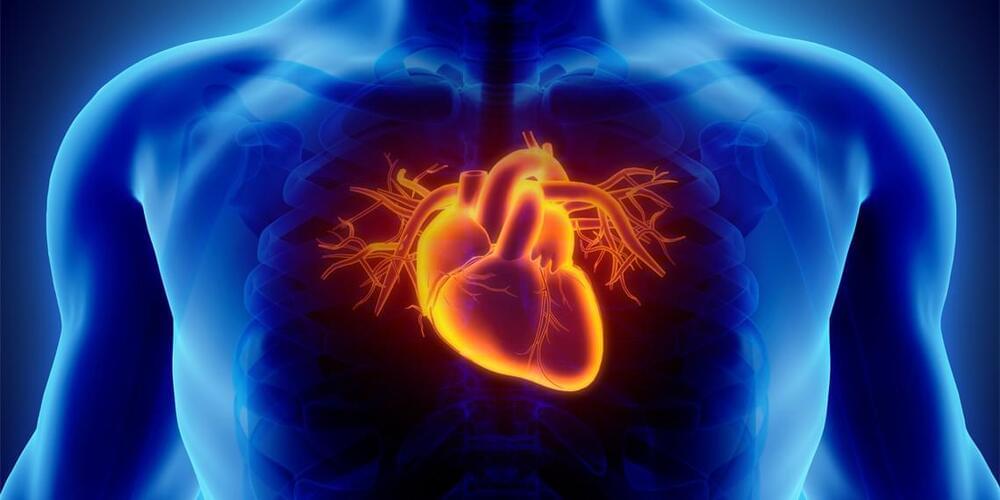
New research has found that blind individuals tend to have better interoceptive abilities than sighted individuals, particularly when it comes to detecting signals related to the heart. The new findings have been published in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: General.
The study aimed to investigate how blindness affects interoception, which refers to the ability to perceive internal bodily sensations. The researchers were specifically interested in examining how blindness affects cardiac interoception, which involves perceiving the sensations of the heartbeat.
The study was motivated by previous research that has shown that blindness can lead to heightened crossmodal plasticity, which is the ability of the brain to reorganize and compensate for sensory deprivation by enhancing other senses.

Join top executives in San Francisco on July 11–12, to hear how leaders are integrating and optimizing AI investments for success. Learn More
Ever since the launch of ChatGPT in late 2022, AI has grabbed the attention of people and businesses around the world. This technology was previously understood as highly promising but a topic for the future. Today, it has loudly announced itself, catching businesses off-guard as they mobilize to make sense of its exciting potential to automate processes and supercharge efficiencies.
One important aspect to examine is where investors are currently focusing their attention. This latest wave of AI has focused early attention on those startups and businesses already using AI in their products and services (loosely termed AI adopters). Other factors to consider are whether investors are pausing their investments and causing illiquidity in the market. In this, investors consider likely consequences and disruptions across industries and update their commercial and technical due diligence approaches as they look to side-step hazards and seize opportunities.


Elon Musk, the genius behind SpaceX and Tesla Inc., has declared that humanity must embrace the merging of man and machine if we hope to survive in a world dominated by artificial intelligence (AI).
In a 2018 appearance on the “Joe Rogan Experience,” Musk teased his company Neuralink has something exciting in store for us. He believes his technology will allow humans to achieve a state of “symbiosis” with AI, where we’ll be able to effortlessly combine our brains with computers. Neuralink has been developing brain implants since 2016 with the goal of curing conditions like paralysis and blindness.
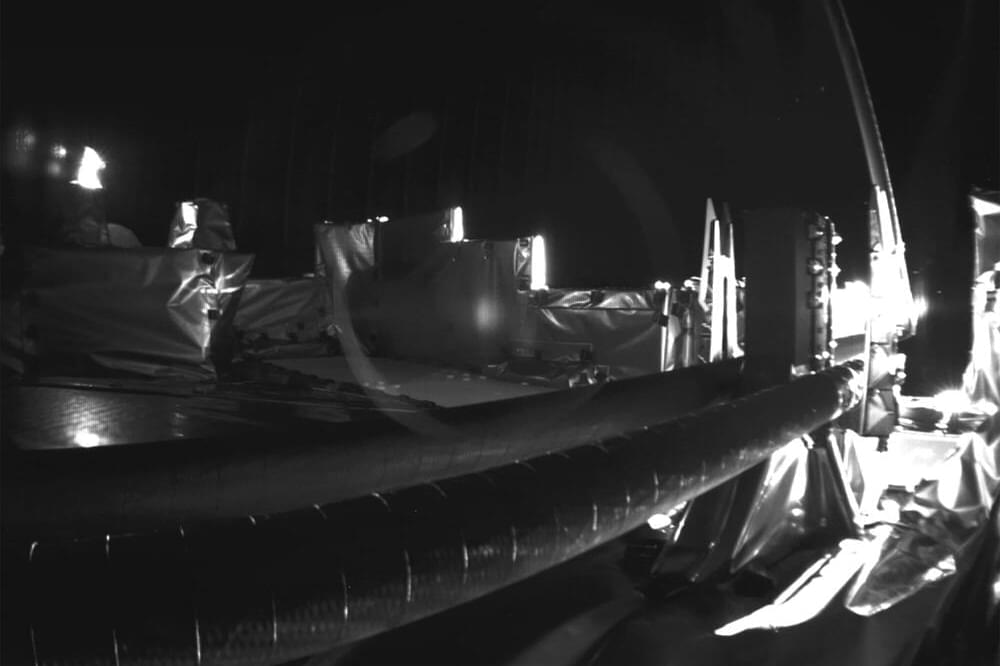

A crucial radar antenna on a European spacecraft bound for Jupiter is no longer jammed.
Flight controllers in Germany freed the 52-foot (16-meter) antenna Friday after nearly a month of effort.
The European Space Agency’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer, nicknamed Juice, blasted off in April on a decade-long voyage. Soon after launch, a tiny pin refused to budge and prevented the antenna from fully opening.